update:内容已更新到 6.0 版本,程序已上架 macOS 苹果商店,点击安装 更方便获取应用的更新。使用 WWDC23 技术重构。6.0版本介绍见戴铭的开发小册子6.0。
新dyld源码透出近期苹果出新系统必然,依苹果 taste,势必要用好技术抛落后技术。漫漫长假我完善了Swift手册内容,字数达到十五万字,内容已压缩压缩再压缩,求全存简,more big, so small 。满满诚意,望有用、值得收藏、求转发。
come on and learn (੭*ˊᵕˋ)੭
– 戴·代码之使徒·画终结者·被光选中的人·铭
背景说明
越来越多同学打算开始用 Swift 来开发了,可很多人以前都没接触过 Swift。这篇和我以前文章不同的是,本篇只是面向 Swift 零基础的同学,内容主要是一些直接可用的小例子,例子可以直接在工程中用或自己调试着看。
记得以前 PHP 有个 chm 的手册,写的很简单,但很全,每个知识点都有例子,社区版每个知识点下面还有留言互动。因此,我弄了个 Swift 的手册,是个 macOS 程序。建议使用我开发的这个 macOS 程序来浏览。

这个程序是Swift写的,按照声明式UI,响应式编程范式开发的,源码也可以看看。与其讲一堆,不如调着试。
下面是文本内容。注:代码中简化变量名是为了能更快速关注到语言用法。
语法速查
基础
变量 let, var
变量是可变的,使用 var 修饰,常量是不可变的,使用 let 修饰。类、结构体和枚举里的变量是属性。
var v1:String = "hi" // 标注类型
var v2 = "类型推导"
let l1 = "标题" // 常量
class a {
let p1 = 3
var p2: Int {
p1 * 3
}
}属性没有 set 可以省略 get,如果有 set 需加 get。变量设置前通过 willSet 访问到,变量设置后通过 didSet 访问。
打印 print(“”)
控制台打印值
print("hi")
let i = 14
print(i)
print("9月\(i)是小柠檬的生日")
for i in 1...3{
print(i)
}
// output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 使用terminator使循环打印更整洁
for i in 1...3 {
print("\(i) ", terminator: "")
}
// output:
// 1 2 3注释 //
// 单行注释
/*
多行注释第一行。
多行注释第二行。
*/
// MARK: 会在 minimap 上展示
// TODO: 待做
// FIXME: 待修复可选 ?, !
可能会是 nil 的变量就是可选变量。当变量为 nil 通过??操作符可以提供一个默认值。
var o: Int? = nil
let i = o ?? 0闭包
闭包也可以叫做 lambda,是匿名函数,对应 OC 的 block。
let a1 = [1,3,2].sorted(by: { (l: Int, r: Int) -> Bool in
return l < r
})
// 如果闭包是唯一的参数并在表达式最后可以使用结尾闭包语法,写法简化为
let a2 = [1,3,2].sorted { (l: Int, r: Int) -> Bool in
return l < r
}
// 已知类型可以省略
let a3 = [1,3,2].sorted { l, r in
return l < r
}
// 通过位置来使用闭包的参数,最后简化如下:
let a4 = [1,3,2].sorted { $0 < $1 }函数也是闭包的一种,函数的参数也可以是闭包。@escaping 表示逃逸闭包,逃逸闭包是可以在函数返回之后继续调用的。@autoclosure 表示自动闭包,可以用来省略花括号。
函数 func
函数可以作为另一个函数的参数,也可以作为另一个函数的返回。函数是特殊的闭包,在类、结构体和枚举中是方法。
// 为参数设置默认值
func f1(p: String = "p") -> String {
"p is \(p)"
}
// 函数作为参数
func f2(fn: (String) -> String, p: String) -> String {
return fn(p)
}
print(f2(fn:f1, p: "d")) // p is d
// 函数作为返回值
func f3(p: String) -> (String) -> String {
return f1
}
print(f3(p: "yes")("no")) // p is no函数可以返回多个值,函数是可以嵌套的,也就是函数里内可以定义函数,函数内定义的函数可以访问自己作用域外函数内的变量。inout 表示的是输入输出参数,函数可以在函数内改变输入输出参数。defer 标识的代码块会在函数返回之前执行。
函数在 Swift 5.4 时开始有了使用多个变量参数的能力,使用方法如下:
func f4(s: String..., i: Int...) {
print(s)
print(i)
}
f4(s: "one", "two", "three", i: 1, 2, 3)
/// ["one", "two", "three"]
/// [1, 2, 3]嵌套函数可以重载,嵌套函数可以在声明函数之前调用他。
func f5() {
nf5()
func nf5() {
print("this is nested function")
}
}
f5() // this is nested function访问控制
在 Xcode 里的 target 就是模块,使用 import 可导入模块。模块内包含源文件,每个源文件里可以有多个类、结构体、枚举和函数等多种类型。访问级别可以通过一些关键字描述,分为如下几种:
- open:在模块外可以调用和继承。
- public:在模块外可调用不可继承,open 只适用类和类成员。
- internal:默认级别,模块内可跨源文件调用,模块外不可调用。
- fileprivate:只能在源文件内访问。
- private:只能在所在的作用域内访问。
重写继承类的成员,可以设置成员比父类的这个成员更高的访问级别。Setter 的级别可以低于对应的 Getter 的级别,比如设置 Setter 访问级别为 private,可以在属性使用 private(set) 来修饰。
基础类型
数字 Int, Float
数字的类型有 Int、Float 和 Double
// Int
let i1 = 100
let i2 = 22
print(i1 / i2) // 向下取整得 4
// Float
let f1: Float = 100.0
let f2: Float = 22.0
print(f1 / f2) // 4.5454545
let f3: Float16 = 5.0 // macOS 还不能用
let f4: Float32 = 5.0
let f5: Float64 = 5.0
let f6: Float80 = 5.0
print(f4, f5, f6) // 5.0 5.0 5.0
// Double
let d1: Double = 100.0
let d2: Double = 22.0
print(d1 / d2) // 4.545454545454546
// 字面量
print(Int(0b10101)) // 0b 开头是二进制
print(Int(0x00afff)) // 0x 开头是十六进制
print(2.5e4) // 2.5x10^4 十进制用 e
print(0xAp2) // 10*2^2 十六进制用 p
print(2_000_000) // 2000000
// isMultiple(of:) 方法检查一个数字是否是另一个数字的倍数
let i3 = 36
print(i3.isMultiple(of: 9)) // true处理数字有 floor、ceil、round。floor 是向下取整,只取整数部分;cell 是向上取整,只要有不为零的小数,整数就加1;round 是四舍五入。
布尔数 Bool
布尔数有 true 和 false 两种值,还有一个能够切换这两个值的 toggle 方法。
var b = false
b.toggle() // true
b.toggle() // false元组 (a, b, c)
元组里的值类型可以是不同的。元组可以看成是匿名的结构体。
let t1 = (p1: 1, p2: "two", p3: [1,2,3])
print(t1.p1)
print(t1.p3)
// 类型推导
let t2 = (1, "two", [1,2,3])
// 通过下标访问
print(t2.1) // two
// 分解元组
let (dp1, dp2, _) = t2
print(dp1)
print(dp2)字符串
let s1 = "Hi! This is a string. Cool?"
/// 转义符 \n 表示换行。
/// 其它转义字符有 \0 空字符)、\t 水平制表符 、\n 换行符、\r 回车符
let s2 = "Hi!\nThis is a string. Cool?"
// 多行
let s3 = """
Hi!
This is a string.
Cool?
"""
// 长度
print(s3.count)
print(s3.isEmpty)
// 拼接
print(s3 + "\nSure!")
// 字符串中插入变量
let i = 1
print("Today is good day, double \(i)\(i)!")
/// 遍历字符串
/// 输出:
/// o
/// n
/// e
for c in "one" {
print(c)
}
// 查找
print(s3.lowercased().contains("cool")) // true
// 替换
let s4 = "one is two"
let newS4 = s4.replacingOccurrences(of: "two", with: "one")
print(newS4)
// 删除空格和换行
let s5 = " Simple line. \n\n "
print(s5.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines))
// 切割成数组
let s6 = "one/two/three"
let a1 = s6.components(separatedBy: "/") // 继承自 NSString 的接口
print(a1) // ["one", "two", "three"]
let a2 = s6.split(separator: "/")
print(a2) // ["one", "two", "three"] 属于切片,性能较 components 更好
// 判断是否是某种类型
let c1: Character = "🤔"
print(c1.isASCII) // false
print(c1.isSymbol) // true
print(c1.isLetter) // false
print(c1.isNumber) // false
print(c1.isUppercase) // false
// 字符串和 Data 互转
let data = Data("hi".utf8)
let s7 = String(decoding: data, as: UTF8.self)
print(s7) // hi
// 字符串可以当作集合来用。
let revered = s7.reversed()
print(String(revered))Unicode、Character 和 SubString 等内容参见官方字符串文档:Strings and Characters — The Swift Programming Language (Swift 5.1)
字符串字面符号可以参看《String literals in Swift》。
原始字符串
// 原始字符串在字符串前加上一个或多个#符号。里面的双引号和转义符号将不再起作用了,如果想让转义符起作用,需要在转义符后面加上#符号。
let s8 = #"\(s7)\#(s7) "one" and "two"\n. \#nThe second line."#
print(s8)
/// \(s7)hi "one" and "two"\n.
/// The second line.
// 原始字符串在正则使用效果更佳,反斜杠更少了。
let s9 = "\\\\[A-Z]+[A-Za-z]+\\.[a-z]+"
let s10 = #"\\[A-Z]+[A-Za-z]+\.[a-z]+"#
print(s9) // \\[A-Z]+[A-Za-z]+\.[a-z]+
print(s10) // \\[A-Z]+[A-Za-z]+\.[a-z]+枚举
Swift的枚举有类的一些特性,比如计算属性、实例方法、扩展、遵循协议等等。
enum E1:String, CaseIterable {
case e1, e2 = "12"
}
// 关联值
enum E2 {
case e1([String])
case e2(Int)
}
let e1 = E2.e1(["one","two"])
let e2 = E2.e2(3)
switch e1 {
case .e1(let array):
print(array)
case .e2(let int):
print(int)
}
print(e2)
// 原始值
print(E1.e1.rawValue)
// 遵循 CaseIterable 协议可迭代
for ie in E1.allCases {
print("show \(ie)")
}
// 递归枚举
enum RE {
case v(String)
indirect case node(l:RE, r:RE)
}
let lNode = RE.v("left")
let rNode = RE.v("right")
let pNode = RE.node(l: lNode, r: rNode)
switch pNode {
case .v(let string):
print(string)
case .node(let l, let r):
print(l,r)
switch l {
case .v(let string):
print(string)
case .node(let l, let r):
print(l, r)
}
switch r {
case .v(let string):
print(string)
case .node(let l, let r):
print(l, r)
}
}@unknown 用来区分固定的枚举和可能改变的枚举的能力。@unknown 用于防止未来新增枚举属性会进行提醒提示完善每个 case 的处理。
// @unknown
enum E3 {
case e1, e2, e3
}
func fe1(e: E3) {
switch e {
case .e1:
print("e1 ok")
case .e2:
print("e2 ok")
case .e3:
print("e3 ok")
@unknown default:
print("not ok")
}
}符合 Comparable 协议的枚举可以进行比较。
// Comparable 枚举比较
enum E4: Comparable {
case e1, e2
case e3(i: Int)
case e4
}
let e3 = E4.e4
let e4 = E4.e3(i: 3)
let e5 = E4.e3(i: 2)
let e6 = E4.e1
print(e3 > e4) // true
let a1 = [e3, e4, e5, e6]
let a2 = a1.sorted()
for i in a2 {
print(i.self)
}
/// e1
/// e3(i: 2)
/// e3(i: 3)
/// e4泛型
泛型可以减少重复代码,是一种抽象的表达方式。where 关键字可以对泛型做约束。
func fn<T>(p: T) -> [T] {
var r = [T]()
r.append(p)
return r
}
print(fn(p: "one"))
// 结构体
struct S1<T> {
var arr = [T]()
mutating func add(_ p: T) {
arr.append(p)
}
}
var s1 = S1(arr: ["zero"])
s1.add("one")
s1.add("two")
print(s1.arr) // ["zero", "one", "two"]关联类型
protocol pc {
associatedtype T
mutating func add(_ p: T)
}
struct S2: pc {
typealias T = String // 类型推导,可省略
var strs = [String]()
mutating func add(_ p: String) {
strs.append(p)
}
}泛型适用于嵌套类型
struct S3<T> {
struct S4 {
var p: T
}
var p1: T
var p2: S4
}
let s2 = S3(p1: 1, p2: S3.S4(p: 3))
let s3 = S3(p1: "one", p2: S3.S4(p: "three"))
print(s2,s3)不透明类型
不透明类型会隐藏类型,让使用者更关注功能。不透明类型和协议很类似,不同的是不透明比协议限定的要多,协议能够对应更多类型。
protocol P {
func f() -> String
}
struct S1: P {
func f() -> String {
return "one\n"
}
}
struct S2<T: P>: P {
var p: T
func f() -> String {
return p.f() + "two\n"
}
}
struct S3<T1: P, T2: P>: P {
var p1: T1
var p2: T2
func f() -> String {
return p1.f() + p2.f() + "three\n"
}
}
func someP() -> some P {
return S3(p1: S1(), p2: S2(p: S1()))
}
let r = someP()
print(r.f())函数调用者决定返回什么类型是泛型,函数自身决定返回什么类型使用不透明返回类型。
Result
Result 类型用来处理错误,特别适用异步接口的错误处理。
extension URLSession {
func dataTaskWithResult(
with url: URL,
handler: @escaping (Result<Data, Error>) -> Void
) -> URLSessionDataTask {
dataTask(with: url) { data, _, err in
if let err = err {
handler(.failure(err))
} else {
handler(.success(data ?? Data()))
}
}
}
}
let url = URL(string: "https://ming1016.github.io/")!
// 以前网络请求
let t1 = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: url) {
data, _, error in
if let err = error {
print(err)
} else if let data = data {
print(String(decoding: data, as: UTF8.self))
}
}
t1.resume()
// 使用 Result 网络请求
let t2 = URLSession.shared.dataTaskWithResult(with: url) { result in
switch result {
case .success(let data):
print(String(decoding: data, as: UTF8.self))
case .failure(let err):
print(err)
}
}
t2.resume()类型转换
使用 is 关键字进行类型判断, 使用as 关键字来转换成子类。
class S0 {}
class S1: S0 {}
class S2: S0 {}
var a = [S0]()
a.append(S1())
a.append(S2())
for e in a {
// 类型判断
if e is S1 {
print("Type is S1")
} else if e is S2 {
print("Type is S2")
}
// 使用 as 关键字转换成子类
if let s1 = e as? S1 {
print("As S1 \(s1)")
} else if let s2 = e as? S2 {
print("As S2 \(s2)")
}
}类和结构体
类
类可以定义属性、方法、构造器、下标操作。类使用扩展来扩展功能,遵循协议。类还以继承,运行时检查实例类型。
class C {
var p: String
init(_ p: String) {
self.p = p
}
// 下标操作
subscript(s: String) -> String {
get {
return p + s
}
set {
p = s + newValue
}
}
}
let c = C("hi")
print(c.p)
print(c[" ming"])
c["k"] = "v"
print(c.p)结构体
结构体是值类型,可以定义属性、方法、构造器、下标操作。结构体使用扩展来扩展功能,遵循协议。
struct S {
var p1: String = ""
var p2: Int
}
extension S {
func f() -> String {
return p1 + String(p2)
}
}
var s = S(p2: 1)
s.p1 = "1"
print(s.f()) // 11属性
类、结构体或枚举里的变量常量就是他们的属性。
struct S {
static let sp = "类型属性" // 类型属性通过类型本身访问,非实例访问
var p1: String = ""
var p2: Int = 1
// cp 是计算属性
var cp: Int {
get {
return p2 * 2
}
set {
p2 = newValue + 2
}
}
// 只有 getter 的是只读计算属性
var rcp: Int {
p2 * 4
}
}
print(S.sp)
print(S().cp) // 2
var s = S()
s.cp = 3
print(s.p2) // 5
print(S().rcp) // 4willSet 和 didSet 是属性观察器,可以在属性值设置前后插入自己的逻辑处理。
键路径表达式作为函数
struct S2 {
let p1: String
let p2: Int
}
let s2 = S2(p1: "one", p2: 1)
let s3 = S2(p1: "two", p2: 2)
let a1 = [s2, s3]
let a2 = a1.map(\.p1)
print(a2) // ["one", "two"]方法
enum E: String {
case one, two, three
func showRawValue() {
print(rawValue)
}
}
let e = E.three
e.showRawValue() // three
// 可变的实例方法,使用 mutating 标记
struct S {
var p: String
mutating func addFullStopForP() {
p += "."
}
}
var s = S(p: "hi")
s.addFullStopForP()
print(s.p)
// 类方法
class C {
class func cf() {
print("类方法")
}
}static和class关键字修饰的方法类似 OC 的类方法。static 可以修饰存储属性,而 class 不能;class 修饰的方法可以继承,而 static 不能。在协议中需用 static 来修饰。
静态下标方法
// 静态下标
struct S2 {
static var sp = [String: Int]()
static subscript(_ s: String, d: Int = 10) -> Int {
get {
return sp[s] ?? d
}
set {
sp[s] = newValue
}
}
}
S2["key1"] = 1
S2["key2"] = 2
print(S2["key2"]) // 2
print(S2["key3"]) // 10
自定义类型中实现了 callAsFunction() 的话,该类型的值就可以直接调用。
// callAsFunction()
struct S3 {
var p1: String
func callAsFunction() -> String {
return "show \(p1)"
}
}
let s2 = S3(p1: "hi")
print(s2()) // show hi继承
类能继承另一个类,继承它的方法、属性等。
// 类继承
class C1 {
var p1: String
var cp1: String {
get {
return p1 + " like ATM"
}
set {
p1 = p1 + newValue
}
}
init(p1: String) {
self.p1 = p1
}
func sayHi() {
print("Hi! \(p1)")
}
}
class C2: C1 {
var p2: String
init(p2: String) {
self.p2 = p2
super.init(p1: p2 + "'s father")
}
}
C2(p2: "Lemon").sayHi() // Hi! Lemon's father
// 重写父类方法
class C3: C2 {
override func sayHi() {
print("Hi! \(p2)")
}
}
C3(p2: "Lemon").sayHi() // Hi! Lemon
// 重写计算属性
class C4: C1 {
override var cp1: String {
get {
return p1 + " like Out of the blade"
}
set {
p1 = p1 + newValue
}
}
}
print(C1(p1: "Lemon").cp1) // Lemon like ATM
print(C4(p1: "Lemon").cp1) // Lemon like Out of the blade通过 final 关键字可以防止类被继承,final 还可以用于属性和方法。使用 super 关键字指代父类。
函数式
map
map 可以依次处理数组中元素,并返回一个处理后的新数组。
let a1 = ["a", "b", "c"]
let a2 = a1.map {
"\($0)2"
}
print(a2) // ["a2", "b2", "c2"]使用 compactMap 可以过滤 nil 的元素。flatMap 会将多个数组合成一个数组返回。
filter
根据指定条件返回
let a1 = ["a", "b", "c", "call my name"]
let a2 = a1.filter {
$0.prefix(1) == "c"
}
print(a2) // ["c", "call my name"]reduce
reduce 可以将迭代中返回的结果用于下个迭代中,并,还能让你设个初始值。
let a1 = ["a", "b", "c", "call my name.", "get it?"]
let a2 = a1.reduce("Hey u,", { partialResult, s in
// partialResult 是前面返回的值,s 是遍历到当前的值
partialResult + " \(s)"
})
print(a2) // Hey u, a b c call my name. get it?sorted
排序
// 类型遵循 Comparable
let a1 = ["a", "b", "c", "call my name.", "get it?"]
let a2 = a1.sorted()
let a3 = a1.sorted(by: >)
let a4 = a1.sorted(by: <)
print(a2) // Hey u, a b c call my name. get it?
print(a3) // ["get it?", "call my name.", "c", "b", "a"]
print(a4) // ["a", "b", "c", "call my name.", "get it?"]
// 类型不遵循 Comparable
struct S {
var s: String
var i: Int
}
let a5 = [S(s: "a", i: 0), S(s: "b", i: 1), S(s: "c", i: 2)]
let a6 = a5
.sorted { l, r in
l.i > r.i
}
.map {
$0.i
}
print(a6) // [2, 1, 0]控制流
If • If let • If case let
// if
let s = "hi"
if s.isEmpty {
print("String is Empty")
} else {
print("String is \(s)")
}
// 三元条件
s.isEmpty ? print("String is Empty again") : print("String is \(s) again")
// if let-else
func f(s: String?) {
if let s1 = s {
print("s1 is \(s1)")
} else {
print("s1 is nothing")
}
// nil-coalescing
let s2 = s ?? "nothing"
print("s2 is \(s2)")
}
f(s: "something")
f(s: nil)
// if case let
enum E {
case c1(String)
case c2([String])
func des() {
switch self {
case .c1(let string):
print(string)
case .c2(let array):
print(array)
}
}
}
E.c1("enum c1").des()
E.c2(["one", "two", "three"]).des()Guard guard, guard let
更好地处理异常情况
// guard
func f1(p: String) -> String {
guard p.isEmpty != true else {
return "Empty string."
}
return "String \(p) is not empty."
}
print(f1(p: "")) // Empty string.
print(f1(p: "lemon")) // String lemon is not empty.
// guard let
func f2(p1: String?) -> String {
guard let p2 = p1 else {
return "Nil."
}
return "String \(p2) is not nil."
}
print(f2(p1: nil)) // Nil.
print(f2(p1: "lemon")) // String lemon is not nil.遍历 For-in
let a = ["one", "two", "three"]
for str in a {
print(str)
}
// 使用下标范围
for i in 0..<10 {
print(i)
}
// 使用 enumerated
for (i, str) in a.enumerated() {
print("第\(i + 1)个是:\(str)")
}
// for in where
for str in a where str.prefix(1) == "t" {
print(str)
}
// 字典 for in,遍历是无序的
let dic = [
"one": 1,
"two": 2,
"three": 3
]
for (k, v) in dic {
print("key is \(k), value is \(v)")
}
// stride
for i in stride(from: 10, through: 0, by: -2) {
print(i)
}
/*
10
8
6
4
2
0
*/While while, repeat-while
// while
var i1 = 10
while i1 > 0 {
print("positive even number \(i1)")
i1 -= 2
}
// repeat while
var i2 = 10
repeat {
print("positive even number \(i2)")
i2 -= 2
} while i2 > 0使用 break 结束遍历,使用 continue 跳过当前作用域,继续下个循环
Switch
func f1(pa: String, t:(String, Int)) {
var p1 = 0
var p2 = 10
switch pa {
case "one":
p1 = 1
case "two":
p1 = 2
fallthrough // 继续到下个 case 中
default:
p2 = 0
}
print("p1 is \(p1)")
print("p2 is \(p2)")
// 元组
switch t {
case ("0", 0):
print("zero")
case ("1", 1):
print("one")
default:
print("no")
}
}
f1(pa: "two", t:("1", 1))
/*
p1 is 2
p2 is 0
one
*/
// 枚举
enum E {
case one, two, three, unknown(String)
}
func f2(pa: E) {
var p: String
switch pa {
case .one:
p = "1"
case .two:
p = "2"
case .three:
p = "3"
case let .unknown(u) where Int(u) ?? 0 > 0 : // 枚举关联值,使用 where 增加条件
p = u
case .unknown(_):
p = "negative number"
}
print(p)
}
f2(pa: E.one) // 1
f2(pa: E.unknown("10")) // 10
f2(pa: E.unknown("-10")) // negative number集合
数组 [1, 2, 3]
数组是有序集合
var a0: [Int] = [1, 10]
a0.append(2)
a0.remove(at: 0)
print(a0) // [10, 2]
let a1 = ["one", "two", "three"]
let a2 = ["three", "four"]
// 找两个集合的不同
let dif = a1.difference(from: a2) // swift的 diffing 算法在这 http://www.xmailserver.org/diff2.pdf swift实现在 swift/stdlib/public/core/Diffing.swift
for c in dif {
switch c {
case .remove(let o, let e, let a):
print("offset:\(o), element:\(e), associatedWith:\(String(describing: a))")
case .insert(let o, let e, let a):
print("offset:\(o), element:\(e), associatedWith:\(String(describing: a))")
}
}
/*
remove offset:1, element:four, associatedWith:nil
insert offset:0, element:one, associatedWith:nil
insert offset:1, element:two, associatedWith:nil
*/
let a3 = a2.applying(dif) ?? [] // 可以用于添加删除动画
print(a3) // ["one", "two", "three"]dif 有第三个 case 值 .insert(let offset, let element, let associatedWith) 可以跟踪成对的变化,用于高级动画。
从数组中随机取一个元素
print(a0.randomElement() ?? 0)数组排序
// 排序
struct S1 {
let n: Int
var b = true
}
let a4 = [
S1(n: 1),
S1(n: 10),
S1(n: 3),
S1(n: 2)
]
let a5 = a4.sorted { i1, i2 in
i1.n < i2.n
}
for n in a5 {
print(n)
}
/// S1(n: 1)
/// S1(n: 2)
/// S1(n: 3)
/// S1(n: 10)
let a6 = [1,10,4,7,2]
print(a6.sorted(by: >)) // [10, 7, 4, 2, 1]可以加到数组扩展中,通过扩展约束能够指定特定元素类型的排序,代码如下:
extension Array where Element == Int {
// 升序
func intSortedASC() -> [Int] {
return self.sorted(by: <)
}
// 降序
func intSortedDESC() -> [Int] {
return self.sorted(by: <)
}
}
print(a6.intSortedASC()) // 使用扩展增加自定义排序能力在数组中检索满足条件的元素,代码如下:
// 第一个满足条件了就返回
let a7 = a4.first {
$0.n == 10
}
print(a7?.n ?? 0)
// 是否都满足了条件
print(a4.allSatisfy { $0.n == 1 }) // false
print(a4.allSatisfy(\.b)) // true
// 找出最大的那个
print(a4.max(by: { e1, e2 in
e1.n < e2.n
}) ?? S1(n: 0))
// S1(n: 10, b: true)
// 看看是否包含某个元素
print(a4.contains(where: {
$0.n == 7
}))
// false一些切割数组的方法。
// 切片
// 取前3个,并不是直接复制,对于大的数组有性能优势。
print(a6[..<3]) // [1, 10, 4] 需要做越界检查
print(a6.prefix(30)) // [1, 10, 4, 7, 2] 不需要做越界检查,也是切片,性能一样
// 去掉前3个
print(a6.dropFirst(3)) // [7, 2]prefix(while:) 和 drop(while:) 方法,顺序遍历执行闭包里的逻辑判断,满足条件就返回,遇到不匹配就会停止遍历。prefix 返回满足条件的元素集合,drop 返回停止遍历之后那些元素集合。
let a8 = [8, 9, 20, 1, 35, 3]
let a9 = a8.prefix {
$0 < 30
}
print(a9) // [8, 9, 20, 1]
let a10 = a8.drop {
$0 < 30
}
print(a10) // [35, 3]比 filter 更高效的删除元素的方法 removeAll
// 删除所有不满足条件的元素
var a11 = [1, 3, 5, 12, 25]
a11.removeAll { $0 < 10 }
print(a11) // [4, 3, 1, 3, 3] 随机
// 创建未初始化的数组
let a12 = (0...4).map { _ in
Int.random(in: 0...5)
}
print(a12) // [0, 3, 3, 2, 5] 随机#if 用于后缀表达式
// #if 用于后缀表达式
let a13 = a11
#if os(iOS)
.count
#else
.reduce(0, +)
#endif
print(a13) //37Sets Set<Int>
Set 是无序集合,元素唯一
let s0: Set<Int> = [2, 4]
let s1: Set = [2, 10, 6, 4, 8]
let s2: Set = [7, 3, 5, 1, 9, 10]
let s3 = s1.union(s2) // 合集
let s4 = s1.intersection(s2) // 交集
let s5 = s1.subtracting(s2) // 非交集部分
let s6 = s1.symmetricDifference(s2) // 非交集的合集
print(s3) // [4, 2, 1, 7, 3, 10, 8, 9, 6, 5]
print(s4) // [10]
print(s5) // [8, 4, 2, 6]
print(s6) // [9, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 6, 8, 7]
// s0 是否被 s1 包含
print(s0.isSubset(of: s1)) // true
// s1 是否包含了 s0
print(s1.isSuperset(of: s0)) // true
let s7: Set = [3, 5]
// s0 和 s7 是否有交集
print(s0.isDisjoint(with: s7)) // true
// 可变 Set
var s8: Set = ["one", "two"]
s8.insert("three")
s8.remove("one")
print(s8) // ["two", "three"]字典 [:]
字典是无序集合,键值对应。
var d1 = [
"k1": "v1",
"k2": "v2"
]
d1["k3"] = "v3"
d1["k4"] = nil
print(d1) // ["k2": "v2", "k3": "v3", "k1": "v1"]
for (k, v) in d1 {
print("key is \(k), value is \(v)")
}
/*
key is k1, value is v1
key is k2, value is v2
key is k3, value is v3
*/
if d1.isEmpty == false {
print(d1.count) // 3
}
// mapValues
let d2 = d1.mapValues {
$0 + "_new"
}
print(d2) // ["k2": "v2_new", "k3": "v3_new", "k1": "v1_new"]
// 对字典的值或键进行分组
let d3 = Dictionary(grouping: d1.values) {
$0.count
}
print(d3) // [2: ["v1", "v2", "v3"]]
// 从字典中取值,如果键对应无值,则使用通过 default 指定的默认值
d1["k5", default: "whatever"] += "."
print(d1["k5"] ?? "") // whatever.
let v1 = d1["k3", default: "whatever"]
print(v1) // v3
// compactMapValues() 对字典值进行转换和解包。可以解可选类型,并去掉 nil 值
let d4 = [
"k1": 1,
"k2": 2,
"k3": nil
]
let d5 = d4.mapValues { $0 }
let d6 = d4.compactMapValues{ $0 }
print(d5)
// ["k3": nil, "k1": Optional(1), "k2": Optional(2)]
print(d6)
// ["k1": 1, "k2": 2]操作符
赋值 =, +=. -=, *=, /=
let i1 = 1
var i2 = i1
i2 = 2
print(i2) // 2
i2 += 1
print(i2) // 3
i2 -= 2
print(i2) // 1
i2 *= 10
print(i2) // 10
i2 /= 2
print(i2) // 5计算符 +, -, *, /, %
let i1 = 1
let i2 = i1
print((i1 + i2 - 1) * 10 / 2 % 3) // 2
print("i" + "1") // i1
// 一元运算符
print(-i1) // -1比较运算符 ==, >
遵循 Equatable 协议可以使用 == 和 != 来判断是否相等
print(1 > 2) // false
struct S: Equatable {
var p1: String
var p2: Int
}
let s1 = S(p1: "one", p2: 1)
let s2 = S(p1: "two", p2: 2)
let s3 = S(p1: "one", p2: 2)
let s4 = S(p1: "one", p2: 1)
print(s1 == s2) // false
print(s1 == s3) // false
print(s1 == s4) // true类需要实现 == 函数
class C: Equatable {
var p1: String
var p2: Int
init(p1: String, p2: Int) {
self.p1 = p1
self.p2 = p2
}
static func == (l: C, r: C) -> Bool {
return l.p1 == r.p1 && l.p2 == r.p2
}
}
let c1 = C(p1: "one", p2: 1)
let c2 = C(p1: "one", p2: 1)
print(c1 == c2)// 元组比较
// 会先比较第一个数,第一个无法比较才会比较第二个数
// 字符串比较和字母大小还有长度有关。先比较字母大小,在比较长度
("apple", 1) < ("apple", 2) // true
("applf", 1) < ("apple", 2) // false
("appl", 2) < ("apple", 1) // true
("appm", 2) < ("apple", 1) // false三元 _ ? _ : _
简化 if else 写法
// if else
func f1(p: Int) {
if p > 0 {
print("positive number")
} else {
print("negative number")
}
}
// 三元
func f2(p: Int) {
p > 0 ? print("positive number") : print("negative number")
}
f1(p: 1)
f2(p: 1)Nil-coalescing ??
简化 if let else 写法
// if else
func f1(p: Int?) {
if let i = p {
print("p have value is \(i)")
} else {
print("p is nil, use defalut value")
}
}
// 使用 ??
func f2(p: Int?) {
let i = p ?? 0
print("p is \(i)")
}范围 a…b
简化的值范围表达方式。
// 封闭范围
for i in 0...10 {
print(i)
}
// 半开范围
for i in 0..<10 {
print(i)
}// 单侧区间
let nums = [5,6,7,8]
print(nums[2...]) // 7 8逻辑 !, &&, ||
let i1 = -1
let i2 = 2
if i1 != i2 && (i1 < 0 || i2 < 0) {
print("i1 and i2 not equal, and one of them is negative number.")
}恒等 ===, !==
恒等返回是否引用了相同实例。
class C {
var p: String
init(p: String) {
self.p = p
}
}
let c1 = C(p: "one")
let c2 = C(p: "one")
let c3 = c1
print(c1 === c2) // false
print(c1 === c3) // true
print(c1 !== c2) // true运算符
位运算符
let i1: UInt8 = 0b00001111
let i2 = ~i1 // Bitwise NOT Operator(按位取反运算符),取反
let i3: UInt8 = 0b00111111
let i4 = i1 & i3 // Bitwise AND Operator(按位与运算符),都为1才是1
let i5 = i1 | i3 // Bitwise OR Operator(按位或运算符),有一个1就是1
let i6 = i1 ^ i3 // Bitwise XOR Operator(按位异或运算符),不同为1,相同为0
print(i1,i2,i3,i4,i5,i6)
// << 按位左移,>> 按位右移
let i7 = i1 << 1
let i8 = i1 >> 2
print(i7,i8)溢出运算符,有 &+、&- 和 &*
var i1 = Int.max
print(i1) // 9223372036854775807
i1 = i1 &+ 1
print(i1) // -9223372036854775808
i1 = i1 &+ 10
print(i1) // -9223372036854775798
var i2 = UInt.max
i2 = i2 &+ 1
print(i2) // 0运算符函数包括前缀运算符、后缀运算符、复合赋值运算符以及等价运算符。另,还可以自定义运算符,新的运算符要用 operator 关键字进行定义,同时要指定 prefix、infix 或者 postfix 修饰符。
基础库
时间
Date 的基本用法如下:
let now = Date()
// Date 转 时间戳
let interval = now.timeIntervalSince1970 // 时间戳
let df = DateFormatter()
df.dateFormat = "yyyy 年 MM 月 dd 日 HH:mm:ss"
print("时间戳:\(Int(interval))") // 时间戳:1642399901
print("格式化的时间:" + df.string(from: now)) // 格式化的时间:2022 年 01 月 17 日 14:11:41
df.dateStyle = .short
print("short 样式时间:" + df.string(from: now)) // short 样式时间:2022/1/17
df.locale = Locale(identifier: "zh_Hans_CN")
df.dateStyle = .full
print("full 样式时间:" + df.string(from: now)) // full 样式时间:2022年1月17日 星期一
// 时间戳转 Date
let date = Date(timeIntervalSince1970: interval)
print(date) // 2022-01-17 06:11:41 +0000复杂的时间操作,比如说 GitHub 接口使用的是 ISO 标准,RSS 输出的是 RSS 标准字符串,不同标准对应不同时区的时间计算处理,可以使用开源库 SwiftDate 来完成。示例代码如下:
import SwiftDate
// 使用 SwiftDate 库
let cn = Region(zone: Zones.asiaShanghai, locale: Locales.chineseChina)
SwiftDate.defaultRegion = cn
print("2008-02-14 23:12:14".toDate()?.year ?? "") // 2008
let d1 = "2022-01-17T23:20:35".toISODate(region: cn)
guard let d1 = d1 else {
return
}
print(d1.minute) // 20
let d2 = d1 + 1.minutes
print(d2.minute)
// 两个 DateInRegion 相差时间 interval
let i1 = DateInRegion(Date(), region: cn) - d1
let s1 = i1.toString {
$0.maximumUnitCount = 4
$0.allowedUnits = [.day, .hour, .minute]
$0.collapsesLargestUnit = true
$0.unitsStyle = .abbreviated
$0.locale = Locales.chineseChina
}
print(s1) // 9小时45分钟格式化
使用标准库的格式来描述不同场景的情况可以不用去考虑由于不同地区的区别,这些在标准库里就可以自动完成了。
描述两个时间之间相差多长时间
// 计算两个时间之间相差多少时间,支持多种语言字符串
let d1 = Date().timeIntervalSince1970 - 60 * 60 * 24
let f1 = RelativeDateTimeFormatter()
f1.dateTimeStyle = .named
f1.formattingContext = .beginningOfSentence
f1.locale = Locale(identifier: "zh_Hans_CN")
let str = f1.localizedString(for: Date(timeIntervalSince1970: d1), relativeTo: Date())
print(str) // 昨天
// 简写
let str2 = Date.now.addingTimeInterval(-(60 * 60 * 24))
.formatted(.relative(presentation: .named))
print(str2) // yesterday描述多个事物
// 描述多个事物
let s1 = ListFormatter.localizedString(byJoining: ["冬天","春天","夏天","秋天"])
print(s1)描述名字
// 名字
let f2 = PersonNameComponentsFormatter()
var nc1 = PersonNameComponents()
nc1.familyName = "戴"
nc1.givenName = "铭"
nc1.nickname = "铭哥"
print(f2.string(from: nc1)) // 戴铭
f2.style = .short
print(f2.string(from: nc1)) // 铭哥
f2.style = .abbreviated
print(f2.string(from: nc1)) // 戴
var nc2 = PersonNameComponents()
nc2.familyName = "Dai"
nc2.givenName = "Ming"
nc2.nickname = "Starming"
f2.style = .default
print(f2.string(from: nc2)) // Ming Dai
f2.style = .short
print(f2.string(from: nc2)) // Starming
f2.style = .abbreviated
print(f2.string(from: nc2)) // MD
// 取出名
let componets = f2.personNameComponents(from: "戴铭")
print(componets?.givenName ?? "") // 铭描述数字
// 数字
let f3 = NumberFormatter()
f3.locale = Locale(identifier: "zh_Hans_CN")
f3.numberStyle = .currency
print(f3.string(from: 123456) ?? "") // ¥123,456.00
f3.numberStyle = .percent
print(f3.string(from: 123456) ?? "") // 12,345,600%
let n1 = 1.23456
let n1Str = n1.formatted(.number.precision(.fractionLength(3)).rounded())
print(n1Str) // 1.235描述地址
// 地址
import Contacts
let f4 = CNPostalAddressFormatter()
let address = CNMutablePostalAddress()
address.street = "海淀区王庄路XX号院X号楼X门XXX"
address.postalCode = "100083"
address.city = "北京"
address.country = "中国"
print(f4.string(from: address))
/// 海淀区王庄路XX号院X号楼X门XXX
/// 北京 100083
/// 中国度量值
标准库里的物理量,在这个文档里有详细列出,包括角度、平方米等。
// 参考:https://developer.apple.com/documentation/foundation/nsdimension
let m1 = Measurement(value: 1, unit: UnitLength.kilometers)
let m2 = m1.converted(to: .meters) // 千米转米
print(m2) // 1000.0 m
// 度量值转为本地化的值
let mf = MeasurementFormatter()
mf.locale = Locale(identifier: "zh_Hans_CN")
print(mf.string(from: m1)) // 1公里一些物理公式供参考:
面积 = 长度 × 长度
体积 = 长度 × 长度 × 长度 = 面积 × 长度
速度=长度/时间
加速度=速度/时间
力 = 质量 × 加速度
扭矩 = 力 × 长度
压力 = 力 / 面积
密度=质量 / 体积
能量 = 功率 × 时间
电阻 = 电压 / 电流Data
数据压缩和解压
// 对数据的压缩
let d1 = "看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?".data(using: .utf8)! as NSData
print("ori \(d1.count) bytes")
do {
/// 压缩算法
/// * lz4
/// * lzma
/// * zlib
/// * lzfse
let compressed = try d1.compressed(using: .zlib)
print("comp \(compressed.count) bytes")
// 对数据解压
let decomressed = try compressed.decompressed(using: .zlib)
let deStr = String(data: decomressed as Data, encoding: .utf8)
print(deStr ?? "")
} catch {}
/// ori 297 bytes
/// comp 37 bytes文件
文件的一些基本操作的代码如下:
let path1 = "/Users/mingdai/Downloads/1.html"
let path2 = "/Users/mingdai/Documents/GitHub/"
let u1 = URL(string: path1)
do {
// 写入
let url1 = try FileManager.default.url(for: .itemReplacementDirectory, in: .userDomainMask, appropriateFor: u1, create: true) // 保证原子性安全保存
print(url1)
// 读取
let s1 = try String(contentsOfFile: path1, encoding: .utf8)
print(s1)
} catch {}
// 检查路径是否可用
let u2 = URL(fileURLWithPath:path2)
do {
let values = try u2.resourceValues(forKeys: [.volumeAvailableCapacityForImportantUsageKey])
if let capacity = values.volumeAvailableCapacityForImportantUsage {
print("可用: \(capacity)")
} else {
print("不可用")
}
} catch {
print("错误: \(error.localizedDescription)")
}怎么遍历多级目录结构中的文件呢?看下面的代码的实现:
// 遍历路径下所有目录
let u3 = URL(fileURLWithPath: FileManager.default.currentDirectoryPath)
let fm = FileManager.default
fm.enumerator(atPath: u3.path)?.forEach({ path in
guard let path = path as? String else {
return
}
let url = URL(fileURLWithPath: path, relativeTo: u3)
print(url.lastPathComponent)
})可以使用 FileWrapper 来创建文件夹和文件。举个例子:
// FileWrapper 的使用
// 创建文件
let f1 = FileWrapper(regularFileWithContents: Data("# 第 n 个文件\n ## 标题".utf8))
f1.fileAttributes[FileAttributeKey.creationDate.rawValue] = Date()
f1.fileAttributes[FileAttributeKey.modificationDate.rawValue] = Date()
// 创建文件夹
let folder1 = FileWrapper(directoryWithFileWrappers: [
"file1.md": f1
])
folder1.fileAttributes[FileAttributeKey.creationDate.rawValue] = Date()
folder1.fileAttributes[FileAttributeKey.modificationDate.rawValue] = Date()
do {
try folder1.write(
to: URL(fileURLWithPath: FileManager.default.currentDirectoryPath).appendingPathComponent("NewFolder"),
options: .atomic,
originalContentsURL: nil
)
} catch {}
print(FileManager.default.currentDirectoryPath)上面代码写起来比较繁琐,对 FileWrapper 更好的封装可以参考这篇文章《 A Type-Safe FileWrapper | Heberti Almeida 》。
文件读写处理完整能力可以参看这个库 GitHub - JohnSundell/Files: A nicer way to handle files & folders in Swift
本地或者网络上,比如网盘和FTP的文件发生变化时,怎样知道能够观察到呢?
通过 HTTPHeader 里的 If-Modified-Since、Last-Modified、If-None-Match 和 Etag 等字段来判断文件的变化,本地则是使用 DispatchSource.makeFileSystemObjectSource 来进行的文件变化监听。可以参考 KZFileWatchers 库的做法。
Scanner
let s1 = """
one1,
two2,
three3.
"""
let sn1 = Scanner(string: s1)
while !sn1.isAtEnd {
if let r1 = sn1.scanUpToCharacters(from: .newlines) {
print(r1 as String)
}
}
/// one1,
/// two2,
/// three3.
// 找出数字
let sn2 = Scanner(string: s1)
sn2.charactersToBeSkipped = CharacterSet.decimalDigits.inverted // 不是数字的就跳过
var p: Int = 0
while !sn2.isAtEnd {
if sn2.scanInt(&p) {
print(p)
}
}
/// 1
/// 2
/// 3上面的代码还不是那么 Swifty,可以通过用AnySequence和AnyIterator来包装下,将序列中的元素推迟到实际需要时再来处理,这样性能也会更好些。具体实现可以参看《 String parsing in Swift 》这篇文章。
AttributeString
效果如下:

代码如下:
var aStrs = [AttributedString]()
var aStr1 = AttributedString("""
标题
正文内容,具体查看链接。
这里摘出第一个重点,还要强调的内容。
""")
// 标题
let title = aStr1.range(of: "标题")
guard let title = title else {
return aStrs
}
var c1 = AttributeContainer() // 可复用容器
c1.inlinePresentationIntent = .stronglyEmphasized
c1.font = .largeTitle
aStr1[title].setAttributes(c1)
// 链接
let link = aStr1.range(of: "链接")
guard let link = link else {
return aStrs
}
var c2 = AttributeContainer() // 链接
c2.strokeColor = .blue
c2.link = URL(string: "https://ming1016.github.io/")
aStr1[link].setAttributes(c2.merging(c1)) // 合并 AttributeContainer
// Runs
let i1 = aStr1.range(of: "重点")
let i2 = aStr1.range(of: "强调")
guard let i1 = i1, let i2 = i2 else {
return aStrs
}
var c3 = AttributeContainer()
c3.foregroundColor = .yellow
c3.inlinePresentationIntent = .stronglyEmphasized
aStr1[i1].setAttributes(c3)
aStr1[i2].setAttributes(c3)
for r in aStr1.runs {
print("-------------")
print(r.attributes)
}
aStrs.append(aStr1)
// Markdown
do {
let aStr2 = try AttributedString(markdown: """
内容[链接](https://ming1016.github.io/)。需要**强调**的内容。
""")
aStrs.append(aStr2)
} catch {}SwiftUI 的 Text 可以直接读取 AttributedString 来进行显示。
随机
用法:
let ri = Int.random(in: 0..<10)
print(ri) // 0到10随机数
let a = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(a.randomElement() ?? 0) // 数组中随机取个数
print(a.shuffled()) // 随机打乱数组顺序UserDefaults
使用方法如下:
enum UDKey {
static let k1 = "token"
}
let ud = UserDefaults.standard
ud.set("xxxxxx", forKey: UDKey.k1)
let tk = ud.string(forKey: UDKey.k1)
print(tk ?? "")模式
单例
struct S {
static let shared = S()
private init() {
// 防止实例初始化
}
}系统及设备
系统判断
#if os(tvOS)
// do something in tvOS
#elseif os(iOS)
// do somthing in iOS
#elseif os(macOS)
// do somthing in macOS
#endif版本兼容
// 版本
@available(iOS 15, *)
func f() {
}
// 版本检查
if #available(iOS 15, macOS 12, *) {
f()
} else {
// nothing happen
}canImport 判断库是否可使用
#if canImport(SpriteKit)
// iOS 等苹果系统执行
#else
// 非苹果系统
#endiftargetEnvironment 环境的判断
#if targetEnvironment(simulator)
// 模拟器
#else
// 真机
#endif自带属性包装
@resultBuilder
结果生成器(Result builders),通过传递序列创建新值,SwiftUI就是使用的结果生成器将多个视图生成一个视图
@resultBuilder
struct RBS {
// 基本闭包支持
static func buildBlock(_ components: Int...) -> Int {
components.reduce(0) { partialResult, i in
partialResult + i
}
}
// 支持条件判断
static func buildEither(first component: Int) -> Int {
component
}
static func buildEither(second component: Int) -> Int {
component
}
// 支持循环
static func buildArray(_ components: [Int]) -> Int {
components.reduce(0) { partialResult, i in
partialResult + i
}
}
}
let a = RBS.buildBlock(
1,
2,
3
)
print(a) // 6
// 应用到函数中
@RBS func f1() -> Int {
1
2
3
}
print(f1()) // 6
// 设置了 buildEither 就可以在闭包中进行条件判断。
@RBS func f2(stopAtThree: Bool) -> Int {
1
2
3
if stopAtThree == true {
0
} else {
4
5
6
}
}
print(f2(stopAtThree: false)) // 21
// 设置了 buildArray 就可以在闭包内使用循环了
@RBS func f3() -> Int {
for i in 1...3 {
i * 2
}
}
print(f3()) // 12@dynamicMemberLookup 动态成员查询
@dynamicMemberLookup 指示访问属性时调用一个已实现的处理动态查找的下标方法 subscript(dynamicMemeber:),通过指定属性字符串名返回值。使用方法如下:
@dynamicMemberLookup
struct D {
// 找字符串
subscript(dynamicMember m: String) -> String {
let p = ["one": "first", "two": "second"]
return p[m, default: ""]
}
// 找整型
subscript(dynamicMember m: String) -> Int {
let p = ["one": 1, "two": 2]
return p[m, default: 0]
}
// 找闭包
subscript(dynamicMember m: String) -> (_ s: String) -> Void {
return {
print("show \($0)")
}
}
// 静态数组成员
var p = ["This is a member"]
// 动态数组成员
subscript(dynamicMember m: String) -> [String] {
return ["This is a dynamic member"]
}
}
let d = D()
let s1: String = d.one
print(s1) // first
let i1: Int = d.one
print(i1) // 1
d.show("something") // show something
print(d.p) // ["This is a member"]
let dynamicP:[String] = d.dp
print(dynamicP) // ["This is a dynamic member"]类使用 @dynamicMemberLookup,继承的类也会自动加上 @dynamicMemberLookup。协议上定义 @dynamicMemberLookup,通过扩展可以默认实现 subscript(dynamicMember:) 方法。
@dynamicCallable 动态可调用类型
@dynamicCallable 动态可调用类型。通过实现 dynamicallyCall 方法来定义变参的处理。
@dynamicCallable
struct D {
// 带参数说明
func dynamicallyCall(withKeywordArguments args: KeyValuePairs<String, Int>) -> Int {
let firstArg = args.first?.value ?? 0
return firstArg * 2
}
// 无参数说明
func dynamicallyCall(withArguments args: [String]) -> String {
var firstArg = ""
if args.count > 0 {
firstArg = args[0]
}
return "show \(firstArg)"
}
}
let d = D()
let i = d(numberIs: 2)
print(i) // 4
let s = d("hi")
print(s) // show hi自带协议
Hashable
struct H: Hashable {
var p1: String
var p2: Int
// 提供随机 seed
func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
hasher.combine(p1)
}
}
let h1 = H(p1: "one", p2: 1)
let h2 = H(p1: "two", p2: 2)
var hs1 = Hasher()
hs1.combine(h1)
hs1.combine(h2)
print(h1.hashValue) // 7417088153212460033 随机值
print(h2.hashValue) // -6972912482785541972 随机值
print(hs1.finalize()) // 7955861102637572758 随机值
print(h1.hashValue) // 7417088153212460033 和前面 h1 一样
let h3 = H(p1: "one", p2: 1)
print(h3.hashValue) // 7417088153212460033 和前面 h1 一样
var hs2 = Hasher()
hs2.combine(h3)
hs2.combine(h2)
print(hs2.finalize()) // 7955861102637572758 和前面 hs1 一样应用生命周期内,调用 combine() 添加相同属性哈希值相同,由于 Hasher 每次都会使用随机的 seed,因此不同应用生命周期,也就是下次启动的哈希值,就会和上次的哈希值不同。
Codable
JSON 没有 id 字段
如果SwiftUI要求数据Model都是遵循Identifiable协议的,而有的json没有id这个字段,可以使用扩展struct的方式解决:
struct CommitModel: Decodable, Hashable {
var sha: String
var author: AuthorModel
var commit: CommitModel
}
extension CommitModel: Identifiable {
var id: String {
return sha
}
}网络
网络状态检查
通过 Network 库的 NWPathMonitor 来检查
import Combine
import Network
// 网络状态检查 network state check
final class Nsck: ObservableObject {
static let shared = Nsck()
private(set) lazy var pb = mkpb()
@Published private(set) var pt: NWPath
private let monitor: NWPathMonitor
private lazy var sj = CurrentValueSubject<NWPath, Never>(monitor.currentPath)
private var sb: AnyCancellable?
init() {
monitor = NWPathMonitor()
pt = monitor.currentPath
monitor.pathUpdateHandler = { [weak self] path in
self?.pt = path
self?.sj.send(path)
}
monitor.start(queue: DispatchQueue.global())
}
deinit {
monitor.cancel()
sj.send(completion: .finished)
}
private func mkpb() -> AnyPublisher<NWPath, Never> {
return sj.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
}使用方法
var sb = Set<AnyCancellable>()
var alertMsg = ""
Nsck.shared.pb
.sink { _ in
//
} receiveValue: { path in
alertMsg = path.debugDescription
switch path.status {
case .satisfied:
alertMsg = ""
case .unsatisfied:
alertMsg = "😱"
case .requiresConnection:
alertMsg = "🥱"
@unknown default:
alertMsg = "🤔"
}
if path.status == .unsatisfied {
switch path.unsatisfiedReason {
case .notAvailable:
alertMsg += "网络不可用"
case .cellularDenied:
alertMsg += "蜂窝网不可用"
case .wifiDenied:
alertMsg += "Wifi不可用"
case .localNetworkDenied:
alertMsg += "网线不可用"
@unknown default:
alertMsg += "网络不可用"
}
}
}
.store(in: &sb)动画
布局动画
import SwiftUI
struct AnimateLayout: View {
@State var changeLayout: Bool = true
@Namespace var namespace
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 30) {
if changeLayout {
HStack { items }
} else {
VStack { items }
}
Button("切换布局") {
withAnimation { changeLayout.toggle() }
}
}
.padding()
}
@ViewBuilder var items: some View {
Text("one")
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "one", in: namespace)
Text("Two")
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "Two", in: namespace)
Text("Three")
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "Three", in: namespace)
}
}安全
Keychain
使用方法:
let d1 = Data("keyChain github token".utf8)
let service = "access-token"
let account = "github"
let q1 = [
kSecValueData: d1,
kSecClass: kSecClassGenericPassword,
kSecAttrService: service,
kSecAttrAccount: account
] as CFDictionary
// 添加一个 keychain
let status = SecItemAdd(q1, nil)
// 如果已经添加过会抛出 -25299 错误代码,需要调用 SecItemUpdate 来进行更新
if status == errSecDuplicateItem {
let q2 = [
kSecClass: kSecClassGenericPassword,
kSecAttrService: service,
kSecAttrAccount: account
] as CFDictionary
let q3 = [
kSecValueData: d1
] as CFDictionary
SecItemUpdate(q2, q3)
}
// 读取
let q4 = [
kSecAttrService: service,
kSecAttrAccount: account,
kSecClass: kSecClassGenericPassword,
kSecReturnData: true
] as CFDictionary
var re: AnyObject?
SecItemCopyMatching(q4, &re)
guard let reData = re as? Data else { return }
print(String(decoding: reData, as: UTF8.self)) // keyChain github token
// 删除
let q5 = [
kSecAttrService: service,
kSecAttrAccount: account,
kSecClass: kSecClassGenericPassword,
] as CFDictionary
SecItemDelete(q5)工程
程序入口点
Swift 允许全局编写 Swift 代码,实际上 clang 会自动将代码包进一个模拟 C 的函数中。Swift 也能够指定入口点,比如 @UIApplicationMain 或 @NSApplicationMain,UIKit 启动后生命周期管理是 AppDelegate 和 SceneDelegate,《 Understanding the iOS 13 Scene Delegate 》这篇有详细介绍。
@UIApplicationMain 和 @NSApplicationMain 会自动生成入口点。这些入口点都是平台相关的,Swift 发展来看是多平台的,这样在 Swift 5.3 时引入了 @main,可以方便的指定入口点。代码如下:
@main // 要定义个静态的 main 函数
struct M {
static func main() {
print("let's begin")
}
}ArgumentParser 库,Swift 官方开源的一个开发命令行工具的库,也支持 @main。使用方法如下:
import ArgumentParser
@main
struct C: ParsableCommand {
@Argument(help: "Start")
var phrase: String
func run() throws {
for _ in 1...5 {
print(phrase)
}
}
}专题
Swift 那些事
语法速查
基础
变量 let, var
变量是可变的,使用 var 修饰,常量是不可变的,使用 let 修饰。类、结构体和枚举里的变量是属性。
var v1:String = "hi" // 标注类型
var v2 = "类型推导"
let l1 = "标题" // 常量
class a {
let p1 = 3
var p2: Int {
p1 * 3
}
}属性没有 set 可以省略 get,如果有 set 需加 get。变量设置前通过 willSet 访问到,变量设置后通过 didSet 访问。
打印 print(“”)
控制台打印值
print("hi")
let i = 14
print(i)
print("9月\(i)是小柠檬的生日")
for i in 1...3{
print(i)
}
// output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 使用terminator使循环打印更整洁
for i in 1...3 {
print("\(i) ", terminator: "")
}
// output:
// 1 2 3注释 //
// 单行注释
/*
多行注释第一行。
多行注释第二行。
*/
// MARK: 会在 minimap 上展示
// TODO: 待做
// FIXME: 待修复可选 ?, !
可能会是 nil 的变量就是可选变量。当变量为 nil 通过??操作符可以提供一个默认值。
var o: Int? = nil
let i = o ?? 0SE-0345 if let shorthand for shadowing an existing optional variable 引入的新语法,用于 unwrapping optinal。
let s1: String? = "hey"
let s2: String? = "u"
if let s1 {
print(s1)
}
guard let s1, let s2 else { return }
print(s1 + " " + s2)闭包
闭包也可以叫做 lambda,是匿名函数,对应 OC 的 block。
let a1 = [1,3,2].sorted(by: { (l: Int, r: Int) -> Bool in
return l < r
})
// 如果闭包是唯一的参数并在表达式最后可以使用结尾闭包语法,写法简化为
let a2 = [1,3,2].sorted { (l: Int, r: Int) -> Bool in
return l < r
}
// 已知类型可以省略
let a3 = [1,3,2].sorted { l, r in
return l < r
}
// 通过位置来使用闭包的参数,最后简化如下:
let a4 = [1,3,2].sorted { $0 < $1 }函数也是闭包的一种,函数的参数也可以是闭包。@escaping 表示逃逸闭包,逃逸闭包是可以在函数返回之后继续调用的。@autoclosure 表示自动闭包,可以用来省略花括号。
SE-0326 提高了 Swift 对闭包使用参数和类型推断的能力。如下代码:
let a = [1,2,3]
let r = a.map { i in
if i >= 2 {
return "\(i) 大于等于2"
} else {
return "\(i) 小于2"
}
}
print(r)函数 func
函数可以作为另一个函数的参数,也可以作为另一个函数的返回。函数是特殊的闭包,在类、结构体和枚举中是方法。
// 为参数设置默认值
func f1(p: String = "p") -> String {
"p is \(p)"
}
// 函数作为参数
func f2(fn: (String) -> String, p: String) -> String {
return fn(p)
}
print(f2(fn:f1, p: "d")) // p is d
// 函数作为返回值
func f3(p: String) -> (String) -> String {
return f1
}
print(f3(p: "yes")("no")) // p is no函数可以返回多个值,函数是可以嵌套的,也就是函数里内可以定义函数,函数内定义的函数可以访问自己作用域外函数内的变量。inout 表示的是输入输出参数,函数可以在函数内改变输入输出参数。defer 标识的代码块会在函数返回之前执行。
函数在 Swift 5.4 时开始有了使用多个变量参数的能力,使用方法如下:
func f4(s: String..., i: Int...) {
print(s)
print(i)
}
f4(s: "one", "two", "three", i: 1, 2, 3)
/// ["one", "two", "three"]
/// [1, 2, 3]嵌套函数可以重载,嵌套函数可以在声明函数之前调用他。
func f5() {
nf5()
func nf5() {
print("this is nested function")
}
}
f5() // this is nested function访问控制
在 Xcode 里的 target 就是模块,使用 import 可导入模块。模块内包含源文件,每个源文件里可以有多个类、结构体、枚举和函数等多种类型。访问级别可以通过一些关键字描述,分为如下几种:
- open:在模块外可以调用和继承。
- public:在模块外可调用不可继承,open 只适用类和类成员。
- internal:默认级别,模块内可跨源文件调用,模块外不可调用。
- fileprivate:只能在源文件内访问。
- private:只能在所在的作用域内访问。
重写继承类的成员,可以设置成员比父类的这个成员更高的访问级别。Setter 的级别可以低于对应的 Getter 的级别,比如设置 Setter 访问级别为 private,可以在属性使用 private(set) 来修饰。
Regex
标准库多了个 Regex<Output> 类型,Regex 语法与 Perl、Python、Ruby、Java、NSRegularExpression 和许多其他语言兼容。可以用 let regex = try! Regex("a[bc]+") 或 let regex = /a[bc]+/ 写法来使用。SE-0350 Regex Type and Overview 引入 Regex 类型。SE-0351 Regex builder DSL 使用 result builder 来构建正则表达式的 DSL。SE-0354 Regex Literals 简化的正则表达式。SE-0357 Regex-powered string processing algorithms 提案里有基于正则表达式的新字符串处理算法。
session Meet Swift Regex 、Swift Regex: Beyond the basics
Regex 示例代码如下:
let s1 = "I am not a good painter"
print(s1.ranges(of: /good/))
do {
let regGood = try Regex("[a-z]ood")
print(s1.replacing(regGood, with: "bad"))
} catch {
print(error)
}
print(s1.trimmingPrefix(/i am /.ignoresCase()))
let reg1 = /(.+?) read (\d+) books./
let reg2 = /(?<name>.+?) read (?<books>\d+) books./
let s2 = "Jack read 3 books."
do {
if let r1 = try reg1.wholeMatch(in: s2) {
print(r1.1)
print(r1.2)
}
if let r2 = try reg2.wholeMatch(in: s2) {
print("name:" + r2.name)
print("books:" + r2.books)
}
} catch {
print(error)
}使用 regex builders 的官方示例:
// Text to parse:
// CREDIT 03/02/2022 Payroll from employer $200.23
// CREDIT 03/03/2022 Suspect A $2,000,000.00
// DEBIT 03/03/2022 Ted's Pet Rock Sanctuary $2,000,000.00
// DEBIT 03/05/2022 Doug's Dugout Dogs $33.27
import RegexBuilder
let fieldSeparator = /\s{2,}|\t/
let transactionMatcher = Regex {
/CREDIT|DEBIT/
fieldSeparator
One(.date(.numeric, locale: Locale(identifier: "en_US"), timeZone: .gmt)) // 👈🏻 we define which data locale/timezone we want to use
fieldSeparator
OneOrMore {
NegativeLookahead { fieldSeparator } // 👈🏻 we stop as soon as we see one field separator
CharacterClass.any
}
fieldSeparator
One(.localizedCurrency(code: "USD").locale(Locale(identifier: "en_US")))
}在正则表达式中捕获数据,使用 Capture:
let fieldSeparator = /\s{2,}|\t/
let transactionMatcher = Regex {
Capture { /CREDIT|DEBIT/ } // 👈🏻
fieldSeparator
Capture { One(.date(.numeric, locale: Locale(identifier: "en_US"), timeZone: .gmt)) } // 👈🏻
fieldSeparator
Capture { // 👈🏻
OneOrMore {
NegativeLookahead { fieldSeparator }
CharacterClass.any
}
}
fieldSeparator
Capture { One(.localizedCurrency(code: "USD").locale(Locale(identifier: "en_US"))) } // 👈🏻
}
// transactionMatcher: Regex<(Substring, Substring, Date, Substring, Decimal)>基础类型
数字 Int, Float
数字的类型有 Int、Float 和 Double
// Int
let i1 = 100
let i2 = 22
print(i1 / i2) // 向下取整得 4
// Float
let f1: Float = 100.0
let f2: Float = 22.0
print(f1 / f2) // 4.5454545
let f3: Float16 = 5.0 // macOS 还不能用
let f4: Float32 = 5.0
let f5: Float64 = 5.0
let f6: Float80 = 5.0
print(f4, f5, f6) // 5.0 5.0 5.0
// Double
let d1: Double = 100.0
let d2: Double = 22.0
print(d1 / d2) // 4.545454545454546
// 字面量
print(Int(0b10101)) // 0b 开头是二进制
print(Int(0x00afff)) // 0x 开头是十六进制
print(2.5e4) // 2.5x10^4 十进制用 e
print(0xAp2) // 10*2^2 十六进制用 p
print(2_000_000) // 2000000
// isMultiple(of:) 方法检查一个数字是否是另一个数字的倍数
let i3 = 36
print(i3.isMultiple(of: 9)) // true处理数字有 floor、ceil、round。floor 是向下取整,只取整数部分;cell 是向上取整,只要有不为零的小数,整数就加1;round 是四舍五入。
布尔数 Bool
布尔数有 true 和 false 两种值,还有一个能够切换这两个值的 toggle 方法。
var b = false
b.toggle() // true
b.toggle() // false元组 (a, b, c)
元组里的值类型可以是不同的。元组可以看成是匿名的结构体。
let t1 = (p1: 1, p2: "two", p3: [1,2,3])
print(t1.p1)
print(t1.p3)
// 类型推导
let t2 = (1, "two", [1,2,3])
// 通过下标访问
print(t2.1) // two
// 分解元组
let (dp1, dp2, _) = t2
print(dp1)
print(dp2)字符串
let s1 = "Hi! This is a string. Cool?"
/// 转义符 \n 表示换行。
/// 其它转义字符有 \0 空字符)、\t 水平制表符 、\n 换行符、\r 回车符
let s2 = "Hi!\nThis is a string. Cool?"
// 多行
let s3 = """
Hi!
This is a string.
Cool?
"""
// 长度
print(s3.count)
print(s3.isEmpty)
// 拼接
print(s3 + "\nSure!")
// 字符串中插入变量
let i = 1
print("Today is good day, double \(i)\(i)!")
/// 遍历字符串
/// 输出:
/// o
/// n
/// e
for c in "one" {
print(c)
}
// 查找
print(s3.lowercased().contains("cool")) // true
// 替换
let s4 = "one is two"
let newS4 = s4.replacingOccurrences(of: "two", with: "one")
print(newS4)
// 删除空格和换行
let s5 = " Simple line. \n\n "
print(s5.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines))
// 切割成数组
let s6 = "one/two/three"
let a1 = s6.components(separatedBy: "/") // 继承自 NSString 的接口
print(a1) // ["one", "two", "three"]
let a2 = s6.split(separator: "/")
print(a2) // ["one", "two", "three"] 属于切片,性能较 components 更好
// 判断是否是某种类型
let c1: Character = "🤔"
print(c1.isASCII) // false
print(c1.isSymbol) // true
print(c1.isLetter) // false
print(c1.isNumber) // false
print(c1.isUppercase) // false
// 字符串和 Data 互转
let data = Data("hi".utf8)
let s7 = String(decoding: data, as: UTF8.self)
print(s7) // hi
// 字符串可以当作集合来用。
let revered = s7.reversed()
print(String(revered))Unicode、Character 和 SubString 等内容参见官方字符串文档:Strings and Characters — The Swift Programming Language (Swift 5.1)
字符串字面符号可以参看《String literals in Swift》。
原始字符串
// 原始字符串在字符串前加上一个或多个#符号。里面的双引号和转义符号将不再起作用了,如果想让转义符起作用,需要在转义符后面加上#符号。
let s8 = #"\(s7)\#(s7) "one" and "two"\n. \#nThe second line."#
print(s8)
/// \(s7)hi "one" and "two"\n.
/// The second line.
// 原始字符串在正则使用效果更佳,反斜杠更少了。
let s9 = "\\\\[A-Z]+[A-Za-z]+\\.[a-z]+"
let s10 = #"\\[A-Z]+[A-Za-z]+\.[a-z]+"#
print(s9) // \\[A-Z]+[A-Za-z]+\.[a-z]+
print(s10) // \\[A-Z]+[A-Za-z]+\.[a-z]+Swift5.7 String Index 大升级 String Index Overhaul
枚举
Swift的枚举有类的一些特性,比如计算属性、实例方法、扩展、遵循协议等等。
enum E1:String, CaseIterable {
case e1, e2 = "12"
}
// 关联值
enum E2 {
case e1([String])
case e2(Int)
}
let e1 = E2.e1(["one","two"])
let e2 = E2.e2(3)
switch e1 {
case .e1(let array):
print(array)
case .e2(let int):
print(int)
}
print(e2)
// 原始值
print(E1.e1.rawValue)
// 遵循 CaseIterable 协议可迭代
for ie in E1.allCases {
print("show \(ie)")
}
// 递归枚举
enum RE {
case v(String)
indirect case node(l:RE, r:RE)
}
let lNode = RE.v("left")
let rNode = RE.v("right")
let pNode = RE.node(l: lNode, r: rNode)
switch pNode {
case .v(let string):
print(string)
case .node(let l, let r):
print(l,r)
switch l {
case .v(let string):
print(string)
case .node(let l, let r):
print(l, r)
}
switch r {
case .v(let string):
print(string)
case .node(let l, let r):
print(l, r)
}
}@unknown 用来区分固定的枚举和可能改变的枚举的能力。@unknown 用于防止未来新增枚举属性会进行提醒提示完善每个 case 的处理。
// @unknown
enum E3 {
case e1, e2, e3
}
func fe1(e: E3) {
switch e {
case .e1:
print("e1 ok")
case .e2:
print("e2 ok")
case .e3:
print("e3 ok")
@unknown default:
print("not ok")
}
}符合 Comparable 协议的枚举可以进行比较。
// Comparable 枚举比较
enum E4: Comparable {
case e1, e2
case e3(i: Int)
case e4
}
let e3 = E4.e4
let e4 = E4.e3(i: 3)
let e5 = E4.e3(i: 2)
let e6 = E4.e1
print(e3 > e4) // true
let a1 = [e3, e4, e5, e6]
let a2 = a1.sorted()
for i in a2 {
print(i.self)
}
/// e1
/// e3(i: 2)
/// e3(i: 3)
/// e4泛型和协议
泛型可以减少重复代码,是一种抽象的表达方式。where 关键字可以对泛型做约束。
func fn<T>(p: T) -> [T] {
var r = [T]()
r.append(p)
return r
}
print(fn(p: "one"))
// 结构体
struct S1<T> {
var arr = [T]()
mutating func add(_ p: T) {
arr.append(p)
}
}
var s1 = S1(arr: ["zero"])
s1.add("one")
s1.add("two")
print(s1.arr) // ["zero", "one", "two"]关联类型
protocol pc {
associatedtype T
mutating func add(_ p: T)
}
struct S2: pc {
typealias T = String // 类型推导,可省略
var strs = [String]()
mutating func add(_ p: String) {
strs.append(p)
}
}泛型适用于嵌套类型
struct S3<T> {
struct S4 {
var p: T
}
var p1: T
var p2: S4
}
let s2 = S3(p1: 1, p2: S3.S4(p: 3))
let s3 = S3(p1: "one", p2: S3.S4(p: "three"))
print(s2,s3)session Embrace Swift generics 、Design protocol interfaces in Swift
swift 5.6 和之前编写泛型接口如下:
func feed<A>(_ animal: A) where A: Animal
// 👆🏻👇🏻 Equivalents
func feed<A: Animal>(_ animal: A)swift 5.7 可以这样写:
func feed(_ animal: some Animal)some 关键字可以用于参数和结构类型。some 会保证类型关系,而 any 会持有任意具体类型,删除类型关系。
SE-0347 Type inference from default expressions 扩展 Swift 泛型参数类型的默认值能力。如下代码示例:
func suffledArray<T: Sequence>(from options: T = 1...100) -> [T.Element] {
Array(options.shuffled())
}
print(suffledArray())
print(suffledArray(from: ["one", "two", "three"]))SE-0341 Opaque Parameter Declarations 使用 some 参数简化泛型参数声明。SE-0328 Structural opaque result types 扩大不透明结果返回类型可以使用的范围。SE-0360 Opaque result types with limited availability 可用性有限的不透明结果类型,比如 if #available(macOS 13.0, *) {} 就可以根据系统不同版本返回不同类型,新版本出现新类型的 View 就可以和以前的 View 类型区别开。
SE-0309 Unlock existentials for all protocols 改进了 existentials 和 泛型的交互。这样就可以更方便的检查 Any 类型的两个值是否相等
any 关键字充当的是类型擦除的助手,是通过告知编译器你使用 existential 作为类型,此语法可兼容以前系统。
SE-0346 Lightweight same-type requirements for primary associated types 引入一种新语法,用于符合泛型参数并通过相同类型要求约束关联类型。SE-0358 Primary Associated Types in the Standard Library 引入主要关联类型概念,并将其带入了标准库。这些关联类型很像泛型,允许开发者将给定关联类型的类型指定为通用约束。
SE-0353 Constrained Existential Types 基于 SE-0309 和 SE-0346 提案,在 existential 类型的上下文中重用轻量关联类型的约束。
SE-0352 Implicitly Opened Existentials 允许 Swift 在很多情况下使用协议调用泛型函数。
Swift 论坛上一个对 any 和 some 关键字语法使用场景的讨论,Do any and some help with “Protocol Oriented Testing” at all? 。
不透明类型
不透明类型会隐藏类型,让使用者更关注功能。不透明类型和协议很类似,不同的是不透明比协议限定的要多,协议能够对应更多类型。
protocol P {
func f() -> String
}
struct S1: P {
func f() -> String {
return "one\n"
}
}
struct S2<T: P>: P {
var p: T
func f() -> String {
return p.f() + "two\n"
}
}
struct S3<T1: P, T2: P>: P {
var p1: T1
var p2: T2
func f() -> String {
return p1.f() + p2.f() + "three\n"
}
}
func someP() -> some P {
return S3(p1: S1(), p2: S2(p: S1()))
}
let r = someP()
print(r.f())函数调用者决定返回什么类型是泛型,函数自身决定返回什么类型使用不透明返回类型。
Result
Result 类型用来处理错误,特别适用异步接口的错误处理。
extension URLSession {
func dataTaskWithResult(
with url: URL,
handler: @escaping (Result<Data, Error>) -> Void
) -> URLSessionDataTask {
dataTask(with: url) { data, _, err in
if let err = err {
handler(.failure(err))
} else {
handler(.success(data ?? Data()))
}
}
}
}
let url = URL(string: "https://ming1016.github.io/")!
// 以前网络请求
let t1 = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: url) {
data, _, error in
if let err = error {
print(err)
} else if let data = data {
print(String(decoding: data, as: UTF8.self))
}
}
t1.resume()
// 使用 Result 网络请求
let t2 = URLSession.shared.dataTaskWithResult(with: url) { result in
switch result {
case .success(let data):
print(String(decoding: data, as: UTF8.self))
case .failure(let err):
print(err)
}
}
t2.resume()类型转换
使用 is 关键字进行类型判断, 使用as 关键字来转换成子类。
class S0 {}
class S1: S0 {}
class S2: S0 {}
var a = [S0]()
a.append(S1())
a.append(S2())
for e in a {
// 类型判断
if e is S1 {
print("Type is S1")
} else if e is S2 {
print("Type is S2")
}
// 使用 as 关键字转换成子类
if let s1 = e as? S1 {
print("As S1 \(s1)")
} else if let s2 = e as? S2 {
print("As S2 \(s2)")
}
}类和结构体
类
类可以定义属性、方法、构造器、下标操作。类使用扩展来扩展功能,遵循协议。类还以继承,运行时检查实例类型。
class C {
var p: String
init(_ p: String) {
self.p = p
}
// 下标操作
subscript(s: String) -> String {
get {
return p + s
}
set {
p = s + newValue
}
}
}
let c = C("hi")
print(c.p)
print(c[" ming"])
c["k"] = "v"
print(c.p)结构体
结构体是值类型,可以定义属性、方法、构造器、下标操作。结构体使用扩展来扩展功能,遵循协议。
struct S {
var p1: String = ""
var p2: Int
}
extension S {
func f() -> String {
return p1 + String(p2)
}
}
var s = S(p2: 1)
s.p1 = "1"
print(s.f()) // 11属性
类、结构体或枚举里的变量常量就是他们的属性。
struct S {
static let sp = "类型属性" // 类型属性通过类型本身访问,非实例访问
var p1: String = ""
var p2: Int = 1
// cp 是计算属性
var cp: Int {
get {
return p2 * 2
}
set {
p2 = newValue + 2
}
}
// 只有 getter 的是只读计算属性
var rcp: Int {
p2 * 4
}
}
print(S.sp)
print(S().cp) // 2
var s = S()
s.cp = 3
print(s.p2) // 5
print(S().rcp) // 4willSet 和 didSet 是属性观察器,可以在属性值设置前后插入自己的逻辑处理。
键路径表达式作为函数
struct S2 {
let p1: String
let p2: Int
}
let s2 = S2(p1: "one", p2: 1)
let s3 = S2(p1: "two", p2: 2)
let a1 = [s2, s3]
let a2 = a1.map(\.p1)
print(a2) // ["one", "two"]方法
enum E: String {
case one, two, three
func showRawValue() {
print(rawValue)
}
}
let e = E.three
e.showRawValue() // three
// 可变的实例方法,使用 mutating 标记
struct S {
var p: String
mutating func addFullStopForP() {
p += "."
}
}
var s = S(p: "hi")
s.addFullStopForP()
print(s.p)
// 类方法
class C {
class func cf() {
print("类方法")
}
}static和class关键字修饰的方法类似 OC 的类方法。static 可以修饰存储属性,而 class 不能;class 修饰的方法可以继承,而 static 不能。在协议中需用 static 来修饰。
静态下标方法
// 静态下标
struct S2 {
static var sp = [String: Int]()
static subscript(_ s: String, d: Int = 10) -> Int {
get {
return sp[s] ?? d
}
set {
sp[s] = newValue
}
}
}
S2["key1"] = 1
S2["key2"] = 2
print(S2["key2"]) // 2
print(S2["key3"]) // 10
自定义类型中实现了 callAsFunction() 的话,该类型的值就可以直接调用。
// callAsFunction()
struct S3 {
var p1: String
func callAsFunction() -> String {
return "show \(p1)"
}
}
let s2 = S3(p1: "hi")
print(s2()) // show hi继承
类能继承另一个类,继承它的方法、属性等。
// 类继承
class C1 {
var p1: String
var cp1: String {
get {
return p1 + " like ATM"
}
set {
p1 = p1 + newValue
}
}
init(p1: String) {
self.p1 = p1
}
func sayHi() {
print("Hi! \(p1)")
}
}
class C2: C1 {
var p2: String
init(p2: String) {
self.p2 = p2
super.init(p1: p2 + "'s father")
}
}
C2(p2: "Lemon").sayHi() // Hi! Lemon's father
// 重写父类方法
class C3: C2 {
override func sayHi() {
print("Hi! \(p2)")
}
}
C3(p2: "Lemon").sayHi() // Hi! Lemon
// 重写计算属性
class C4: C1 {
override var cp1: String {
get {
return p1 + " like Out of the blade"
}
set {
p1 = p1 + newValue
}
}
}
print(C1(p1: "Lemon").cp1) // Lemon like ATM
print(C4(p1: "Lemon").cp1) // Lemon like Out of the blade通过 final 关键字可以防止类被继承,final 还可以用于属性和方法。使用 super 关键字指代父类。
函数式
map
map 可以依次处理数组中元素,并返回一个处理后的新数组。
let a1 = ["a", "b", "c"]
let a2 = a1.map {
"\($0)2"
}
print(a2) // ["a2", "b2", "c2"]使用 compactMap 可以过滤 nil 的元素。flatMap 会将多个数组合成一个数组返回。
filter
根据指定条件返回
let a1 = ["a", "b", "c", "call my name"]
let a2 = a1.filter {
$0.prefix(1) == "c"
}
print(a2) // ["c", "call my name"]reduce
reduce 可以将迭代中返回的结果用于下个迭代中,并,还能让你设个初始值。
let a1 = ["a", "b", "c", "call my name.", "get it?"]
let a2 = a1.reduce("Hey u,", { partialResult, s in
// partialResult 是前面返回的值,s 是遍历到当前的值
partialResult + " \(s)"
})
print(a2) // Hey u, a b c call my name. get it?sorted
排序
// 类型遵循 Comparable
let a1 = ["a", "b", "c", "call my name.", "get it?"]
let a2 = a1.sorted()
let a3 = a1.sorted(by: >)
let a4 = a1.sorted(by: <)
print(a2) // Hey u, a b c call my name. get it?
print(a3) // ["get it?", "call my name.", "c", "b", "a"]
print(a4) // ["a", "b", "c", "call my name.", "get it?"]
// 类型不遵循 Comparable
struct S {
var s: String
var i: Int
}
let a5 = [S(s: "a", i: 0), S(s: "b", i: 1), S(s: "c", i: 2)]
let a6 = a5
.sorted { l, r in
l.i > r.i
}
.map {
$0.i
}
print(a6) // [2, 1, 0]控制流
If • If let • If case let
// if
let s = "hi"
if s.isEmpty {
print("String is Empty")
} else {
print("String is \(s)")
}
// 三元条件
s.isEmpty ? print("String is Empty again") : print("String is \(s) again")
// if let-else
func f(s: String?) {
if let s1 = s {
print("s1 is \(s1)")
} else {
print("s1 is nothing")
}
// nil-coalescing
let s2 = s ?? "nothing"
print("s2 is \(s2)")
}
f(s: "something")
f(s: nil)
// if case let
enum E {
case c1(String)
case c2([String])
func des() {
switch self {
case .c1(let string):
print(string)
case .c2(let array):
print(array)
}
}
}
E.c1("enum c1").des()
E.c2(["one", "two", "three"]).des()Guard guard, guard let
更好地处理异常情况
// guard
func f1(p: String) -> String {
guard p.isEmpty != true else {
return "Empty string."
}
return "String \(p) is not empty."
}
print(f1(p: "")) // Empty string.
print(f1(p: "lemon")) // String lemon is not empty.
// guard let
func f2(p1: String?) -> String {
guard let p2 = p1 else {
return "Nil."
}
return "String \(p2) is not nil."
}
print(f2(p1: nil)) // Nil.
print(f2(p1: "lemon")) // String lemon is not nil.遍历 For-in
let a = ["one", "two", "three"]
for str in a {
print(str)
}
// 使用下标范围
for i in 0..<10 {
print(i)
}
// 使用 enumerated
for (i, str) in a.enumerated() {
print("第\(i + 1)个是:\(str)")
}
// for in where
for str in a where str.prefix(1) == "t" {
print(str)
}
// 字典 for in,遍历是无序的
let dic = [
"one": 1,
"two": 2,
"three": 3
]
for (k, v) in dic {
print("key is \(k), value is \(v)")
}
// stride
for i in stride(from: 10, through: 0, by: -2) {
print(i)
}
/*
10
8
6
4
2
0
*/While while, repeat-while
// while
var i1 = 10
while i1 > 0 {
print("positive even number \(i1)")
i1 -= 2
}
// repeat while
var i2 = 10
repeat {
print("positive even number \(i2)")
i2 -= 2
} while i2 > 0使用 break 结束遍历,使用 continue 跳过当前作用域,继续下个循环
Switch
func f1(pa: String, t:(String, Int)) {
var p1 = 0
var p2 = 10
switch pa {
case "one":
p1 = 1
case "two":
p1 = 2
fallthrough // 继续到下个 case 中
default:
p2 = 0
}
print("p1 is \(p1)")
print("p2 is \(p2)")
// 元组
switch t {
case ("0", 0):
print("zero")
case ("1", 1):
print("one")
default:
print("no")
}
}
f1(pa: "two", t:("1", 1))
/*
p1 is 2
p2 is 0
one
*/
// 枚举
enum E {
case one, two, three, unknown(String)
}
func f2(pa: E) {
var p: String
switch pa {
case .one:
p = "1"
case .two:
p = "2"
case .three:
p = "3"
case let .unknown(u) where Int(u) ?? 0 > 0 : // 枚举关联值,使用 where 增加条件
p = u
case .unknown(_):
p = "negative number"
}
print(p)
}
f2(pa: E.one) // 1
f2(pa: E.unknown("10")) // 10
f2(pa: E.unknown("-10")) // negative number集合
数组 [1, 2, 3]
数组是有序集合
var a0: [Int] = [1, 10]
a0.append(2)
a0.remove(at: 0)
print(a0) // [10, 2]
let a1 = ["one", "two", "three"]
let a2 = ["three", "four"]
// 找两个集合的不同
let dif = a1.difference(from: a2) // swift的 diffing 算法在这 http://www.xmailserver.org/diff2.pdf swift实现在 swift/stdlib/public/core/Diffing.swift
for c in dif {
switch c {
case .remove(let o, let e, let a):
print("offset:\(o), element:\(e), associatedWith:\(String(describing: a))")
case .insert(let o, let e, let a):
print("offset:\(o), element:\(e), associatedWith:\(String(describing: a))")
}
}
/*
remove offset:1, element:four, associatedWith:nil
insert offset:0, element:one, associatedWith:nil
insert offset:1, element:two, associatedWith:nil
*/
let a3 = a2.applying(dif) ?? [] // 可以用于添加删除动画
print(a3) // ["one", "two", "three"]dif 有第三个 case 值 .insert(let offset, let element, let associatedWith) 可以跟踪成对的变化,用于高级动画。
从数组中随机取一个元素
print(a0.randomElement() ?? 0)数组排序
// 排序
struct S1 {
let n: Int
var b = true
}
let a4 = [
S1(n: 1),
S1(n: 10),
S1(n: 3),
S1(n: 2)
]
let a5 = a4.sorted { i1, i2 in
i1.n < i2.n
}
for n in a5 {
print(n)
}
/// S1(n: 1)
/// S1(n: 2)
/// S1(n: 3)
/// S1(n: 10)
let a6 = [1,10,4,7,2]
print(a6.sorted(by: >)) // [10, 7, 4, 2, 1]可以加到数组扩展中,通过扩展约束能够指定特定元素类型的排序,代码如下:
extension Array where Element == Int {
// 升序
func intSortedASC() -> [Int] {
return self.sorted(by: <)
}
// 降序
func intSortedDESC() -> [Int] {
return self.sorted(by: <)
}
}
print(a6.intSortedASC()) // 使用扩展增加自定义排序能力在数组中检索满足条件的元素,代码如下:
// 第一个满足条件了就返回
let a7 = a4.first {
$0.n == 10
}
print(a7?.n ?? 0)
// 是否都满足了条件
print(a4.allSatisfy { $0.n == 1 }) // false
print(a4.allSatisfy(\.b)) // true
// 找出最大的那个
print(a4.max(by: { e1, e2 in
e1.n < e2.n
}) ?? S1(n: 0))
// S1(n: 10, b: true)
// 看看是否包含某个元素
print(a4.contains(where: {
$0.n == 7
}))
// false一些切割数组的方法。
// 切片
// 取前3个,并不是直接复制,对于大的数组有性能优势。
print(a6[..<3]) // [1, 10, 4] 需要做越界检查
print(a6.prefix(30)) // [1, 10, 4, 7, 2] 不需要做越界检查,也是切片,性能一样
// 去掉前3个
print(a6.dropFirst(3)) // [7, 2]prefix(while:) 和 drop(while:) 方法,顺序遍历执行闭包里的逻辑判断,满足条件就返回,遇到不匹配就会停止遍历。prefix 返回满足条件的元素集合,drop 返回停止遍历之后那些元素集合。
let a8 = [8, 9, 20, 1, 35, 3]
let a9 = a8.prefix {
$0 < 30
}
print(a9) // [8, 9, 20, 1]
let a10 = a8.drop {
$0 < 30
}
print(a10) // [35, 3]比 filter 更高效的删除元素的方法 removeAll
// 删除所有不满足条件的元素
var a11 = [1, 3, 5, 12, 25]
a11.removeAll { $0 < 10 }
print(a11) // [4, 3, 1, 3, 3] 随机
// 创建未初始化的数组
let a12 = (0...4).map { _ in
Int.random(in: 0...5)
}
print(a12) // [0, 3, 3, 2, 5] 随机#if 用于后缀表达式
// #if 用于后缀表达式
let a13 = a11
#if os(iOS)
.count
#else
.reduce(0, +)
#endif
print(a13) //37Sets Set
Set 是无序集合,元素唯一
let s0: Set<Int> = [2, 4]
let s1: Set = [2, 10, 6, 4, 8]
let s2: Set = [7, 3, 5, 1, 9, 10]
let s3 = s1.union(s2) // 合集
let s4 = s1.intersection(s2) // 交集
let s5 = s1.subtracting(s2) // 非交集部分
let s6 = s1.symmetricDifference(s2) // 非交集的合集
print(s3) // [4, 2, 1, 7, 3, 10, 8, 9, 6, 5]
print(s4) // [10]
print(s5) // [8, 4, 2, 6]
print(s6) // [9, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 6, 8, 7]
// s0 是否被 s1 包含
print(s0.isSubset(of: s1)) // true
// s1 是否包含了 s0
print(s1.isSuperset(of: s0)) // true
let s7: Set = [3, 5]
// s0 和 s7 是否有交集
print(s0.isDisjoint(with: s7)) // true
// 可变 Set
var s8: Set = ["one", "two"]
s8.insert("three")
s8.remove("one")
print(s8) // ["two", "three"]字典 [:]
字典是无序集合,键值对应。
var d1 = [
"k1": "v1",
"k2": "v2"
]
d1["k3"] = "v3"
d1["k4"] = nil
print(d1) // ["k2": "v2", "k3": "v3", "k1": "v1"]
for (k, v) in d1 {
print("key is \(k), value is \(v)")
}
/*
key is k1, value is v1
key is k2, value is v2
key is k3, value is v3
*/
if d1.isEmpty == false {
print(d1.count) // 3
}
// mapValues
let d2 = d1.mapValues {
$0 + "_new"
}
print(d2) // ["k2": "v2_new", "k3": "v3_new", "k1": "v1_new"]
// 对字典的值或键进行分组
let d3 = Dictionary(grouping: d1.values) {
$0.count
}
print(d3) // [2: ["v1", "v2", "v3"]]
// 从字典中取值,如果键对应无值,则使用通过 default 指定的默认值
d1["k5", default: "whatever"] += "."
print(d1["k5"] ?? "") // whatever.
let v1 = d1["k3", default: "whatever"]
print(v1) // v3
// compactMapValues() 对字典值进行转换和解包。可以解可选类型,并去掉 nil 值
let d4 = [
"k1": 1,
"k2": 2,
"k3": nil
]
let d5 = d4.mapValues { $0 }
let d6 = d4.compactMapValues{ $0 }
print(d5)
// ["k3": nil, "k1": Optional(1), "k2": Optional(2)]
print(d6)
// ["k1": 1, "k2": 2]操作符
赋值 =, +=. -=, *=, /=
let i1 = 1
var i2 = i1
i2 = 2
print(i2) // 2
i2 += 1
print(i2) // 3
i2 -= 2
print(i2) // 1
i2 *= 10
print(i2) // 10
i2 /= 2
print(i2) // 5计算符 +, -, *, /, %
let i1 = 1
let i2 = i1
print((i1 + i2 - 1) * 10 / 2 % 3) // 2
print("i" + "1") // i1
// 一元运算符
print(-i1) // -1比较运算符 ==, >
遵循 Equatable 协议可以使用 == 和 != 来判断是否相等
print(1 > 2) // false
struct S: Equatable {
var p1: String
var p2: Int
}
let s1 = S(p1: "one", p2: 1)
let s2 = S(p1: "two", p2: 2)
let s3 = S(p1: "one", p2: 2)
let s4 = S(p1: "one", p2: 1)
print(s1 == s2) // false
print(s1 == s3) // false
print(s1 == s4) // true类需要实现 == 函数
class C: Equatable {
var p1: String
var p2: Int
init(p1: String, p2: Int) {
self.p1 = p1
self.p2 = p2
}
static func == (l: C, r: C) -> Bool {
return l.p1 == r.p1 && l.p2 == r.p2
}
}
let c1 = C(p1: "one", p2: 1)
let c2 = C(p1: "one", p2: 1)
print(c1 == c2)// 元组比较
// 会先比较第一个数,第一个无法比较才会比较第二个数
// 字符串比较和字母大小还有长度有关。先比较字母大小,在比较长度
("apple", 1) < ("apple", 2) // true
("applf", 1) < ("apple", 2) // false
("appl", 2) < ("apple", 1) // true
("appm", 2) < ("apple", 1) // false三元 _ ? _ : _
简化 if else 写法
// if else
func f1(p: Int) {
if p > 0 {
print("positive number")
} else {
print("negative number")
}
}
// 三元
func f2(p: Int) {
p > 0 ? print("positive number") : print("negative number")
}
f1(p: 1)
f2(p: 1)Nil-coalescing ??
简化 if let else 写法
// if else
func f1(p: Int?) {
if let i = p {
print("p have value is \(i)")
} else {
print("p is nil, use defalut value")
}
}
// 使用 ??
func f2(p: Int?) {
let i = p ?? 0
print("p is \(i)")
}范围 a…b
简化的值范围表达方式。
// 封闭范围
for i in 0...10 {
print(i)
}
// 半开范围
for i in 0..<10 {
print(i)
}// 单侧区间
let nums = [5,6,7,8]
print(nums[2...]) // 7 8逻辑 !, &&, ||
let i1 = -1
let i2 = 2
if i1 != i2 && (i1 < 0 || i2 < 0) {
print("i1 and i2 not equal, and one of them is negative number.")
}恒等 ===, !==
恒等返回是否引用了相同实例。
class C {
var p: String
init(p: String) {
self.p = p
}
}
let c1 = C(p: "one")
let c2 = C(p: "one")
let c3 = c1
print(c1 === c2) // false
print(c1 === c3) // true
print(c1 !== c2) // true运算符
位运算符
let i1: UInt8 = 0b00001111
let i2 = ~i1 // Bitwise NOT Operator(按位取反运算符),取反
let i3: UInt8 = 0b00111111
let i4 = i1 & i3 // Bitwise AND Operator(按位与运算符),都为1才是1
let i5 = i1 | i3 // Bitwise OR Operator(按位或运算符),有一个1就是1
let i6 = i1 ^ i3 // Bitwise XOR Operator(按位异或运算符),不同为1,相同为0
print(i1,i2,i3,i4,i5,i6)
// << 按位左移,>> 按位右移
let i7 = i1 << 1
let i8 = i1 >> 2
print(i7,i8)溢出运算符,有 &+、&- 和 &*
var i1 = Int.max
print(i1) // 9223372036854775807
i1 = i1 &+ 1
print(i1) // -9223372036854775808
i1 = i1 &+ 10
print(i1) // -9223372036854775798
var i2 = UInt.max
i2 = i2 &+ 1
print(i2) // 0运算符函数包括前缀运算符、后缀运算符、复合赋值运算符以及等价运算符。另,还可以自定义运算符,新的运算符要用 operator 关键字进行定义,同时要指定 prefix、infix 或者 postfix 修饰符。
基础库
时间
Date 的基本用法如下:
let now = Date()
// Date 转 时间戳
let interval = now.timeIntervalSince1970 // 时间戳
let df = DateFormatter()
df.dateFormat = "yyyy 年 MM 月 dd 日 HH:mm:ss"
print("时间戳:\(Int(interval))") // 时间戳:1642399901
print("格式化的时间:" + df.string(from: now)) // 格式化的时间:2022 年 01 月 17 日 14:11:41
df.dateStyle = .short
print("short 样式时间:" + df.string(from: now)) // short 样式时间:2022/1/17
df.locale = Locale(identifier: "zh_Hans_CN")
df.dateStyle = .full
print("full 样式时间:" + df.string(from: now)) // full 样式时间:2022年1月17日 星期一
// 时间戳转 Date
let date = Date(timeIntervalSince1970: interval)
print(date) // 2022-01-17 06:11:41 +0000复杂的时间操作,比如说 GitHub 接口使用的是 ISO 标准,RSS 输出的是 RSS 标准字符串,不同标准对应不同时区的时间计算处理,可以使用开源库 SwiftDate 来完成。示例代码如下:
import SwiftDate
// 使用 SwiftDate 库
let cn = Region(zone: Zones.asiaShanghai, locale: Locales.chineseChina)
SwiftDate.defaultRegion = cn
print("2008-02-14 23:12:14".toDate()?.year ?? "") // 2008
let d1 = "2022-01-17T23:20:35".toISODate(region: cn)
guard let d1 = d1 else {
return
}
print(d1.minute) // 20
let d2 = d1 + 1.minutes
print(d2.minute)
// 两个 DateInRegion 相差时间 interval
let i1 = DateInRegion(Date(), region: cn) - d1
let s1 = i1.toString {
$0.maximumUnitCount = 4
$0.allowedUnits = [.day, .hour, .minute]
$0.collapsesLargestUnit = true
$0.unitsStyle = .abbreviated
$0.locale = Locales.chineseChina
}
print(s1) // 9小时45分钟格式化
使用标准库的格式来描述不同场景的情况可以不用去考虑由于不同地区的区别,这些在标准库里就可以自动完成了。
描述两个时间之间相差多长时间
// 计算两个时间之间相差多少时间,支持多种语言字符串
let d1 = Date().timeIntervalSince1970 - 60 * 60 * 24
let f1 = RelativeDateTimeFormatter()
f1.dateTimeStyle = .named
f1.formattingContext = .beginningOfSentence
f1.locale = Locale(identifier: "zh_Hans_CN")
let str = f1.localizedString(for: Date(timeIntervalSince1970: d1), relativeTo: Date())
print(str) // 昨天
// 简写
let str2 = Date.now.addingTimeInterval(-(60 * 60 * 24))
.formatted(.relative(presentation: .named))
print(str2) // yesterday描述多个事物
// 描述多个事物
let s1 = ListFormatter.localizedString(byJoining: ["冬天","春天","夏天","秋天"])
print(s1)描述名字
// 名字
let f2 = PersonNameComponentsFormatter()
var nc1 = PersonNameComponents()
nc1.familyName = "戴"
nc1.givenName = "铭"
nc1.nickname = "铭哥"
print(f2.string(from: nc1)) // 戴铭
f2.style = .short
print(f2.string(from: nc1)) // 铭哥
f2.style = .abbreviated
print(f2.string(from: nc1)) // 戴
var nc2 = PersonNameComponents()
nc2.familyName = "Dai"
nc2.givenName = "Ming"
nc2.nickname = "Starming"
f2.style = .default
print(f2.string(from: nc2)) // Ming Dai
f2.style = .short
print(f2.string(from: nc2)) // Starming
f2.style = .abbreviated
print(f2.string(from: nc2)) // MD
// 取出名
let componets = f2.personNameComponents(from: "戴铭")
print(componets?.givenName ?? "") // 铭描述数字
// 数字
let f3 = NumberFormatter()
f3.locale = Locale(identifier: "zh_Hans_CN")
f3.numberStyle = .currency
print(f3.string(from: 123456) ?? "") // ¥123,456.00
f3.numberStyle = .percent
print(f3.string(from: 123456) ?? "") // 12,345,600%
let n1 = 1.23456
let n1Str = n1.formatted(.number.precision(.fractionLength(3)).rounded())
print(n1Str) // 1.235描述地址
// 地址
import Contacts
let f4 = CNPostalAddressFormatter()
let address = CNMutablePostalAddress()
address.street = "海淀区王庄路XX号院X号楼X门XXX"
address.postalCode = "100083"
address.city = "北京"
address.country = "中国"
print(f4.string(from: address))
/// 海淀区王庄路XX号院X号楼X门XXX
/// 北京 100083
/// 中国度量值
标准库里的物理量,在这个文档里有详细列出,包括角度、平方米等。
// 参考:https://developer.apple.com/documentation/foundation/nsdimension
let m1 = Measurement(value: 1, unit: UnitLength.kilometers)
let m2 = m1.converted(to: .meters) // 千米转米
print(m2) // 1000.0 m
// 度量值转为本地化的值
let mf = MeasurementFormatter()
mf.locale = Locale(identifier: "zh_Hans_CN")
print(mf.string(from: m1)) // 1公里一些物理公式供参考:
面积 = 长度 × 长度
体积 = 长度 × 长度 × 长度 = 面积 × 长度
速度=长度/时间
加速度=速度/时间
力 = 质量 × 加速度
扭矩 = 力 × 长度
压力 = 力 / 面积
密度=质量 / 体积
能量 = 功率 × 时间
电阻 = 电压 / 电流Data
数据压缩和解压
// 对数据的压缩
let d1 = "看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?看看能够压缩多少?".data(using: .utf8)! as NSData
print("ori \(d1.count) bytes")
do {
/// 压缩算法
/// * lz4
/// * lzma
/// * zlib
/// * lzfse
let compressed = try d1.compressed(using: .zlib)
print("comp \(compressed.count) bytes")
// 对数据解压
let decomressed = try compressed.decompressed(using: .zlib)
let deStr = String(data: decomressed as Data, encoding: .utf8)
print(deStr ?? "")
} catch {}
/// ori 297 bytes
/// comp 37 bytes文件
文件的一些基本操作的代码如下:
let path1 = "/Users/mingdai/Downloads/1.html"
let path2 = "/Users/mingdai/Documents/GitHub/"
let u1 = URL(string: path1)
do {
// 写入
let url1 = try FileManager.default.url(for: .itemReplacementDirectory, in: .userDomainMask, appropriateFor: u1, create: true) // 保证原子性安全保存
print(url1)
// 读取
let s1 = try String(contentsOfFile: path1, encoding: .utf8)
print(s1)
} catch {}
// 检查路径是否可用
let u2 = URL(fileURLWithPath:path2)
do {
let values = try u2.resourceValues(forKeys: [.volumeAvailableCapacityForImportantUsageKey])
if let capacity = values.volumeAvailableCapacityForImportantUsage {
print("可用: \(capacity)")
} else {
print("不可用")
}
} catch {
print("错误: \(error.localizedDescription)")
}怎么遍历多级目录结构中的文件呢?看下面的代码的实现:
// 遍历路径下所有目录
let u3 = URL(fileURLWithPath: FileManager.default.currentDirectoryPath)
let fm = FileManager.default
fm.enumerator(atPath: u3.path)?.forEach({ path in
guard let path = path as? String else {
return
}
let url = URL(fileURLWithPath: path, relativeTo: u3)
print(url.lastPathComponent)
})可以使用 FileWrapper 来创建文件夹和文件。举个例子:
// FileWrapper 的使用
// 创建文件
let f1 = FileWrapper(regularFileWithContents: Data("# 第 n 个文件\n ## 标题".utf8))
f1.fileAttributes[FileAttributeKey.creationDate.rawValue] = Date()
f1.fileAttributes[FileAttributeKey.modificationDate.rawValue] = Date()
// 创建文件夹
let folder1 = FileWrapper(directoryWithFileWrappers: [
"file1.md": f1
])
folder1.fileAttributes[FileAttributeKey.creationDate.rawValue] = Date()
folder1.fileAttributes[FileAttributeKey.modificationDate.rawValue] = Date()
do {
try folder1.write(
to: URL(fileURLWithPath: FileManager.default.currentDirectoryPath).appendingPathComponent("NewFolder"),
options: .atomic,
originalContentsURL: nil
)
} catch {}
print(FileManager.default.currentDirectoryPath)上面代码写起来比较繁琐,对 FileWrapper 更好的封装可以参考这篇文章《 A Type-Safe FileWrapper | Heberti Almeida 》。
文件读写处理完整能力可以参看这个库 GitHub - JohnSundell/Files: A nicer way to handle files & folders in Swift
本地或者网络上,比如网盘和FTP的文件发生变化时,怎样知道能够观察到呢?
通过 HTTPHeader 里的 If-Modified-Since、Last-Modified、If-None-Match 和 Etag 等字段来判断文件的变化,本地则是使用 DispatchSource.makeFileSystemObjectSource 来进行的文件变化监听。可以参考 KZFileWatchers 库的做法。
Scanner
let s1 = """
one1,
two2,
three3.
"""
let sn1 = Scanner(string: s1)
while !sn1.isAtEnd {
if let r1 = sn1.scanUpToCharacters(from: .newlines) {
print(r1 as String)
}
}
/// one1,
/// two2,
/// three3.
// 找出数字
let sn2 = Scanner(string: s1)
sn2.charactersToBeSkipped = CharacterSet.decimalDigits.inverted // 不是数字的就跳过
var p: Int = 0
while !sn2.isAtEnd {
if sn2.scanInt(&p) {
print(p)
}
}
/// 1
/// 2
/// 3上面的代码还不是那么 Swifty,可以通过用AnySequence和AnyIterator来包装下,将序列中的元素推迟到实际需要时再来处理,这样性能也会更好些。具体实现可以参看《 String parsing in Swift 》这篇文章。
AttributeString
效果如下:

代码如下:
var aStrs = [AttributedString]()
var aStr1 = AttributedString("""
标题
正文内容,具体查看链接。
这里摘出第一个重点,还要强调的内容。
""")
// 标题
let title = aStr1.range(of: "标题")
guard let title = title else {
return aStrs
}
var c1 = AttributeContainer() // 可复用容器
c1.inlinePresentationIntent = .stronglyEmphasized
c1.font = .largeTitle
aStr1[title].setAttributes(c1)
// 链接
let link = aStr1.range(of: "链接")
guard let link = link else {
return aStrs
}
var c2 = AttributeContainer() // 链接
c2.strokeColor = .blue
c2.link = URL(string: "https://ming1016.github.io/")
aStr1[link].setAttributes(c2.merging(c1)) // 合并 AttributeContainer
// Runs
let i1 = aStr1.range(of: "重点")
let i2 = aStr1.range(of: "强调")
guard let i1 = i1, let i2 = i2 else {
return aStrs
}
var c3 = AttributeContainer()
c3.foregroundColor = .yellow
c3.inlinePresentationIntent = .stronglyEmphasized
aStr1[i1].setAttributes(c3)
aStr1[i2].setAttributes(c3)
for r in aStr1.runs {
print("-------------")
print(r.attributes)
}
aStrs.append(aStr1)
// Markdown
do {
let aStr2 = try AttributedString(markdown: """
内容[链接](https://ming1016.github.io/)。需要**强调**的内容。
""")
aStrs.append(aStr2)
} catch {}SwiftUI 的 Text 可以直接读取 AttributedString 来进行显示。
随机
用法:
let ri = Int.random(in: 0..<10)
print(ri) // 0到10随机数
let a = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(a.randomElement() ?? 0) // 数组中随机取个数
print(a.shuffled()) // 随机打乱数组顺序UserDefaults
使用方法如下:
enum UDKey {
static let k1 = "token"
}
let ud = UserDefaults.standard
ud.set("xxxxxx", forKey: UDKey.k1)
let tk = ud.string(forKey: UDKey.k1)
print(tk ?? "")模式
单例
struct S {
static let shared = S()
private init() {
// 防止实例初始化
}
}系统及设备
系统判断
#if os(tvOS)
// do something in tvOS
#elseif os(iOS)
// do somthing in iOS
#elseif os(macOS)
// do somthing in macOS
#endif版本兼容
// 版本
@available(iOS 15, *)
func f() {
}
// 版本检查
if #available(iOS 15, macOS 12, *) {
f()
} else {
// nothing happen
}canImport 判断库是否可使用
#if canImport(SpriteKit)
// iOS 等苹果系统执行
#else
// 非苹果系统
#endiftargetEnvironment 环境的判断
#if targetEnvironment(simulator)
// 模拟器
#else
// 真机
#endif自带属性包装
@resultBuilder
结果生成器(Result builders),通过传递序列创建新值,SwiftUI就是使用的结果生成器将多个视图生成一个视图
@resultBuilder
struct RBS {
// 基本闭包支持
static func buildBlock(_ components: Int...) -> Int {
components.reduce(0) { partialResult, i in
partialResult + i
}
}
// 支持条件判断
static func buildEither(first component: Int) -> Int {
component
}
static func buildEither(second component: Int) -> Int {
component
}
// 支持循环
static func buildArray(_ components: [Int]) -> Int {
components.reduce(0) { partialResult, i in
partialResult + i
}
}
}
let a = RBS.buildBlock(
1,
2,
3
)
print(a) // 6
// 应用到函数中
@RBS func f1() -> Int {
1
2
3
}
print(f1()) // 6
// 设置了 buildEither 就可以在闭包中进行条件判断。
@RBS func f2(stopAtThree: Bool) -> Int {
1
2
3
if stopAtThree == true {
0
} else {
4
5
6
}
}
print(f2(stopAtThree: false)) // 21
// 设置了 buildArray 就可以在闭包内使用循环了
@RBS func f3() -> Int {
for i in 1...3 {
i * 2
}
}
print(f3()) // 12SE-0348 buildPartialBlock for result builders 简化了实现复杂 result buiders 所需的重载。
@dynamicMemberLookup 动态成员查询
@dynamicMemberLookup 指示访问属性时调用一个已实现的处理动态查找的下标方法 subscript(dynamicMemeber:),通过指定属性字符串名返回值。使用方法如下:
@dynamicMemberLookup
struct D {
// 找字符串
subscript(dynamicMember m: String) -> String {
let p = ["one": "first", "two": "second"]
return p[m, default: ""]
}
// 找整型
subscript(dynamicMember m: String) -> Int {
let p = ["one": 1, "two": 2]
return p[m, default: 0]
}
// 找闭包
subscript(dynamicMember m: String) -> (_ s: String) -> Void {
return {
print("show \($0)")
}
}
// 静态数组成员
var p = ["This is a member"]
// 动态数组成员
subscript(dynamicMember m: String) -> [String] {
return ["This is a dynamic member"]
}
}
let d = D()
let s1: String = d.one
print(s1) // first
let i1: Int = d.one
print(i1) // 1
d.show("something") // show something
print(d.p) // ["This is a member"]
let dynamicP:[String] = d.dp
print(dynamicP) // ["This is a dynamic member"]类使用 @dynamicMemberLookup,继承的类也会自动加上 @dynamicMemberLookup。协议上定义 @dynamicMemberLookup,通过扩展可以默认实现 subscript(dynamicMember:) 方法。
@dynamicCallable 动态可调用类型
@dynamicCallable 动态可调用类型。通过实现 dynamicallyCall 方法来定义变参的处理。
@dynamicCallable
struct D {
// 带参数说明
func dynamicallyCall(withKeywordArguments args: KeyValuePairs<String, Int>) -> Int {
let firstArg = args.first?.value ?? 0
return firstArg * 2
}
// 无参数说明
func dynamicallyCall(withArguments args: [String]) -> String {
var firstArg = ""
if args.count > 0 {
firstArg = args[0]
}
return "show \(firstArg)"
}
}
let d = D()
let i = d(numberIs: 2)
print(i) // 4
let s = d("hi")
print(s) // show hi自带协议
Hashable
struct H: Hashable {
var p1: String
var p2: Int
// 提供随机 seed
func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
hasher.combine(p1)
}
}
let h1 = H(p1: "one", p2: 1)
let h2 = H(p1: "two", p2: 2)
var hs1 = Hasher()
hs1.combine(h1)
hs1.combine(h2)
print(h1.hashValue) // 7417088153212460033 随机值
print(h2.hashValue) // -6972912482785541972 随机值
print(hs1.finalize()) // 7955861102637572758 随机值
print(h1.hashValue) // 7417088153212460033 和前面 h1 一样
let h3 = H(p1: "one", p2: 1)
print(h3.hashValue) // 7417088153212460033 和前面 h1 一样
var hs2 = Hasher()
hs2.combine(h3)
hs2.combine(h2)
print(hs2.finalize()) // 7955861102637572758 和前面 hs1 一样应用生命周期内,调用 combine() 添加相同属性哈希值相同,由于 Hasher 每次都会使用随机的 seed,因此不同应用生命周期,也就是下次启动的哈希值,就会和上次的哈希值不同。
Codable
JSON 没有 id 字段
如果SwiftUI要求数据Model都是遵循Identifiable协议的,而有的json没有id这个字段,可以使用扩展struct的方式解决:
struct CommitModel: Decodable, Hashable {
var sha: String
var author: AuthorModel
var commit: CommitModel
}
extension CommitModel: Identifiable {
var id: String {
return sha
}
}网络
网络状态检查
通过 Network 库的 NWPathMonitor 来检查
import Combine
import Network
// 网络状态检查 network state check
final class Nsck: ObservableObject {
static let shared = Nsck()
private(set) lazy var pb = mkpb()
@Published private(set) var pt: NWPath
private let monitor: NWPathMonitor
private lazy var sj = CurrentValueSubject<NWPath, Never>(monitor.currentPath)
private var sb: AnyCancellable?
init() {
monitor = NWPathMonitor()
pt = monitor.currentPath
monitor.pathUpdateHandler = { [weak self] path in
self?.pt = path
self?.sj.send(path)
}
monitor.start(queue: DispatchQueue.global())
}
deinit {
monitor.cancel()
sj.send(completion: .finished)
}
private func mkpb() -> AnyPublisher<NWPath, Never> {
return sj.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
}使用方法
var sb = Set<AnyCancellable>()
var alertMsg = ""
Nsck.shared.pb
.sink { _ in
//
} receiveValue: { path in
alertMsg = path.debugDescription
switch path.status {
case .satisfied:
alertMsg = ""
case .unsatisfied:
alertMsg = "😱"
case .requiresConnection:
alertMsg = "🥱"
@unknown default:
alertMsg = "🤔"
}
if path.status == .unsatisfied {
switch path.unsatisfiedReason {
case .notAvailable:
alertMsg += "网络不可用"
case .cellularDenied:
alertMsg += "蜂窝网不可用"
case .wifiDenied:
alertMsg += "Wifi不可用"
case .localNetworkDenied:
alertMsg += "网线不可用"
@unknown default:
alertMsg += "网络不可用"
}
}
}
.store(in: &sb)动画
布局动画
import SwiftUI
struct AnimateLayout: View {
@State var changeLayout: Bool = true
@Namespace var namespace
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 30) {
if changeLayout {
HStack { items }
} else {
VStack { items }
}
Button("切换布局") {
withAnimation { changeLayout.toggle() }
}
}
.padding()
}
@ViewBuilder var items: some View {
Text("one")
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "one", in: namespace)
Text("Two")
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "Two", in: namespace)
Text("Three")
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "Three", in: namespace)
}
}安全
Keychain
使用方法:
let d1 = Data("keyChain github token".utf8)
let service = "access-token"
let account = "github"
let q1 = [
kSecValueData: d1,
kSecClass: kSecClassGenericPassword,
kSecAttrService: service,
kSecAttrAccount: account
] as CFDictionary
// 添加一个 keychain
let status = SecItemAdd(q1, nil)
// 如果已经添加过会抛出 -25299 错误代码,需要调用 SecItemUpdate 来进行更新
if status == errSecDuplicateItem {
let q2 = [
kSecClass: kSecClassGenericPassword,
kSecAttrService: service,
kSecAttrAccount: account
] as CFDictionary
let q3 = [
kSecValueData: d1
] as CFDictionary
SecItemUpdate(q2, q3)
}
// 读取
let q4 = [
kSecAttrService: service,
kSecAttrAccount: account,
kSecClass: kSecClassGenericPassword,
kSecReturnData: true
] as CFDictionary
var re: AnyObject?
SecItemCopyMatching(q4, &re)
guard let reData = re as? Data else { return }
print(String(decoding: reData, as: UTF8.self)) // keyChain github token
// 删除
let q5 = [
kSecAttrService: service,
kSecAttrAccount: account,
kSecClass: kSecClassGenericPassword,
] as CFDictionary
SecItemDelete(q5)工程
程序入口点
Swift 允许全局编写 Swift 代码,实际上 clang 会自动将代码包进一个模拟 C 的函数中。Swift 也能够指定入口点,比如 @UIApplicationMain 或 @NSApplicationMain,UIKit 启动后生命周期管理是 AppDelegate 和 SceneDelegate,《 Understanding the iOS 13 Scene Delegate 》这篇有详细介绍。
@UIApplicationMain 和 @NSApplicationMain 会自动生成入口点。这些入口点都是平台相关的,Swift 发展来看是多平台的,这样在 Swift 5.3 时引入了 @main,可以方便的指定入口点。代码如下:
@main // 要定义个静态的 main 函数
struct M {
static func main() {
print("let's begin")
}
}ArgumentParser 库,Swift 官方开源的一个开发命令行工具的库,也支持 @main。使用方法如下:
import ArgumentParser
@main
struct C: ParsableCommand {
@Argument(help: "Start")
var phrase: String
func run() throws {
for _ in 1...5 {
print(phrase)
}
}
}工具
Swift-DocC
现在支持 Swift、OC 和 C,文档标记一样。.doccarchive 包含可部署的网站内容,兼容大多数托管服务,比如 Github pages。部署到在线服务上可参考 Generating Documentation for Hosting Online 和 Publishing to GitHub Pages 文档。
和 SPM 集成参看 SwiftDocCPlugin 。
session 有 What’s new in Swift -DocC 和 Improve the discoverability of your Swift-DocC content
SE-0356 Swift Snippets 代码片段用于示例文档的提案。
专题
Swift 那些事
Swift 各版本演进
Swift 1.1
- countElements() 改成了 count()。
- @NSApplicationMain 可以在 macOS 上使用。
Swift 1.2
- 引入 Set 类型。
- if let 可以放到一起,使用逗号分隔。
- 新增 zip() 和 flatMap()。
- 类增加静态方法和静态属性,使用 static 关键字描述。
- as! 用于类型强转,失败会崩溃。
- @noescape 用于描述作为参数闭包,用来告诉 Swift 闭包将在函数返回前使用。
- 常量可以延后初始化。
Swift 2.0
- 增加 guard 关键字,用于解可选项值。
- defer 关键字用来延迟执行,即使抛出错误了都会在最后执行。
- ErrorType 协议,以及 throws、do、try 和 catch 的引入用来处理错误。
- characters 加上 count,用来替代 count()。
- #available 用来检查系统版本。
Swift 2.1
- 字符串插值可以包含字符串字面符号。
Swift 2.2
官方博客介绍:Swift 2.2 Released!、New Features in Swift 2.2、Swift 2.2 Release Process
- FILE, LINE 和 FUNCTION 换成 #file,#line 和 #function。
- 废弃 ++ 和 – 操作符。
- C 语言风格 for 循环废弃。
- 废弃变量参数,因为变量参数容易和 inout 搞混。
- 废弃字符串化的选择器,选择器不再能写成字符串了。
- 元组可直接比较是否相等。
Swift 3.0
官方博客介绍:Swift 3.0 Released!、Swift 3.0 Preview 1 Released!、Swift 3.0 Release Process
- 规范动词和名词来命名。
- 去掉 NS 前缀。
- 方法名描述参数部分变为参数名。
- 省略没必要的单词,命名做了简化呢。比如 stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet 就换成了 trimmingCharacters。
- 枚举的属性使用小写开头。
- 引入 C 函数的属性。
Swift 3.1
官方博客介绍:Swift 3.1 Released!、Swift 3.1 Release Process
- 序列新增 prefix(while:) 和 drop(while:) 方法,顺序遍历执行闭包里的逻辑判断,满足条件就返回,遇到不匹配就会停止遍历。prefix 返回满足条件的元素集合,drop 返回停止遍历之后那些元素集合。
- 泛型适用于嵌套类型。
- 类型的扩展可以使用约束条件,比如扩展数组时,加上元素为整数的约束,这样的扩展就只会对元素为整数的数组有效。
Swift 4.0
官方博客介绍:Swift 4.0 Released!、Swift 4 Release Process
- 加入 Codable 协议,更 Swifty 的编码和解码。提案 SE-0167 Swift Encoders
- 字符串加入三个双引号的支持,让多行字符串编写更加直观。提案 SE-0168 Multi-Line String Literals
- 字符串变成集合,表示可以对字符串进行逐字遍历、map 和反转等操作。
- keypaths 语法提升。提案见 SE-0161 Smart KeyPaths: Better Key-Value Coding for Swift
- 集合加入
..<10这样语法的单边切片。提案 SE-0172 One-sided Ranges - 字典新增 mapValues,可 map 字典的值。通过 grouping 可对字典进行分组生成新字典,键和值都可以。从字典中取值,如果键对应无值,则使用通过 default 指定的默认值。提案 SE-0165 Dictionary & Set Enhancements
Swift 4.1
官方博客介绍:Swift 4.1 Released!、Swift 4.1 Release Process
- Hashable 也不需要返回一个唯一的 hashValue 哈希值属性。
- Equatable 和 Hashable 自动合成的提案参见 SE-0185 Synthesizing Equatable and Hashable conformance。
- 两个自定类型比较是否相等时,不再需要比较每个属性,Swift 会自动生成 == 方法,你只需要声明 Equatable 协议。
- 引入 KeyDecodingStrategy属性,其中 .convertFromSnakeCase 可以将下划线的命名转化成驼峰的命名。
- 引入条件符合性,只有满足一定条件才符合协议。比如扩展数组要求当里面元素满足某协议数组才符合这个协议。提案见 SE-0143 Conditional conformances。
- 引入 canImport 宏条件关键字,判断是否可以使用某库,以前只能通过判断操作系统平台来判断。提案见 SE-0075 Adding a Build Configuration Import Test。
- 新增能够去除为零项目的 compactMap()。提案 SE-0187 Introduce Sequence.compactMap(_:)
- 关联类型可以创建递归约束,提案见 SE-0157 Support recursive constraints on associated types
- targetEnvironment 环境的判断,比如模拟器。提案见 SE-0190 Target environment platform condition 。
Swift 4.2
官方博客介绍:Swift 4.2 Released!、Swift 4.2 Release Process
- 新增动态成员查询,@dynamicMemberLookup 新属性,指示访问属性时调用一个已实现的处理动态查找的下标方法 subscript(dynamicMemeber:),通过指定属性字符串名返回值。提案 SE-0195 Introduce User-defined “Dynamic Member Lookup” Types
- 集合新加 removeAll(where:) 方法,过滤满足条件所有元素。比 filter 更高效。提案 SE-0197 Adding in-place removeAll(where:) to the Standard Library
- 布尔值增加 toggle() 方法,用来切换布尔值。提案见 SE-0199 Adding toggle to Bool
- 引入 CaseIterable 协议,可以将枚举中所有 case 生成 allCases 数组。提案 SE-0194 Derived Collection of Enum Cases
- 引入 #warning 和 #error 两个新的编译器指令。#warning 会产生一个警告,#error 会直接让编译出错。比如必须要填写 token 才能编译的话可以在设置 token 的代码前加上 #error 和说明。提案见 SE-0196 Compiler Diagnostic Directives
- 新增加密安全的随机 API。直接在数字类型上调用 random() 方法生成随机数。shuffle() 方法可以对数组进行乱序重排。提案 SE-0202 Random Unification
- 更简单更安全的哈希协议,引入新的 Hasher 结构,通过 combine() 方法为哈希值添加更多属性,调用 finalize() 方法生成最终哈希值。提案 SE-0206 Hashable Enhancements
- 集合增加 allSatisfy() 用来判断集合中的元素是否都满足了一个条件。提案 SE-0207 Add an allSatisfy algorithm to Sequence
Swift 5.0
官方博客介绍:Swift 5 Released!、Swift 5.0 Release Process
- @dynamicCallable 动态可调用类型。通过实现 dynamicallyCall 方法来定义变参的处理。提案 SE-0216 Introduce user-defined dynamically “callable” types
- 新加 Result 类型用来处理错误。提案 SE-0235 Add Result to the Standard Library
- 新增原始字符串能力,在字符串前加上一个或多个#符号。里面的双引号和转义符号将不再起作用了,如果想让转义符起作用,需要在转义符后面加上#符号。提案见 SE-0200 Enhancing String Literals Delimiters to Support Raw Text
- 自定义字符串插值。提案 SE-0228 Fix ExpressibleByStringInterpolation
- 枚举新增 @unknown 用来区分固定的枚举和可能改变的枚举的能力。用于防止未来新增枚举属性会进行提醒提示完善每个 case 的处理。提案 SE-0192 Handling Future Enum Cases
- compactMapValues() 对字典值进行转换和解包。可以解可选类型,并去掉 nil 值。提案 SE-0218 Introduce compactMapValues to Dictionary
- 扁平化 try?。提案 SE-0230 Flatten nested optionals resulting from ‘try?’
- isMultiple(of:) 方法检查一个数字是否是另一个数字的倍数。提案见 SE-0225 Adding isMultiple to BinaryInteger
Swift 5.1
官方博客介绍:Swift 5.1 Released!、Swift 5.1 Release Process
- 有序集合的 diff,通过 difference(from:) 方法,可以返回要删除哪些和添加哪些项目能够让两个集合相等。提案 SE-0240 Ordered Collection Diffing
- 属性包装。提案 SE-0258 Property Wrappers
- 不透明返回类型。函数调用者决定返回什么类型是泛型,函数自身决定返回什么类型使用不透明返回类型。提案 SE-0244 Opaque Result Types
- 初始化有默认值的属性可不设置。提案 SE-0242 Synthesize default values for the memberwise initializer
- 单行表达式函数隐式返回,返回一个单行表达式的函数可以不用 return 关键字。提案 SE-0255 Implicit returns from single-expression functions
- 在类、结构体和枚举里使用 Self,Self 可以指代包含的类型。提案见 SE-0068 Expanding Swift Self to class members and value types
- 静态下标。提案 SE-0254 Static and class subscripts
- 枚举里有 none 的 case 编译器会提示换成 Optional.none。
- 引入未初始化数组。提案 SE-0245 Add an Array Initializer with Access to Uninitialized Storage
Swift 5.2
官方博客介绍:Swift 5.2 Released!、Swift 5.2 Release Process
- 自定义类型中实现了 callAsFunction() 的话,该类型的值就可以直接调用。提案 SE-0253 Callable values of user-defined nominal types
- 键路径表达式作为函数。提案 SE-0249 Key Path Expressions as Functions
Swift 5.3
官方博客介绍:Swift 5.3 released!、Swift 5.3 Release Process
- SPM 包管理资源,SPM 可以包含资源文件,比如多媒体或文本等。通过 Bundle.module 访问这些资源。提案 SE-0271 Package Manager Resources
- SPM 包里资源本地化。提案 SE-0278 Package Manager Localized Resources
- SPM 可以整合二进制包依赖。提案 SE-0272 Package Manager Binary Dependencies
- SPM 可以设置特定平台的依赖。提案 SE-0273 Package Manager Conditional Target Dependencies
- 单个 catch 块中捕获多个 Error 的 case。提案 SE-0276 Multi-Pattern Catch Clauses
- 支持多个尾部闭包。提案见 SE-0279 Multiple Trailing Closures
- 符合 Comparable 协议的枚举可以进行比较。提案 SE-0266 Synthesized Comparable conformance for enum types
- 很多地方可以不用加 self 来指代实例自己了。提案见 SE-0269 Increase availability of implicit self in @escaping closures when reference cycles are unlikely to occur
- @main 可以方便指定程序入口点。提案 SE-0281 @main: Type-Based Program Entry Points
- where 子句可以用到泛型和扩展函数中。提案 SE-0267 where clauses on contextually generic declarations
- 枚举的 case 也可以符合协议。提案 SE-0280 Enum cases as protocol witnesses
- 完善 didSet,性能提升。提案 SE-0268 Refine didSet Semantics
- 新增 Float16 类型,即半精度浮点类型。提案 SE-0277 Float16
Swift 5.4
官方博客介绍:Swift 5.4 Released!
- SPM 支持 @main。提案见 SE-0294 Declaring executable targets in Package Manifests
- 结果生成器(Result builders),通过传递序列创建新值,SwiftUI就是使用的结果生成器将多个视图生成一个视图。提案 SE-0289 Result builders
- 增强隐式成员语法,即使用了隐式的成员可以进行链式处理。提案见 SE-0287 Extend implicit member syntax to cover chains of member references
- 函数开始有了使用多个变量参数的能力。提案 SE-0284 Allow Multiple Variadic Parameters in Functions, Subscripts, and Initializers
- 嵌套函数可以重载,嵌套函数可以在声明函数之前调用他。
- 属性包装支持局部变量。
Swift 5.5
官方博客介绍:Swift 5.5 Released!
- Async await,用同步写法来处理异步。提案 SE-0296 Async/await
- Async sequences,异步序列上的循环能力。符合 AsyncSequence 协议的序列可以通过 for await 来进行异步循环。提案见 SE-0298 Async/Await: Sequences
- 结构化的并发,使用 Task 和 TaskGroup 执行、取消和监听当前操作的方法。复杂的并发处理可以使用 withTaskGroup() 来创建一组 Task,addTask() 用来添加任务,cancelAll() 可以取消任务,addTask() 在取消任务后可以继续添加任务,如果使用了 addTaskUnlessCancelled() 方法就可以避免取消后会继续添加任务这种情况。提案见 SE-0304 Structured concurrency
- 只读属性支持 async 和 throws 关键字。提案 SE-0310 Effectful Read-only Properties
- async let,可以创建 await 子任务。提案 SE-0317 async let bindings
- 以前异步代码的适配。比如 DispatchQueue.main.async,外部库可以通过 withCheckedContinuation() 函数来对以前异步代码进行封装。 提案见 SE-0300 Continuations for interfacing async tasks with synchronous code
- Actor,可以确保内部只能被一个线程访问,避免存储属性和方法出现竞争条件。提案在这 SE-0306 Actors
- 全局 actors,通过 actor 将全局状态隔离出来,避免数据竞争。比如主线程 @MainActor 这个属性包装可以将属性和方法标记为只能在主线程上访问。提案 SE-0316 Global actors
- Sendable 协议和 @Sendable 属性包装,目的是支持安全的将数据从一个线程传给另一个线程。Swift 的核心数据类型比如字符、集合等已符合 Sendable 协议。提案 SE-0302 Sendable and @Sendable closures
- 局部变量可以使用 lazy。
- 属性包装可以用到函数和闭包参数上。提案SE-0293 Extend Property Wrappers to Function and Closure Parameters
- 泛型支持静态成员查找。提案 SE-0299 Extending Static Member Lookup in Generic Contexts
- #if 用于后缀成员表达式。提案见 SE-0308 #if for postfix member expressions
- CGFloat 和 Double 之间可以隐式转换。提案 SE-0307 Allow interchangeable use of CGFloat and Double types
- Codable 支持关联值枚举。提案 SE-0295 Codable synthesis for enums with associated values
Swift 5.6
- 使用 any 注释此类类型,使存在类型的影响在语言中明确。提案 SE-0335 Introduce existential any
- 类型占位符。SE-0315 Type placeholders (formerly, “Placeholder types”)
- 新增 CodingKeyRepresentable 协议将非字符串和整数类型自定义表现。提案 SE-0320 Allow coding of non String / Int keyed Dictionary into a KeyedContainer
- 增加 Unavailability 用来在检查不可用时可以做些事情。SE-0290 Unavailability Condition
- 增加了
@preconcurrency属性。提案 SE-0337 Incremental migration to concurrency checking - actor 的 init 和 deinit。SE-0327 On Actors and Initialization
Package Manage 的一些提案
- SE-0303 Package Manager Extensible Build Tools
- SE-0305 Package Manager Binary Target Improvements
- SE-0325 Additional Package Plugin APIs
- SE-0332 Package Manager Command Plugins
Swift 5.7
- 标准库多了个
Regex<Output>类型,Regex 语法与 Perl、Python、Ruby、Java、NSRegularExpression 和许多其他语言兼容。可以用let regex = try! Regex("a[bc]+")或let regex = /a[bc]+/写法来使用。SE-0350 Regex Type and Overview 引入 Regex 类型。SE-0351 Regex builder DSL 使用 result builder 来构建正则表达式的 DSL。SE-0354 Regex Literals 简化的正则表达式。SE-0357 Regex-powered string processing algorithms 提案里有基于正则表达式的新字符串处理算法。 - SE-0347 Type inference from default expressions 扩展 Swift 泛型参数类型的默认值能力。
- SE-0341 Opaque Parameter Declarations 使用 some 参数简化泛型参数声明。SE-0328 Structural opaque result types 扩大不透明结果返回类型可以使用的范围。SE-0360 Opaque result types with limited availability 可用性有限的不透明结果类型,比如
if #available(macOS 13.0, *) {}就可以根据系统不同版本返回不同类型,新版本出现新类型的 View 就可以和以前的 View 类型区别开。 - SE-0309 Unlock existentials for all protocols 改进了 existentials 和 泛型的交互。这样就可以更方便的检查 Any 类型的两个值是否相等.
- SE-0346 Lightweight same-type requirements for primary associated types 引入一种新语法,用于符合泛型参数并通过相同类型要求约束关联类型。SE-0358 Primary Associated Types in the Standard Library 引入主要关联类型概念,并将其带入了标准库。这些关联类型很像泛型,允许开发者将给定关联类型的类型指定为通用约束。
- SE-0353 Constrained Existential Types 基于 SE-0309 和 SE-0346 提案,在 existential 类型的上下文中重用轻量关联类型的约束。
- SE-0352 Implicitly Opened Existentials 允许 Swift 在很多情况下使用协议调用泛型函数。
- 新增 SE-0338 Clarify the Execution of Non-Actor-Isolated Async Functions 通过收紧可发送性检查的规则来避免潜在的数据竞争。
- SE-0343 Concurrency in Top-level Code 这个提案主要是更好地支持命令行工具的开发,可以直接将 concurrency 代码写到 main.swift 文件里。
- SE-0340 Unavailable From Async Attribute 提供 noasync 语法以允许我们将类型和函数标记为在异步上下文不可用。
- SE-0336 Distributed Actor Isolation 和 SE-0344 Distributed Actor Runtime 是两个 Distributed Actors 的相关提案。
- SE-0345 if let shorthand for shadowing an existing optional variable 引入的新语法,用于 unwrapping optinal。
- SE-0326 提高了 Swift 对闭包使用参数和类型推断的能力。
- SE-0348 buildPartialBlock for result builders 简化了实现复杂 result buiders 所需的重载。
- SE-0356 Swift Snippets 代码片段用于示例文档的提案。
- 内存管理相关提案包括 SE-0349 Unaligned Loads and Stores from Raw Memory 、SE-0334 Pointer API Usability Improvements 、SE-0333 Expand usability of withMemoryRebound 。
规范
注意事项
参考:
多用静态特性。swift 在编译期间所做的优化比 OC 要多,这是由于他的静态派发、泛型特化、写时复制这些静态特性决定的。另外通过 final 和 private 这样的表示可将动态特性转化为静态方式,编译开启 WMO 可以自动推导出哪些动态派发可转化为静态派发。
如何避免崩溃?
- 字典:用结构体替代
- Any:可用泛型或关联关联类型替代
- as? :少用 AnyObject,多用泛型或不透明类型
- !:要少用
好的实践?
- 少用继承,多用 protocol
- 多用 extension 对自己代码进行管理
资料推荐
书单
- 《Thinking in SwiftUI》
- 《Swift 进阶》
- 《函数式Swift》
- 《深入解析Mac OS X & iOS操作系统》
- 《LLVM Techniques, Tips, and Best Practices Clang and Middle-End Libraries》
- 《Learn LLVM 12》
- 《Crafting Interpreters》
- 《TCP/IP Illustrated》
- 《松本行弘的程序世界》
- 《现代操作系统》
- 《深入理解计算机系统》
- 《程序员的自我修养》
- 《Head First 设计模式》
三方库使用
SQLite.swift 的使用
下面是 SQLite.swift 库的使用介绍,包括了数据库创建,表创建,表的添加、更新、删除、查找等处理方法
import SQLite
struct DB {
static let shared = DB()
static let path = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(
.applicationSupportDirectory, .userDomainMask, true
).first!
let BBDB: Connection?
private init() {
do {
print(DB.path)
BBDB = try Connection("\(DB.path)/github.sqlite3")
} catch {
BBDB = nil
}
/// Swift 类型和 SQLite 类型对标如下:
/// Int64 = INTEGER
/// Double = REAL
/// String = TEXT
/// nil = NULL
/// SQLite.Blob = BLOB
}
// 创建表
func cTbs() throws {
do {
try ReposNotiDataHelper.createTable()
try DevsNotiDataHelper.createTable()
} catch {
throw DBError.connectionErr
}
}
}
enum DBError: Error {
case connectionErr, insertErr, deleteErr, searchErr, updateErr, nilInData
}
protocol DataHelperProtocol {
associatedtype T
static func createTable() throws -> Void
static func insert(i: T) throws -> Int64
static func delete(i: T) throws -> Void
static func findAll() throws -> [T]?
}
// MARK: 开发者更新提醒
typealias DBDevNoti = (
login: String,
lastReadId: String,
unRead: Int
)
struct DevsNotiDataHelper: DataHelperProtocol {
static let table = Table("devsNoti")
static let login = Expression<String>("login")
static let lastReadId = Expression<String>("lastReadId")
static let unRead = Expression<Int>("unRead")
typealias T = DBDevNoti
static func createTable() throws {
guard let db = DB.shared.BBDB else {
throw DBError.connectionErr
}
do {
let _ = try db.run(table.create(ifNotExists: true) { t in
t.column(login, unique: true)
t.column(lastReadId, defaultValue: "")
t.column(unRead, defaultValue: 0)
})
} catch _ {
throw DBError.connectionErr
}
} // end createTable
static func insert(i: DBDevNoti) throws -> Int64 {
guard let db = DB.shared.BBDB else {
throw DBError.connectionErr
}
let insert = table.insert(login <- i.login, lastReadId <- i.lastReadId, unRead <- i.unRead)
do {
let rowId = try db.run(insert)
guard rowId > 0 else {
throw DBError.insertErr
}
return rowId
} catch {
throw DBError.insertErr
}
} // end insert
static func delete(i: DBDevNoti) throws {
guard let db = DB.shared.BBDB else {
throw DBError.connectionErr
}
let query = table.filter(login == i.login)
do {
let tmp = try db.run(query.delete())
guard tmp == 1 else {
throw DBError.deleteErr
}
} catch {
throw DBError.deleteErr
}
} // end delete
static func find(sLogin: String) throws -> DBDevNoti? {
guard let db = DB.shared.BBDB else {
throw DBError.connectionErr
}
let query = table.filter(login == sLogin)
let items = try db.prepare(query)
for i in items {
return DBDevNoti(login: i[login], lastReadId: i[lastReadId], unRead: i[unRead])
}
return nil
} // end find
static func update(i: DBDevNoti) throws {
guard let db = DB.shared.BBDB else {
throw DBError.connectionErr
}
let query = table.filter(login == i.login)
do {
if try db.run(query.update(lastReadId <- i.lastReadId, unRead <- i.unRead)) > 0 {
} else {
throw DBError.updateErr
}
} catch {
throw DBError.updateErr
}
} // end update
static func findAll() throws -> [DBDevNoti]? {
guard let db = DB.shared.BBDB else {
throw DBError.connectionErr
}
var arr = [DBDevNoti]()
let items = try db.prepare(table)
for i in items {
arr.append(DBDevNoti(login: i[login], lastReadId: i[lastReadId], unRead: i[unRead]))
}
return arr
} // end find all
}
使用时,可以在初始化时这么做:
// MARK: 初始化数据库
et db = DB.shared
do {
try db.cTbs() // 创建表
} catch {
}使用的操作示例如下:
do {
if let fd = try ReposNotiDataHelper.find(sFullName: r.id) {
reposDic[fd.fullName] = fd.unRead
} else {
do {
let _ = try ReposNotiDataHelper.insert(i: DBRepoNoti(fullName: r.id, lastReadCommitSha: "", unRead: 0))
reposDic[r.id] = 0
} catch {
return reposDic
}
}
} catch {
return reposDic
}macOS
范例
- 官方提供的两个例子,Creating a macOS App,Building a Great Mac App with SwiftUI (有table和LazyVGrid的用法)。
- GitHub - adamayoung/Movies: Movies and TV Shows App for iOS, iPadOS, watchOS and macOS 使用了SwiftUI和Combine,电影数据使用的是The Movie Database (TMDB)的API
三栏结构
三栏结构架子搭建,代码如下:
import SwiftUI
struct SwiftPamphletApp: View {
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
SPSidebar()
Text("第二栏")
Text("第三栏")
}
.navigationTitle("Swift 小册子")
.toolbar {
ToolbarItem(placement: ToolbarItemPlacement.navigation) {
Button {
NSApp.keyWindow?.firstResponder?.tryToPerform(#selector(NSSplitViewController.toggleSidebar(_:)), with: nil)
} label: {
Label("Sidebar", systemImage: "sidebar.left")
}
}
}
}
}
struct SPSidebar: View {
var body: some View {
List {
Section("第一组") {
NavigationLink("第一项", destination: SPList(title: "列表1"))
.badge(3)
NavigationLink("第二项", destination: SPList(title: "列表2"))
}
Section("第二组") {
NavigationLink("第三项", destination: SPList(title: "列表3"))
NavigationLink("第四项", destination: SPList(title: "列表4"))
}
}
.listStyle(SidebarListStyle())
.frame(minWidth: 160)
.toolbar {
ToolbarItem {
Menu {
Text("1")
Text("2")
} label: {
Label("Label", systemImage: "slider.horizontal.3")
}
}
}
}
}
struct SPList: View {
var title: String
@State var searchText: String = ""
var body: some View {
List(0..<3) { i in
Text("内容\(i)")
}
.toolbar(content: {
Button {
//
} label: {
Label("Add", systemImage: "plus")
}
})
.navigationTitle(title)
.navigationSubtitle("副标题")
.searchable(text: $searchText)
}
}显示效果如下:
全屏模式
将 NSSplitView 里的其中一个 NSView 设置为全屏和退出全屏的函数如下:
// MARK: - 获取 NSSplitViewController
func splitVC() -> NSSplitViewController {
return ((NSApp.keyWindow?.contentView?.subviews.first?.subviews.first?.subviews.first as? NSSplitView)?.delegate as? NSSplitViewController)!
}
// MARK: - 全屏
func fullScreen(isEnter: Bool) {
if isEnter == true {
// 进入全屏
let presOptions:
NSApplication.PresentationOptions = ([.autoHideDock,.autoHideMenuBar])
let optionsDictionary = [NSView.FullScreenModeOptionKey.fullScreenModeApplicationPresentationOptions : NSNumber(value: presOptions.rawValue)]
let v = splitVC().splitViewItems[2].viewController.view
v.enterFullScreenMode(NSScreen.main!, withOptions: optionsDictionary)
v.wantsLayer = true
} else {
// 退出全屏
NSApp.keyWindow?.contentView?.exitFullScreenMode()
} // end if
}使用方法
struct V: View {
@StateObject var appVM = AppVM()
@State var isEnterFullScreen: Bool = false // 全屏控制
var body: some View {
Button {
isEnterFullScreen.toggle()
appVM.fullScreen(isEnter: isEnterFullScreen)
} label: {
Image(systemName: isEnterFullScreen == true ? "arrow.down.right.and.arrow.up.left" : "arrow.up.left.and.arrow.down.right")
}
}
}共享菜单
struct ShareView: View {
var s: String
var body: some View {
Menu {
Button {
let p = NSPasteboard.general
p.declareTypes([.string], owner: nil)
p.setString(s, forType: .string)
} label: {
Text("拷贝链接")
Image(systemName: "doc.on.doc")
}
Divider()
ForEach(NSSharingService.sharingServices(forItems: [""]), id: \.title) { item in
Button {
item.perform(withItems: [s])
} label: {
Text(item.title)
Image(nsImage: item.image)
}
}
} label: {
Text("分享")
Image(systemName: "square.and.arrow.up")
}
}
}剪贴板
添加和读取剪贴板的方法如下:
// 读取剪贴板内容
let s = NSPasteboard.general.string(forType: .string)
guard let s = s else {
return
}
print(s)
// 设置剪贴板内容
let p = NSPasteboard.general
p.declareTypes([.string], owner: nil)
p.setString(s, forType: .string)性能和构建
调试
session Debug Swift debugging with LLDB
编译器编译 swift 文件生成 .o 文件会有 __debug_info 段,其中有可以映射到源文件和行号的地址。debug 信息可以链接到 .dSYM 包。debug 信息链接器叫 dsymutil,dsymutil 可以为每个动态库、framework 或 dylib 和可执行文件打包一个 debug 信息存档(.dSYM 包)。
image 和路径怎么重映射。使用 image list nameOfFramework 来检查 LLDB 是否找到了我们应用程序里嵌入的第三方框架的 debug dSYM。使用 image lookup 0xMemoryAddressHere 获取当前地址更多信息。要重新映射源文件 .dSYM 路径,使用 settings set target.source-map old/path new/path。每个 .dSYM 都有一个 UUID.plist,我们可以在其中设置 DBGSourcePathRemapping 这个字典。
Xcode 14 新增 swift-healthcheck 命令,这个命令可以了解 module 为何导入失败。
LLDB 怎么找到 Swift module?每个 .dSYM 包都可以包含二级制 swift module,其中可能包含桥头文件、swift 接口文件 .swiftinterface,还有 debug 信息。静态存档不是由链接器生成的,需要向链接器注册 swift module,使用 ld ... -add-ast-path /path/to/My.swiftmodule ,动态库和可执行文件的话,Xcode 会自动完成此操作。可以使用 dsymutil 来 dump 你可执行文件的符号表,并用 grep 找 swiftmodule,命令是 dsymutil -s MyApp | grep .swiftmodule 。
内存管理
相关提案包括 SE-0349 Unaligned Loads and Stores from Raw Memory 、SE-0334 Pointer API Usability Improvements 、SE-0333 Expand usability of withMemoryRebound
Set 使用新的 Temporary Buffers 功能,让 intersect 速度提升了 4 到 6 倍。
链接器
Link fast: Improve build and launch time 详细讲了 Apple 今年怎么改进了 link,思路很棒,很值得学习。
Static linking 和 Dynamic linking ,也就是静态链接和动态链接。
静态链接就是链接各个编译好的源文件以及链接源文件和编译好的库文件,通过将函数名放到符号表,链接新文件时确定先前是否有包含的 undefined 符号,给函数的数据指令分配地址,最后生成一个有 TEXT、DATA、LINKEDIT 段的可执行文件。
今年 Apple 通过利用多核优势让静态链接快了两倍。
具体做法是,并行的拷贝文件内容。并行构建 LINKEDIT 段的各个不同部分。并行改变 UUID 计算和 codesigning 哈希。然后是提高 exports-trie 构建器的算法。使用最新的 Crypto 库利用硬件加速的优势加速 UUID 计算。提高其它静态库处理算法库,debug-notes 生成也更快了。
Apple 推荐静态库最佳实践是:
使用 -all_load 或 -force_load 可以让 .a 文件像 .o 文件那样并行处理,不过开启这个选项需要先处理重复的符号。另外一个副作用是会将一些被判断无用的代码也被链接进来,使包体变大,因此开启之前可以先使用静态分析工具分析处理,这个过程定期做就行,不用放到每次编译过程中。演讲者推荐使用 -dead_strip 选项,但是这样做并没有真实去掉费代码,以后这些代码还是会被编译分析,如果只是暂时不用,可以先注释掉。
使用 -no_exported_symbols 选项。链接器生成的 LINKEDIT 段的一部分是 exports trie,这是一个前缀树,对所有导出的符号名称、地址和标志进行编码。动态库 是会导出符号的,但运行的二进制文件其实是不用这些符号的,因此可以用 -no_exported_symbols 选项来跳过 LINKEDIT 中 trie 数据结构的创建,这样链接起来就快多了。如果程序导出符号是一百万个,这个选项就可以减少 2 到 3 秒的时间。但需要注意的是,如果要加载插件链接回主程序就需要所有的导出的 trie 数据,无法用这个选项。
另外一个是 -no_deduplicate 选项。先前 Apple 给链接器加了个 pass 用来合并函数的指令相同,函数名不相同,这个 pass 会对每个函数的指令进行递归散列,用这种方式来找重复指令,这样做比较费 CPU,由于调试时其实是不需要关注包大小,因此可以加上 -no_deduplicate 选项来跳过这个 pass。
这些选项在 Xcode 的 Other Linker Flags 里进行设置即可。
动态库也就是 dylib,其它平台就是 DSO 或 DLL。 动态链接器不是将代码从库里考到主二进制里,而是记录某种承诺,记录从动态库中使用符号名称,还有库路径。这样做好处就是好复用动态库,不用拷贝多份。虚拟内存看到多进程使用相同动态库,就会重新给这个动态库用相同的物理内存页。
动态库好处是构建快了,启动加载慢了,多个动态库不光要加载,还要在启动时链接。也就是把链接成本从本地构建换到了用户启动时。动态库还有个缺点是基于动态库的程序会有更多的 dirty 页,因为静态链接时会把全局数据放到主程序同一个 DATA 页中,动态库的话,每个都在自己的 DATA 页中。
动态库工作的原理是,可执行的二进制会有不同权限的段,至少会有 TEXT、DATA 和 LINKEDIT。分段总是操作系统页大小的倍数。TEXT 段有执行的权限,CPU 可以将页上的字节当做机器代码指令。运行时,dyld 会根据每个段权限将可执行文件 mmap() 到内存,这些段是页大小和页对齐的,虚拟内存系统可以直接将程序或动态库文件设置为 VM 范围的备份存储。在这些页的内存访问前是不会被加载到 RAM 里,就会触发一个页 fault,导致 VM 去读取文件的子范围,将内存填充到需要 RAM 页中。光映射不够,还要用某种方式“wired up”或绑到动态库上。比如要调用动态库上的某个函数,会转换成调用 site,调用 site 成为一个在相同 TEXT 段合成的 sub 的调用,相对地址在构建时就知道了,就意味着可以正确的形成 BL 指令。这样做的好处是,stub 从 DATA 加载一个指针并跳到对应的位置,不用在运行时修改 TEXT 段,dyld 只在运行时改 DATA 段。dyld 所进行的修改很简单,就是在 DATA 段里设置了一个指针而已。
当 dyld 或应用程序的指针指向自己时要 rebase,ASLR 使 dyld 以随机地址加载动态库,内部指针不能在构建时设置,dyld 在启动时 rebase 这些指针,磁盘上,如果动态库在地址零出被加载,这些指针包含它们的目标地址。LINKEDIT 需要记录的就是每个重定位的位置。然后,dyld 只需将动态库的实际加载地址添加到每个 rebase 位置。还有种修改方式是绑定,绑定就是符号引用,符号存储在 LINKEDIT 中,dyld 在动态库的 exports tire 中找实际地址,然后 dyld 将该值存储在绑定指定的位置。
今年 Apple 发布了一个新的修改方式 chained fixups。较前面两种的优势就是可以使 LINKEDIT 更小。新格式只存储每个 DATA 页中第一个 fixup 位置和一个导入的符号列表。其它信息编码到 DATA 段。iOS 13.4 就开始支持了。
下面先说下 dyld 原理介绍。
dyld 从主可执行文件开始,解析 mach-o 找依赖动态库,对动态库进行 mmap()。然后对每个动态库进行遍历并解析 mach-o 结构,根据需要加载其它动态库。加载完毕,dyld 会查找所有需要绑定符号,并在修改时使用这些地址。最后修改完,dyld 自下而上运行初始化程序。先前做的优化是只要程序和动态库,dyld 很多步骤都可以在首次启动时被缓存。
今年 Apple 做了更多的优化,这个优化叫 page-in linking,就是 dyld 在启动时做的 DATA 页面修改放到 page-in 时,也可以理解为懒修改。以前,在 mmap() 区域的某些页面中第一次使用某些地址会触发内核读入该页面。现在如果它是一个数据页,内核会应用改页需要的修改。这种机制减少了 dirty 内存和启动时间。意味着 DATA_CONST 也是干净的,可以像 TEXT 页一样被 evicted 和重新创建,以减少内存压力。需要注意的是 page-in linking 只用于启动,dlopen() 不支持。你看,Apple 优化启动的思路也是按需加载。
Apple 还提供了追踪 dyld 运行情况的 dyld_usage 工具。检查磁盘和 dyld 缓存中的二进制文件的 dyld_info 工具。
2022年 Apple 性能更新
Improve app size and runtime performance
今年苹果通过更有效的检查 Swift 协议,使 OC 消息发送调用更小,使 autorelease elision 更快更小这几个个方面来让 App 体积更小,性能更高。
Swift 协议检查。
一个协议通过 as 操作符检查传递值是否符合协议,这种检查会在编译器的构建时间被优化掉,所以往往需要在运行时借助之前计算协议检查元数据来看对象是否真的符合了协议。一些元数据是在编译时建的,但还有很多元数据只能在启动时建立,特别是使用泛型时。协议多了,会增加耗时,差不多会多一半启动时间。
今年 Apple 推出新的 Swift 运行时,可以提前计算 Swift 协议元数据,作为 App 可执行文件和它在启动时使用的任何动态库的 dyld 闭包的一部分。这个是在系统上的,因此,只要是使用了今年最新系统的 App 都会享受这个优化,可以理解为,新系统上启动老 App 也会快些。
消息发送。
Xcode 14 中新的编译器和链接器已经将 ARM64 的消息发送调用从 12 字节减少到 8 字节。因此如果你的 App 都是 OC 代码的话,使用 Xcode 14 编出来的二进制文件可以少 2%。老系统也有效。
使用 objc_stubs_small 选项可以只优化大小,获得最大的大小优化。objc_msgSend 调动有 8 个字节指令,也就是2个指令是专门用来准备 selector 的,对于任何特定的 selector,总是相同的代码,由于始终是相同的代码,那么就可以对其共享,每个 selector 只 emit 一次,而不是每次发送消息时都 emit。共享这段代码地方是一个叫 selector stub 的函数。
ARC 会在编译器插入大量的 c 的 retain/release 函数调用。这些调用遵守平台应用二进制接口(ABI)所定义的 c 语言 call convention。也就意味着我们要更多代码来完成这些调用,用来传递正确寄存器的指针。Apple 今年推出了自定义的 call convention 根据指针位置,适时使用正确变量而不用移动它,从而摆脱了调用里的多余代码。Apple 果然是坚持用户体验优先,为了更好体验不惜修改 c 的 ABI。
autorelease elision 。
App 今年对 objc 运行时进行了修改,使 autorelease elision 更小更快。deployment target 为 iOS 16 今年新系统时才可享用哦。
Apple 怎么做的呢?
ARC 在调用方插入一个 retain,在被调用的函数中插入一个 release。当我们返回我们的临时对象时,我们需要在函数中先释放它,因为它要离开 scope。在它还没有任何其它引用时还不能这么做,不然返回前他就会被销毁。Apple 现在使用一个新的 convention ,让其可以返回临时对象。做法是当返回一个自动释放值,编译器会发出一个特殊标记,这个标记会告诉运行时这是符合自动释放条件的。它的后面是 retain,我们会在后面执行。获取返回地址,也就是一个指针,将它先保存起来,然后离开运行时的自动释放调用。在运行时,可以将保留时得到的指正和先前做自动释放时保存的指针进行比较,这样标记指令不再是数据之间的比较,比较指针内存访问少。比较成功就可以省去 autorelease/retain。
autorelease elision 的优化同样也可以减少 2% 大小。感谢 Apple 为了用户和开发者 OKR 的付出。
Combine
介绍
Combine 是什么?
WWDC 2019苹果推出Combine,Combine是一种响应式编程范式,采用声明式的Swift API。
Combine 写代码的思路是你写代码不同于以往命令式的描述如何处理数据,Combine 是要去描述好数据会经过哪些逻辑运算处理。这样代码更好维护,可以有效的减少嵌套闭包以及分散的回调等使得代码维护麻烦的苦恼。
声明式和过程时区别可见如下代码:
// 所有数相加
// 命令式思维
func sum1(arr: [Int]) -> Int {
var sum: Int = 0
for v in arr {
sum += v
}
return sum
}
// 声明式思维
func sum2(arr: [Int]) -> Int {
return arr.reduce(0, +)
}Combine 主要用来处理异步的事件和值。苹果 UI 框架都是在主线程上进行 UI 更新,Combine 通过 Publisher 的 receive 设置回主线程更新UI会非常的简单。
已有的 RxSwift 和 ReactiveSwift 框架和 Combine 的思路和用法类似。
Combine 的三个核心概念
- 发布者
- 订阅者
- 操作符
简单举个发布数据和类属性绑定的例子:
let pA = Just(0)
let _ = pA.sink { v in
print("pA is: \(v)")
}
let pB = [7,90,16,11].publisher
let _ = pB
.sink { v in
print("pB: \(v)")
}
class AClass {
var p: Int = 0 {
didSet {
print("property update to \(p)")
}
}
}
let o = AClass()
let _ = pB.assign(to: \.p, on: o)Combine 资料
官方文档链接 Combine | Apple Developer Documentation 。还有 Using Combine 这里有大量使用示例,内容较全。官方讨论Combine的论坛 Topics tagged combine 。StackOverflow上相关问题 Newest ‘combine’ Questions 。
WWDC上关于Combine的Session如下:
和Combine相关的Session:
- Modern Swift API Design
- Data Flow Through SwiftUI
- Introducing Combine and Advances in Foundation
- Advances in Networking, Part 1
- Building Collaborative AR Experiences
- Expanding the Sensory Experience with Core Haptics
使用说明
publisher
publisher 是发布者,sink 是订阅者
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
struct S {
let p1: String
let p2: String
}
[S(p1: "1", p2: "one"), S(p1: "2", p2: "two")]
.publisher
.print("array")
.sink {
print($0)
}
.store(in: &cc) 输出
array: receive subscription: ([戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $10ac82d20).(unknown context at $10ac82da4).S(p1: "1", p2: "one"), 戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $10ac82d20).(unknown context at $10ac82da4).S(p1: "2", p2: "two")])
array: request unlimited
array: receive value: (S(p1: "1", p2: "one"))
S(p1: "1", p2: "one")
array: receive value: (S(p1: "2", p2: "two"))
S(p1: "2", p2: "two")
array: receive finishedJust
Just 是发布者,发布的数据在初始化时完成
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
struct S {
let p1: String
let p2: String
}
let pb = Just(S(p1: "1", p2: "one"))
pb
.print("pb")
.sink {
print($0)
}
.store(in: &cc)输出
pb: receive subscription: (Just)
pb: request unlimited
pb: receive value: (S(p1: "1", p2: "one"))
S(p1: "1", p2: "one")
pb: receive finishedPassthroughSubject
PassthroughSubject 可以传递多值,订阅者可以是一个也可以是多个,send 指明 completion 后,订阅者就没法接收到新发送的值了。
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
struct S {
let p1: String
let p2: String
}
enum CError: Error {
case aE, bE
}
let ps1 = PassthroughSubject<S, CError>()
ps1
.print("ps1")
.sink { c in
print("completion:", c) // send 了 .finished 后会执行
} receiveValue: { s in
print("receive:", s)
}
.store(in: &cc)
ps1.send(S(p1: "1", p2: "one"))
ps1.send(completion: .failure(CError.aE)) // 和 .finished 一样后面就不会发送了
ps1.send(S(p1: "2", p2: "two"))
ps1.send(completion: .finished)
ps1.send(S(p1: "3", p2: "three"))
// 多个订阅者
let ps2 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
ps2.send("one") // 订阅之前 send 的数据没有订阅者可以接收
ps2.send("two")
let sb1 = ps2
.print("ps2 sb1")
.sink { s in
print(s)
}
ps2.send("three") // 这个 send 的值会被 sb1
let sb2 = ps2
.print("ps2 sb2")
.sink { s in
print(s)
}
ps2.send("four") // 这个 send 的值会被 sb1 和 sb2 接受
sb1.store(in: &cc)
sb2.store(in: &cc)
ps2.send(completion: .finished)
输出
ps1: receive subscription: (PassthroughSubject)
ps1: request unlimited
ps1: receive value: (S(p1: "1", p2: "one"))
receive: S(p1: "1", p2: "one")
ps1: receive error: (aE)
completion: failure(戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $10b15ce10).(unknown context at $10b15cf3c).CError.aE)
ps2 sb1: receive subscription: (PassthroughSubject)
ps2 sb1: request unlimited
ps2 sb1: receive value: (three)
three
ps2 sb2: receive subscription: (PassthroughSubject)
ps2 sb2: request unlimited
ps2 sb1: receive value: (four)
four
ps2 sb2: receive value: (four)
four
ps2 sb1: receive finished
ps2 sb2: receive finishedEmpty
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
struct S {
let p1: String
let p2: String
}
let ept = Empty<S, Never>() // 加上 completeImmediately: false 后面即使用 replaceEmpty 也不会接受值
ept
.print("ept")
.sink { c in
print("completion:", c)
} receiveValue: { s in
print("receive:", s)
}
.store(in: &cc)
ept.replaceEmpty(with: S(p1: "1", p2: "one"))
.sink { c in
print("completion:", c)
} receiveValue: { s in
print("receive:", s)
}
.store(in: &cc)输出
ept: receive subscription: (Empty)
ept: request unlimited
ept: receive finished
completion: finished
receive: S(p1: "1", p2: "one")
completion: finishedCurrentValueSubject
CurrentValueSubject 的订阅者可以收到订阅时已发出的那条数据
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let cs = CurrentValueSubject<String, Never>("one")
cs.send("two")
cs.send("three")
let sb1 = cs
.print("cs sb1")
.sink {
print($0)
}
cs.send("four")
cs.send("five")
let sb2 = cs
.print("cs sb2")
.sink {
print($0)
}
cs.send("six")
sb1.store(in: &cc)
sb2.store(in: &cc)输出
cs sb1: receive subscription: (CurrentValueSubject)
cs sb1: request unlimited
cs sb1: receive value: (three)
three
cs sb1: receive value: (four)
four
cs sb1: receive value: (five)
five
cs sb2: receive subscription: (CurrentValueSubject)
cs sb2: request unlimited
cs sb2: receive value: (five)
five
cs sb1: receive value: (six)
six
cs sb2: receive value: (six)
six
cs sb1: receive cancel
cs sb2: receive cancelremoveDuplicates
使用 removeDuplicates,重复的值就不会发送了。
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let pb = ["one","two","three","three","four"]
.publisher
let sb = pb
.print("sb")
.removeDuplicates()
.sink {
print($0)
}
sb.store(in: &cc)输出
sb: receive subscription: (["one", "two", "three", "three", "four"])
sb: request unlimited
sb: receive value: (one)
one
sb: receive value: (two)
two
sb: receive value: (three)
three
sb: receive value: (three)
sb: request max: (1) (synchronous)
sb: receive value: (four)
four
sb: receive finishedflatMap
flatMap 能将多个发布者的值打平发送给订阅者
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
struct S {
let p: AnyPublisher<String, Never>
}
let s1 = S(p: Just("one").eraseToAnyPublisher())
let s2 = S(p: Just("two").eraseToAnyPublisher())
let s3 = S(p: Just("three").eraseToAnyPublisher())
let pb = [s1, s2, s3].publisher
let sb = pb
.print("sb")
.flatMap {
$0.p
}
.sink {
print($0)
}
sb.store(in: &cc)输出
sb: receive subscription: ([戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $101167070).(unknown context at $1011670f4).S(p: AnyPublisher), 戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $101167070).(unknown context at $1011670f4).S(p: AnyPublisher), 戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $101167070).(unknown context at $1011670f4).S(p: AnyPublisher)])
sb: request unlimited
sb: receive value: (S(p: AnyPublisher))
one
sb: receive value: (S(p: AnyPublisher))
two
sb: receive value: (S(p: AnyPublisher))
three
sb: receive finishedappend
append 会在发布者发布结束后追加发送数据,发布者不结束,append 的数据不会发送。
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let pb = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let sb = pb
.print("sb")
.append("five", "six")
.sink {
print($0)
}
sb.store(in: &cc)
pb.send("one")
pb.send("two")
pb.send("three")
pb.send(completion: .finished)输出
sb: receive subscription: ([戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $101167070).(unknown context at $1011670f4).S(p: AnyPublisher), 戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $101167070).(unknown context at $1011670f4).S(p: AnyPublisher), 戴铭的开发小册子.AppDelegate.(unknown context at $101167070).(unknown context at $1011670f4).S(p: AnyPublisher)])
sb: request unlimited
sb: receive value: (S(p: AnyPublisher))
one
sb: receive value: (S(p: AnyPublisher))
two
sb: receive value: (S(p: AnyPublisher))
three
sb: receive finishedprepend
prepend 会在发布者发布前先发送数据,发布者不结束也不会受影响。发布者和集合也可以被打平发布。
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let pb1 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let pb2 = ["nine", "ten"].publisher
let sb = pb1
.print("sb")
.prepend(pb2)
.prepend(["seven","eight"])
.prepend("five", "six")
.sink {
print($0)
}
sb.store(in: &cc)
pb1.send("one")
pb1.send("two")
pb1.send("three")输出
five
six
seven
eight
nine
ten
sb: receive subscription: (PassthroughSubject)
sb: request unlimited
sb: receive value: (one)
one
sb: receive value: (two)
two
sb: receive value: (three)
three
sb: receive cancelmerge
订阅者可以通过 merge 合并多个发布者发布的数据
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let ps1 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let ps2 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let sb1 = ps1.merge(with: ps2)
.sink {
print($0)
}
ps1.send("one")
ps1.send("two")
ps2.send("1")
ps2.send("2")
ps1.send("three")
sb1.store(in: &cc)输出
sb1: receive subscription: (Merge)
sb1: request unlimited
sb1: receive value: (one)
one
sb1: receive value: (two)
two
sb1: receive value: (1)
1
sb1: receive value: (2)
2
sb1: receive value: (three)
three
sb1: receive cancelzip
zip 会合并多个发布者发布的数据,只有当多个发布者都发布了数据后才会组合成一个数据给订阅者。
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let ps1 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let ps2 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let ps3 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let sb1 = ps1.zip(ps2, ps3)
.print("sb1")
.sink {
print($0)
}
ps1.send("one")
ps1.send("two")
ps1.send("three")
ps2.send("1")
ps2.send("2")
ps1.send("four")
ps2.send("3")
ps3.send("一")
sb1.store(in: &cc)输出
sb1: receive subscription: (Zip)
sb1: request unlimited
sb1: receive value: (("one", "1", "一"))
("one", "1", "一")
sb1: receive cancelcombineLatest
combineLatest 会合并多个发布者发布的数据,只有当多个发布者都发布了数据后才会触发合并,合并每个发布者发布的最后一个数据。
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let ps1 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let ps2 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let ps3 = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
let sb1 = ps1.combineLatest(ps2, ps3)
.print("sb1")
.sink {
print($0)
}
ps1.send("one")
ps1.send("two")
ps1.send("three")
ps2.send("1")
ps2.send("2")
ps1.send("four")
ps2.send("3")
ps3.send("一")
ps3.send("二")
sb1.store(in: &cc)输出
sb1: receive subscription: (CombineLatest)
sb1: request unlimited
sb1: receive value: (("four", "3", "一"))
("four", "3", "一")
sb1: receive value: (("four", "3", "二"))
("four", "3", "二")
sb1: receive cancelScheduler
Scheduler 处理队列。
import Combine
var cc = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let sb1 = ["one","two","three"].publisher
.print("sb1")
.subscribe(on: DispatchQueue.global())
.handleEvents(receiveOutput: {
print("receiveOutput",$0)
})
.receive(on: DispatchQueue.main)
.sink {
print($0)
}
sb1.store(in: &cc)输出
sb1: receive subscription: ([1, 2, 3])
sb1: request unlimited
sb1: receive value: (1)
receiveOutput 1
sb1: receive value: (2)
receiveOutput 2
sb1: receive value: (3)
receiveOutput 3
sb1: receive finished
1
2
3使用场景
网络请求
网络URLSession.dataTaskPublisher使用例子如下:
let req = URLRequest(url: URL(string: "http://www.starming.com")!)
let dpPublisher = URLSession.shared.dataTaskPublisher(for: req)一个请求Github接口并展示结果的例子
//
// CombineSearchAPI.swift
// SwiftOnly (iOS)
//
// Created by Ming Dai on 2021/11/4.
//
import SwiftUI
import Combine
struct CombineSearchAPI: View {
var body: some View {
GithubSearchView()
}
}
// MARK: Github View
struct GithubSearchView: View {
@State var str: String = "Swift"
@StateObject var ss: SearchStore = SearchStore()
@State var repos: [GithubRepo] = []
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
List {
TextField("输入:", text: $str, onCommit: fetch)
ForEach(self.ss.repos) { repo -> GithubRepoCell in
GithubRepoCell(repo: repo)
}
}
.navigationTitle("搜索")
}
.onAppear(perform: fetch)
}
private func fetch() {
self.ss.search(str: self.str)
}
}
struct GithubRepoCell: View {
let repo: GithubRepo
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 20) {
Text(self.repo.name)
Text(self.repo.description)
}
}
}
// MARK: Github Service
struct GithubRepo: Decodable, Identifiable {
let id: Int
let name: String
let description: String
}
struct GithubResp: Decodable {
let items: [GithubRepo]
}
final class GithubSearchManager {
func search(str: String) -> AnyPublisher<GithubResp, Never> {
guard var urlComponents = URLComponents(string: "https://api.github.com/search/repositories") else {
preconditionFailure("链接无效")
}
urlComponents.queryItems = [URLQueryItem(name: "q", value: str)]
guard let url = urlComponents.url else {
preconditionFailure("链接无效")
}
let sch = DispatchQueue(label: "API", qos: .default, attributes: .concurrent)
return URLSession.shared
.dataTaskPublisher(for: url)
.receive(on: sch)
.tryMap({ element -> Data in
print(String(decoding: element.data, as: UTF8.self))
return element.data
})
.decode(type: GithubResp.self, decoder: JSONDecoder())
.catch { _ in
Empty().eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
}
final class SearchStore: ObservableObject {
@Published var query: String = ""
@Published var repos: [GithubRepo] = []
private let searchManager: GithubSearchManager
private var cancellable = Set<AnyCancellable>()
init(searchManager: GithubSearchManager = GithubSearchManager()) {
self.searchManager = searchManager
$query
.debounce(for: .milliseconds(500), scheduler: RunLoop.main)
.flatMap { query -> AnyPublisher<[GithubRepo], Never> in
return searchManager.search(str: query)
.map {
$0.items
}
.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
.receive(on: DispatchQueue.main)
.assign(to: \.repos, on: self)
.store(in: &cancellable)
}
func search(str: String) {
self.query = str
}
}抽象基础网络能力,方便扩展,代码如下:
//
// CombineAPI.swift
// SwiftOnly (iOS)
//
// Created by Ming Dai on 2021/11/4.
//
import SwiftUI
import Combine
struct CombineAPI: View {
var body: some View {
RepListView(vm: .init())
}
}
struct RepListView: View {
@ObservedObject var vm: RepListVM
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
List(vm.repos) { rep in
RepListCell(rep: rep)
}
.alert(isPresented: $vm.isErrorShow) { () -> Alert in
Alert(title: Text("出错了"), message: Text(vm.errorMessage))
}
.navigationBarTitle(Text("仓库"))
}
.onAppear {
vm.apply(.onAppear)
}
}
}
struct RepListCell: View {
@State var rep: RepoModel
var body: some View {
HStack() {
VStack() {
AsyncImage(url: URL(string: rep.owner.avatarUrl ?? ""), content: { image in
image
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
},
placeholder: {
ProgressView()
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
})
Text("\(rep.owner.login)")
.font(.system(size: 10))
}
VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 10) {
Text("\(rep.name)")
.font(.title)
Text("\(rep.stargazersCount)")
.font(.title3)
Text("\(String(describing: rep.description ?? ""))")
Text("\(String(describing: rep.language ?? ""))")
.font(.title3)
}
.font(.system(size: 14))
}
}
}
// MARK: Repo View Model
final class RepListVM: ObservableObject, UnidirectionalDataFlowType {
typealias InputType = Input
private var cancellables: [AnyCancellable] = []
// Input
enum Input {
case onAppear
}
func apply(_ input: Input) {
switch input {
case .onAppear:
onAppearSubject.send(())
}
}
private let onAppearSubject = PassthroughSubject<Void, Never>()
// Output
@Published private(set) var repos: [RepoModel] = []
@Published var isErrorShow = false
@Published var errorMessage = ""
@Published private(set) var shouldShowIcon = false
private let resSubject = PassthroughSubject<SearchRepoModel, Never>()
private let errSubject = PassthroughSubject<APISevError, Never>()
private let apiSev: APISev
init(apiSev: APISev = APISev()) {
self.apiSev = apiSev
bindInputs()
bindOutputs()
}
private func bindInputs() {
let req = SearchRepoRequest()
let resPublisher = onAppearSubject
.flatMap { [apiSev] in
apiSev.response(from: req)
.catch { [weak self] error -> Empty<SearchRepoModel, Never> in
self?.errSubject.send(error)
return .init()
}
}
let resStream = resPublisher
.share()
.subscribe(resSubject)
// 其它异步事件,比如日志等操作都可以做成Stream加到下面数组内。
cancellables += [resStream]
}
private func bindOutputs() {
let repStream = resSubject
.map {
$0.items
}
.assign(to: \.repos, on: self)
let errMsgStream = errSubject
.map { error -> String in
switch error {
case .resError: return "network error"
case .parseError: return "parse error"
}
}
.assign(to: \.errorMessage, on: self)
let errStream = errSubject
.map { _ in
true
}
.assign(to: \.isErrorShow, on: self)
cancellables += [repStream,errStream,errMsgStream]
}
}
protocol UnidirectionalDataFlowType {
associatedtype InputType
func apply(_ input: InputType)
}
// MARK: Repo Request and Models
struct SearchRepoRequest: APIReqType {
typealias Res = SearchRepoModel
var path: String {
return "/search/repositories"
}
var qItems: [URLQueryItem]? {
return [
.init(name: "q", value: "Combine"),
.init(name: "order", value: "desc")
]
}
}
struct SearchRepoModel: Decodable {
var items: [RepoModel]
}
struct RepoModel: Decodable, Hashable, Identifiable {
var id: Int64
var name: String
var fullName: String
var description: String?
var stargazersCount: Int = 0
var language: String?
var owner: OwnerModel
}
struct OwnerModel: Decodable, Hashable, Identifiable {
var id: Int64
var login: String
var avatarUrl: String?
}
// MARK: API Request Fundation
protocol APIReqType {
associatedtype Res: Decodable
var path: String { get }
var qItems: [URLQueryItem]? { get }
}
protocol APISevType {
func response<Request>(from req: Request) -> AnyPublisher<Request.Res, APISevError> where Request: APIReqType
}
final class APISev: APISevType {
private let rootUrl: URL
init(rootUrl: URL = URL(string: "https://api.github.com")!) {
self.rootUrl = rootUrl
}
func response<Request>(from req: Request) -> AnyPublisher<Request.Res, APISevError> where Request : APIReqType {
let path = URL(string: req.path, relativeTo: rootUrl)!
var comp = URLComponents(url: path, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: true)!
comp.queryItems = req.qItems
print(comp.url?.description ?? "url wrong")
var req = URLRequest(url: comp.url!)
req.addValue("application/json", forHTTPHeaderField: "Content-Type")
let de = JSONDecoder()
de.keyDecodingStrategy = .convertFromSnakeCase
return URLSession.shared.dataTaskPublisher(for: req)
.map { data, res in
print(String(decoding: data, as: UTF8.self))
return data
}
.mapError { _ in
APISevError.resError
}
.decode(type: Request.Res.self, decoder: de)
.mapError(APISevError.parseError)
.receive(on: RunLoop.main)
.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
}
enum APISevError: Error {
case resError
case parseError(Error)
}KVO
例子如下:
private final class KVOObject: NSObject {
@objc dynamic var intV: Int = 0
@objc dynamic var boolV: Bool = false
}
let o = KVOObject()
let _ = o.publisher(for: \.intV)
.sink { v in
print("value : \(v)")
}通知
使用例子如下:
extension Notification.Name {
static let noti = Notification.Name("nameofnoti")
}
let notiPb = NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: .noti, object: nil)
.sink {
print($0)
}退到后台接受通知的例子如下:
class A {
var storage = Set<AnyCancellable>()
init() {
NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIWindowScene.didEnterBackgroundNotification)
.sink { _ in
print("enter background")
}
.store(in: &self.storage)
}
}Timer
使用方式如下:
let timePb = Timer.publish(every: 1.0, on: RunLoop.main, in: .default)
let timeSk = timePb.sink { r in
print("r is \(r)")
}
let cPb = timePb.connect()Concurrency
介绍
Swift Concurrency 是什么?
ABI 稳定后,Swift 的核心团队可以开始关注 Swift 语言一直缺失的原生并发能力了。最初是由 Chris Lattner 在17年发的 Swift并发宣言 ,从此开阔了大家的眼界。后来 Swift Evolution 社区讨论了十几个提案,几十个方案,以及几百页的设计文件,做了大量的改进,社区中用户积极的参与反馈,Chris 也一直在 Evolution 中积极的参与设计。
Swift Concurrency 的实现用了 LLVM的协程 把 async/await 函数转换为基于回调的代码,这个过程发生在编译后期,这个阶段你的代码都没法辨识了。异步的函数被实现为 coroutines,在每次异步调用时,函数被分割成可调用的函数部分和后面恢复的部分。coroutine 拆分的过程发生在生成LLVM IR阶段。Swift使用了哪些带有自定义调用约定的函数保证尾部调用,并专门为Swift进行了调整。
Swift Concurrency 不是建立在 GCD 上,而是使用的一个全新的线程池。GCD 中启动队列工作会很快在提起线程,一个队列阻塞了线程,就会生成一个新线程。基于这种机制 GCD 线程数很容易比 CPU 核心数量多,线程多了,线程就会有大量的调度开销,大量的上下文切换,会使 CPU 运行效率降低。而 Swift Concurrency 的线程数量不会超过 CPU 内核,将上下文切换放到同一个线程中去做。为了实现线程不被阻塞,需要通过语言特性来做。做法是,每个线程都有一个堆栈记录函数调用情况,一个函数占一个帧。函数返回后,这个函数所占的帧就会从堆栈弹出。await 的 async 函数被作为异步帧保存在堆上等待恢复,而不阻碍其它函数入栈执行。在 await 后运行的代码叫 continuation,continuation 会在要恢复时放回到线程的堆栈里。异步帧会根据需要放回栈上。在一个异步函数中调用同步代码将添加帧到线程的堆栈中。这样线程就能够一直向前跑,而不用创建更多线程减少调度。
Douglas 在 Swift 论坛里发的 Swift Concurrency 下个版本的规划贴 Concurrency in Swift 5 and 6 ,论坛里还有一个帖子是专门用来 征集Swift Concurrency意见 的,帖子本身列出了 Swift Concurrency 相关的所有提案,也提出欢迎有新提案发出来,除了这些提案可以看外,帖子回复目前已经过百,非常热闹,可以看出大家对 Swift Concurrency 的关注度相当的高。
非常多的人参与了 Swift Concurrency 才使其看起来和用起来那么简单。Doug Gregor 在参与 John Sundell 的播客后,发了很多条推聊 Swift Concurrency,可以看到参与的人非常多,可见背后付出的努力有多大。下面我汇总了 Doug Gregor 在推上发的一些信息,你通过这些信息也可以了解 Swift Concurrency 幕后信息,所做的事和负责的人。
@pathofshrines 是 Swift Concurrency 整体架构师,包括低级别运行时和编译器相关细节。 @illian 是 async sequences、stream 和 Fundation 的负责人。 @optshiftk 对 UI 和并发交互的极好的洞察力带来了很棒的 async 接口, @phausler 带来了 async sequences。Arnold Schwaighofer、 @neightchan 、 @typesanitizer 还有 Tim Northover 实现了 async calling convention。
@ktosopl 有很深厚的 actor、分布式计算和 Swift-on-Server 经验,带来了 actor 系统。Erik Eckstein 为 async 函数和actors建立了关键的优化和功能。
SwiftUI是 @ricketson_ 和 @luka_bernardi 完成的async接口。async I/O的接口是 @Catfish_Man 完成的。 @slava_pestov 处理了 Swift 泛型问题,还指导其他人编译器实现的细节。async 重构工具是Ben Barham 做的。大量代码移植到 async 是由 @AirspeedSwift 领导,由 Angela Laar,Clack Cole,Nicole Jacques 和 @mishaldshah 共同完成的。
@lorentey 负责 Swift 接口的改进。 @jckarter 有着敏锐的语言设计洞察力,带来了语言设计经验和编译器及运行时实现技能。 @mikeash 也参与了运行时开发中。操作系统的集成是 @rokhinip 完成的, @chimz 提供了关于 Dispatch 和 OS 很好的建议,Pavel Yaskevich 和
@hollyborla 进行了并发所需要关键类型检查器的改进。 @kastiglione 、Adrian Prantl和 @fred_riss 实现了调试。 @etcwilde 和 @call1cc 实现了语义模型中的重要部分。
@evonox 负责了服务器Linux 的支持。 @compnerd 将 Swift Concurrency 移植到了 Windows。
Swift Concurrency 模型简单,细节都被隐藏了,比 Kotlin 和 C++的 Coroutine 接口要简洁很多。比如 Task 接口形式就很简洁。Swift Concurrency 大体可分为 async/await、Async Sequences、结构化并发和 Actors。
async/await
通过类似 throws 语法的 async 来指定函数为异步函数,异步函数才能够使用 await,使用异步函数要用 await。await 修饰在 suspension point 时当前线程可以让给其它任务执行,而不用阻塞当前线程,等 await 后面的函数执行完成再回来继续执行,这里需要注意的是回来执行不一定是在离开时的线程上。async/await 提案是 SE-0296 。如果想把现有的异步开发带到 async/await 世界,请使用 withCheckedThrowingContinuation。
async/await 还有一个非常明显的好处,就是不会再有[weak self] dance 了。
Async Sequences
AsyncSequence 的使用方式是 for-await-in 和 for-try-await-in,系统提供了一些接口,如下:
- FileHandle.standardInput.bytes.lines
- URL.lines
- URLSession.shared.data(from: URL)
- let (localURL, _ ) = try await session.download(from: url) 下载和get请求数据区别是需要边请求边存储数据以减少内存占用
- let (responseData, response) = try await session.upload(for: request, from: data)
- URLSession.shared.bytes(from: URL)
- NotificationCenter.default.notifications
结构化并发
使用这些接口可以一边接收数据一边进行显示,AsyncSequence 的提案是 SE-0298 (Swift 5.5可用)。AsyncStream 是创建自己异步序列的最简单的方法,处理迭代、取消和缓冲。AsyncStream 正在路上,提案是 SE-0314 。
Task 为一组并发任务创建一个运行环境,async let 可以让任务并发执行,结构化并发(Structured concurrency,提案在路上 SE-0304 )withTaskGroup 中 group.async 可以将并发任务进行分组。
Actors
我们写的程序会在进程中被拆成一个一个小指令,这些指令会在某刻会一个接一个同步的或者并发的执行。系统会用多个线程执行并行的任务,执行顺序是调度器来管理的,现代多核可以同时处理多个线程,当一个资源在多个线程上同时被更改时就会出问题。并发任务对数据资源操作容易造成数据竞争,以前需要手动放到串行队列、使用锁、调度屏障或 Atomics 的方式来避免。以前处理容易导致昂贵的上下文切换,过多线程容易导致线程爆炸,容易意外阻断线程导致后面代码没法执行,多任务相互的等待造成了死锁,block 和内存引用容易出错等等问题。
现在 Swift Concurrency 可以通过 actor 来创建一个区域,在这个区域会自动进行数据安全保护,保证一定时间只有一个线程访问里面数据,防止数据竞争。actor 内部对成员访问是同步的,成员默认是隔离的,actor 外部对 actor 内成员的访问只能是异步的,隐式同步以防止数据竞争。MainActor 继承自能确保全局唯一实例的 GlobalActor,保证任务在主线程执行,这样你就可以抛弃掉在你的 ViewModel 里写 DispatchQueue.main.async 了。
Actors 的概念通常被用于分布式计算,Actor 模型参看 Wikipedia 里的详细解释,Swift 中的实现效果也非常的理想。Actors 的提案 SE-0306 已在 Swift 5.5落实。
很多语言都支持 actors 还有 async/await,实现的方式也类似,actor 使用的不是锁,而是用的 async/await 这样能够在一个线程中切换上下文来避免线程空闲的线程模型。actor 还利用编译器,提前做会引起并发问题的检查。
actor 是遵循 Sendable 协议的,只有结构体和 final 类才能够遵循 Sendable,继承于 Sendable 协议的 Excutor 协议表示方法本身,SerialExecutor 表示以串行方式执行。actor 使用 C++写的,源码在 这里 ,可以看到 actor 主要是通过控制各个 job 执行的状态的管理器。job 执行优先级来自 Task 对象,排队时需要确保高优 job 先被执行。全局 Executor 用来为 job 排队,通知 actor 拥有或者放弃线程,实现在 这里 。由于等待而放弃当前线程让其他 actor 执行的 actor,在收到全局 Executor 创建一个新的 job 的通知,使其可以进入一个可能不同线程,这个过程就是并发模型中描述的 Actor Reentrancy。
Distributed Actors
actor 具有分布式形式工作能力,也就是可以 RPC 通过网络读取和写入属性或者调用方法。设计为保护在跨多个进程中的低级别数据竞争。Distributed actors 可以在两个进程间建立通道,隔离它们状态,并在它们之间异步通信。每个 distributed actors 在 actor 初始化时分配一个不可以手动创建的 id,在它所属整个 distributed actor 系统中唯一标识所指 actor,这样无论 distributed actors 在哪,都可以以相同的方式与之交互。
session Meet distributed actors in Swift 。这里有个 distributed actors 的代码示例 TicTacFish: Implementing a game using distributed actors
SE-0336 Distributed Actor Isolation 和 SE-0344 Distributed Actor Runtime 是两个 Distributed Actors 的相关提案。
Apple 提供了一个参考的服务端 cluster actor 系统实现示例,cluster actor system implementation 。
相关提案
所有相关提案清单如下:
- SE-0296: Async/await 【译】SE-0296 Async/await
- SE-0317: async let
- SE-0300: Continuations for interfacing async tasks with synchronous code 【译】SE-0300 Continuation – 执行同步代码的异步任务接口
- SE-0302: Sendable and @Sendable closures
- SE-0298: Async/Await: Sequences 【译】SE-0298 Async/Await 序列
- SE-0304: Structured concurrency
- SE-0306: Actors 【译】SE-0306 Actors
- SE-0313: Improved control over actor isolation
- SE-0297: Concurrency Interoperability with Objective-C 【译】SE-0297 Concurrency 与 Objective-C 的交互
- SE-0314: AsyncStream and AsyncThrowingStream
- SE-0316: Global actors
- SE-0310: Effectful read-only properties
- SE-0311: Task Local Values
- Custom Executors
学习路径
如果打算尝试 Swift Concurrency 的话,按照先后顺序,可以先看官方手册介绍文章 Concurrency 。再看 Meet async/await in Swift 这个Session,了解背后原理看 Explore structured concurrency in Swift 。动手照着试示例代码,看Paul的 Swift Concurrency by Example 这个系列。接着看 Protect mutable state with Swift actors 来了解 actors 怎么防止数据竞争。通过 Discover concurrency in SwiftUI 看 concurrency 如何在 SwiftUI 中使用, Use async/await with URLSession 来看怎么在 URLSession 中使用 async/await。最后听听负责 Swift Concurrency 的 Doug Gregor 参加的一个 播客的访谈 ,了解下 Swift Concurrency 背后的故事。
Swift Concurrency 和 Combine
由于 Swift Concurrency 的推出和大量的 Session 发布,特别是 AsyncSequence 的出现,以及正在路上的 AsyncStream、AsyncThrowingStream 和 continuation 提案(在Xcode 13.0 beta 3 AsyncStream 正式 release ),这些越来越多和 Combine 功能重叠的特性出现在 Swift Concurrency 蓝图里时,大家开始猜测是否 Combine 会被 Swift Concurrency 替代。关于未来是 Swift Concurrency 还是 Combine,我的感觉是,Combine 更侧重在响应式编程上,而响应式编程并不是所有开发人员都会接受的,而 Swift Concurrency 是所有人都愿意接受的开发方式,从 Swift Concurrency 推出后开发者使用的数量和社区反应火热程度来看都比 Combine 要大。在苹果对 Combine 有下一步动作之前,我还是更偏向 Swift Concurrency。
Concurrency 5.7 版本更新
session Eliminate data races using Swift Concurrency 、Visualize and optimize Swift concurrency 、Meet Swift Async Algorithms 。
表示持续时间有了新的放来来表达,对应提案是 SE-0329 Clock, Instant, and Duration ,continuous clock 是在系统睡眠状态还会增加时间,suspending clock 在系统睡眠状态不会增加时间。Instants 表示一个确定的时间。Duration 表示两个时间经历了多久。
新增 SE-0338 Clarify the Execution of Non-Actor-Isolated Async Functions 通过收紧可发送性检查的规则来避免潜在的数据竞争。
SE-0343 Concurrency in Top-level Code 这个提案主要是更好地支持命令行工具的开发,可以直接将 concurrency 代码写到 main.swift 文件里。
SE-0340 Unavailable From Async Attribute 提供 noasync 语法以允许我们将类型和函数标记为在异步上下文不可用。
Task 是按顺序执行的,是异步的,在 await 时可以暂停任意次数。task 是自包含的,有自己的资源,可以独立于任何其他 task 独立运行。task 通过在 body 末尾返回一个值来传递对象,值类型没问题,如果是引用类型有可能出现数据竞争。
通过 Sendable 协议 Swift 可以帮助告诉我们什么时候 task 之间共享数据是安全的。Sendable 描述的类型可以跨隔离 domain,不会有数据竞争,Swift 编译器会在构建时检查数据竞争。task 的返回类型要符合 Sendable。
引用类型只能在很少的情况下符合 Sendable。比如 final class 只有不可变的存储。对于自己内部同步的引用类型,比如锁,可以用 @unchecked Sendable 。
class ConcurrentCache<Key: Hashable & Sendable, Value: Sendable>: @unchecked Sendable {
var lock: NSLock
var storage: [Key: Value]
// ...
}Actor 提供了一种隔离状态的方法可以消除数据竞争。使用 task 来执行 actor 定义的代码。一次只能在一个 actor 上执行一个 task。actor 也是依赖 Sendable。actor 是引用类型,但隔离了他们所有属性和代码来防止并发访问。@MainActor 表示的是主线程,你要在应用中更新 UI 时来用它。
@MainActor func updateView() { … }
Task { @MainActor in
// update UI here
}@MainActor 也可以用于类,类的属性和方法只能在主 main actor 上访问,除非标记为 nonisolated 。
@MainActor
class ChickenValley: Sendable {
var flock: [Chicken]
var food: [Pineapple]
func advanceTime() {
for chicken in flock {
chicken.eat(from: &food)
}
}
}SwiftUI
介绍
SwiftUI 是什么?
对于一个基于UIKit的项目是没有必要全部用SwiftUI重写的,在UIKit里使用SwiftUI的视图非常容易,UIHostingController是UIViewController的子类,可以直接用在UIKit里,因此直接将SwiftUI视图加到UIHostingController中,就可以在UIKit里使用SwiftUI视图了。
SwiftUI的布局核心是 GeometryReader、View Preferences和Anchor Preferences。如下图所示:
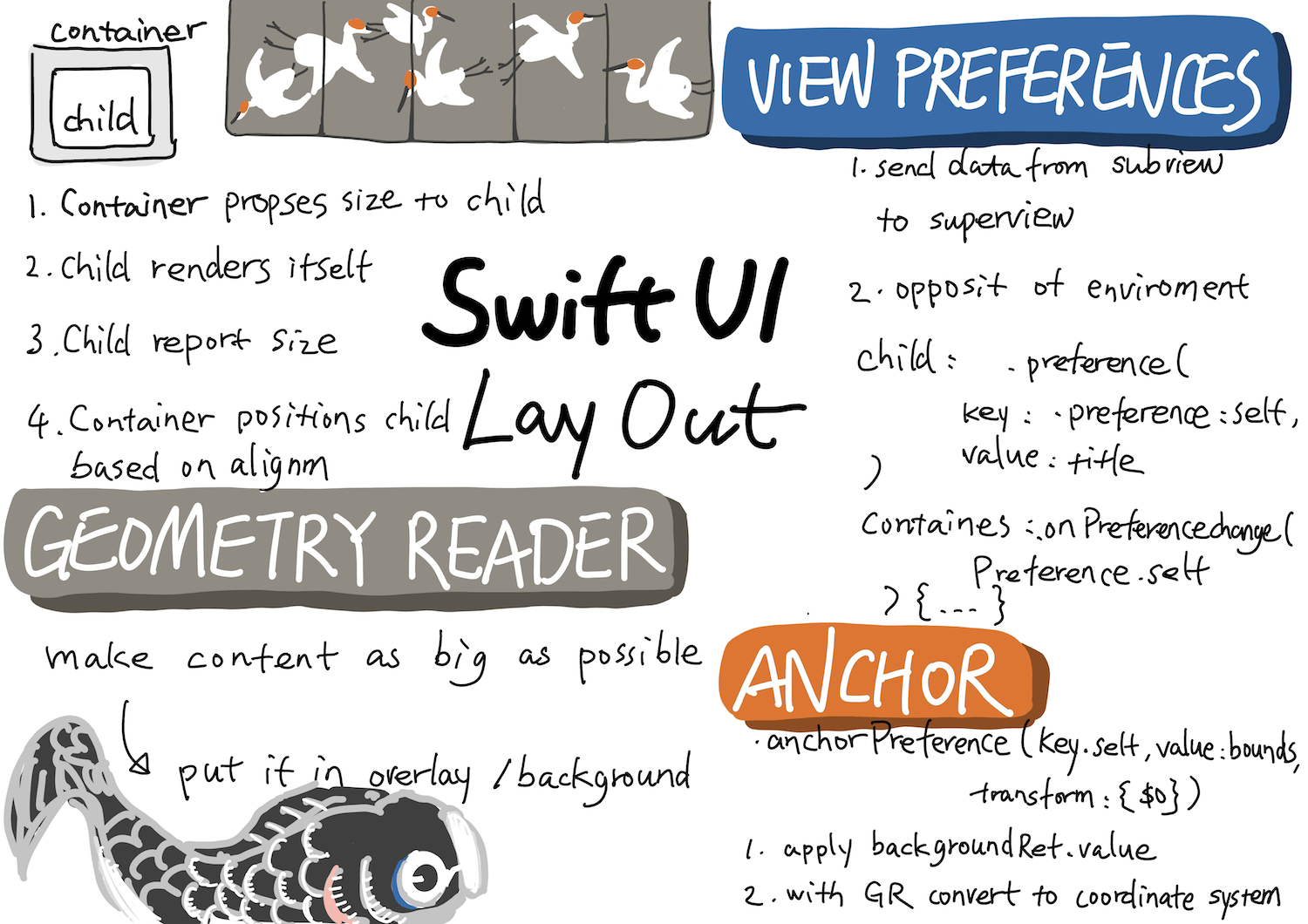
SwiftUI的数据流更适合Redux结构,如下图所示:

如上图,Redux结构是真正的单向单数据源结构,易于分割,能充分利用SwiftUI内置的数据流Property Wrapper。UI组件干净、体量小、可复用并且无业务逻辑,因此开发时可以聚焦于UI代码。业务逻辑放在一起,所有业务逻辑和数据Model都在Reducer里。 ACHNBrowserUI 和 MovieSwiftUI 开源项目都是使用的Redux架构。最近比较瞩目的TCA(The Composable Architecture)也是类Redux/Elm的架构的框架, 项目地址见 。
提到数据流就不得不说下苹果公司新出的Combine,对标的是RxSwift,由于是苹果公司官方的库,所以应该优先选择。不过和SwiftUI一样,这两个新库对APP支持最低的系统版本都要求是iOS13及以上。那么怎么能够提前用上SwiftUI和Combine呢?或者说现在使用什么库可以以相同接口方式暂时替换它们,又能在以后改为SwiftUI和Combine时成本最小化呢?
对于SwiftUI,AcFun自研了声明式UI Ysera,类似SwiftUI的接口,并且重构了AcFun里收藏模块列表视图和交互逻辑,如下图所示:

通过上图可以看到,swift代码量相比较OC减少了65%以上,原先使用Objective-C实现的相同功能代码超过了1000行,而Swift重写只需要350行,对于AcFun的业务研发工程师而言,同样的需求实现代码比之前少了至少30%,面对单周迭代这样的节奏,团队也变得更从容。代码可读性增加了,后期功能迭代和维护更容易了,Swift让AcFun驶入了iOS开发生态的“快车道”。
SwiftUI全部都是基于Swift的各大可提高开发效率特性完成的,比如前面提到的,能够访问只给语言特性级别行为的Property Wrapper,通过Property Wrapper包装代码逻辑,来降低代码复杂度,除了SwiftUI和Combine里@开头的Property Wrapper外,Swift还自带类似 @dynamicMemberLookup 和 @dynamicCallable 这样重量级的Property Wrapper。还有 ResultBuilder 这种能够简化语法的特性,有些如GraphQL、REST和Networking实际使用ResultBuilder的 范例可以参考 。这些Swift的特性如果也能得到充分利用,即使不用SwiftUI也能使开发效率得到大幅提升。
网飞(Netflix)App已使用SwiftUI重构了登录界面,网飞增长团队移动负责人故胤道长记录了SwiftUI在网飞的落地过程,详细描述了 SwiftUI的收益 。网飞能够直接使用SwiftUI得益于他们最低支持iOS 13系统。
不过如最低支持系统低于iOS 13,还有开源项目 AltSwiftUI 也实现了SwiftUI的语法和特性,能够向前兼容到iOS 11。
Kuba Suder 做了一个 SwiftUI Index/Changelog ,从官方文档中提取版本信息,一目了然 SwiftUI 每个版本 view,modifier 还有属性做了哪些增加和改变。当然也包括这次 SwiftUI 4 的更新。还有份对今年更新整理的 cheat sheet What’s New In SwiftUI for iOS Cheat Sheet - WWDC22 。
SwiftUI 4 做了大量细节更新,比如添加了后台任务函数 backgroundTask(_:action:) 。List 改用 UICollectionView。AnyLayout 让 HStack 和 VStack 之间可以自由切换。scrollDismissesKeyboard() modifier 可以让键盘在滚动时自动 dismiss。scrollIndicators() modifier 可以隐藏 ScrollView 和 List 等视图的滚动指示。defersSystemGestures() modifier 允许我们的手势优先于系统的内置手势。颜色的 .gradient 可以获得很简单的渐变,Rectangle().fill(.red.gradient),还有 .shadow 用来创建投影 Rectangle().fill(.red.shadow(.drop(color: .black, radius: 10))),还有 .inner 内阴影。lineLimit() modifier 支持范围设置。还有一些 modifier 支持 toggle 参数,比如 .bold() 和 .italic() 等,这样利于运行时进行调整。
嵌入 UIKit
示例如下:
cell.contentConfiguration = UIHostingConfiguration {
VStack {
Image(systemName: "wand.and.stars")
.font(.title)
Text("Like magic!")
.font(.title2).bold()
}
.foregroundStyle(Color.purple)
}锁屏的 Widget 和 WatchOS 一样,可以瞟一眼就获取信息。
官方指南 Creating Lock Screen Widgets and Watch Complications
可以将 SwiftUI 的 View 生成图片。
官方参考文档 ImageRenderer
session Efficiency awaits: Background tasks in SwiftUI 了解如何使用 SwiftUI 后台任务 API 简洁地处理任务。展示如何使用 Swift Concurrency 来处理网络响应、后台刷新等——同时保持性能和功率。
SwiftUI 参考资料
- WWDC22 SwiftUI 和 UI 库相关专题
- 官方教程 Learnning SwiftUI
- SwiftUI 主题
- SwiftUI Session
- SwiftUI 文档
- Learning SwiftUI 一年一度官方入门教程
- Food Truck: Building a SwiftUI multiplatform app 一套代码适配 Mac、iPad 和 iPhone 的官方示例
- Reda Lemeden 整理的 WWDC22 所有 SwiftUI 相关内容
session:
社区整理的和 SwiftUI 的 digital lounges 内容:
- WWDC swiftui-lounge
- WWDC 2022: Lessons from the SwiftUI Digital Lounges javier 整理的,做了详细的分类
- #swiftui-lounge #wwdc22
视图组件使用
SwiftUI 对标的 UIKit 视图
如下:
| SwiftUI | UIKit |
|---|---|
| Text 和 Label | UILabel |
| TextField | UITextField |
| TextEditor | UITextView |
| Button 和 Link | UIButton |
| Image | UIImageView |
| NavigationView | UINavigationController 和 UISplitViewController |
| ToolbarItem | UINavigationItem |
| ScrollView | UIScrollView |
| List | UITableView |
| LazyVGrid 和 LazyHGrid | UICollectionView |
| HStack 和 LazyHStack | UIStack |
| VStack 和 LazyVStack | UIStack |
| TabView | UITabBarController 和 UIPageViewController |
| Toggle | UISwitch |
| Slider | UISlider |
| Stepper | UIStepper |
| ProgressView | UIProgressView 和 UIActivityIndicatorView |
| Picker | UISegmentedControl |
| DatePicker | UIDatePicker |
| Alert | UIAlertController |
| ActionSheet | UIAlertController |
| Map | MapKit |
Text
基本用法

// MARK: - Text
struct PlayTextView: View {
let manyString = "这是一段长文。总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么,总得说点什么吧。"
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
Group {
Text("大标题").font(.largeTitle)
Text("说点啥呢?")
.tracking(30) // 字间距
.kerning(30) // 尾部留白
Text("划重点")
.underline()
.foregroundColor(.yellow)
.fontWeight(.heavy)
Text("可旋转的文字")
.rotationEffect(.degrees(45))
.fixedSize()
.frame(width: 20, height: 80)
Text("自定义系统字体大小")
.font(.system(size: 30))
Text("使用指定的字体")
.font(.custom("Georgia", size: 24))
}
Group {
Text("有阴影")
.font(.largeTitle)
.foregroundColor(.orange)
.bold()
.italic()
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 1, x: 0, y: 2)
Text("Gradient Background")
.font(.largeTitle)
.padding()
.foregroundColor(.white)
.background(LinearGradient(gradient: Gradient(colors: [.white, .black, .red]), startPoint: .top, endPoint: .bottom))
.cornerRadius(10)
Text("Gradient Background")
.padding(5)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.background(LinearGradient(gradient: Gradient(colors: [.white, .black, .purple]), startPoint: .leading, endPoint: .trailing))
.cornerRadius(10)
ZStack {
Text("渐变透明材质风格")
.padding()
.background(
.regularMaterial,
in: RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10, style: .continuous)
)
.shadow(radius: 10)
.padding()
.font(.largeTitle.weight(.black))
}
.frame(width: 300, height: 200)
.background(
LinearGradient(colors: [.yellow, .pink], startPoint: .topLeading, endPoint: .bottomTrailing)
)
Text("Angular Gradient Background")
.padding()
.background(AngularGradient(colors: [.red, .yellow, .green, .blue, .purple, .red], center: .center))
.cornerRadius(20)
Text("带背景图片的")
.padding()
.font(.largeTitle)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.background {
Rectangle()
.fill(Color(.black))
.cornerRadius(10)
Image("logo")
.resizable()
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
}
.frame(width: 200, height: 100)
}
Group {
// 设置 lineLimit 表示最多支持行数,依据情况依然有会被减少显示行数
Text(manyString)
.lineLimit(3) // 对行的限制,如果多余设定行数,尾部会显示...
.lineSpacing(10) // 行间距
.multilineTextAlignment(.leading) // 对齐
// 使用 fixedSize 就可以在任何时候完整显示
Text(manyString)
.fixedSize(horizontal: false, vertical: true)
}
// 使用 AttributeString
PTextViewAttribute()
.padding()
// 使用 Markdown
PTextViewMarkdown()
.padding()
// 时间
PTextViewDate()
// 插值
PTextViewInterpolation()
}
}
}font 字体设置的样式对应 weight 和 size 可以在官方交互文档中查看 Typography
markdown 使用
// MARK: - Markdown
struct PTextViewMarkdown: View {
let mdaStr: AttributedString = {
var mda = AttributedString(localized: "这是一个 **Attribute** ~string~")
/// 自定义的属性语法是^[string](key:value)
mda = AttributedString(localized: "^[这是](p2:'one')^[一](p3:{k1:1,k2:2})个 **Attribute** ~string~", including: \.newScope)
print(mda)
/// 这是 {
/// NSLanguage = en
/// p2 = one
/// }
/// 一 {
/// NSLanguage = en
/// p3 = P3(k1: 1, k2: 2)
/// }
/// 个 {
/// NSLanguage = en
/// }
/// Attribute {
/// NSLanguage = en
/// NSInlinePresentationIntent = NSInlinePresentationIntent(rawValue: 2)
/// }
/// {
/// NSLanguage = en
/// }
/// string {
/// NSInlinePresentationIntent = NSInlinePresentationIntent(rawValue: 32)
/// NSLanguage = en
/// }
// 从文件中读取 Markdown 内容
let mdUrl = Bundle.main.url(forResource: "1", withExtension: "md")!
mda = try! AttributedString(contentsOf: mdUrl,options: AttributedString.MarkdownParsingOptions(interpretedSyntax: .inlineOnlyPreservingWhitespace), baseURL: nil) // .inlineOnlyPreservingWhitespace 支持 markdown 文件的换行
// Markdown 已转换成 AtrributedString 结构。
for r in mda.runs {
if let ipi = r.inlinePresentationIntent {
switch ipi {
case .lineBreak:
print("paragrahp")
case .code:
print("this is code")
default:
break
}
}
if let pi = r.presentationIntent {
for c in pi.components {
switch c.kind {
case .paragraph:
print("this is paragraph")
case .codeBlock(let lang):
print("this is \(lang ?? "") code")
case .header(let level):
print("this is \(level) level")
default:
break
}
}
}
}
return mda
}()
var body: some View {
Text(mdaStr)
}
}AttributedString 的使用
// MARK: - AttributedString
struct PTextViewAttribute: View {
let aStr: AttributedString = {
var a1 = AttributedString("这是一个 ")
var c1 = AttributeContainer()
c1.font = .footnote
c1.foregroundColor = .secondary
a1.setAttributes(c1)
var a2 = AttributedString("Attribute ")
var c2 = AttributeContainer()
c2.font = .title
a2.setAttributes(c2)
var a3 = AttributedString("String ")
var c3 = AttributeContainer()
c3.baselineOffset = 10
c3.appKit.foregroundColor = .yellow // 仅在 macOS 里显示的颜色
c3.swiftUI.foregroundColor = .secondary
c3.font = .footnote
a3.setAttributes(c3)
// a3 使用自定义属性
a3.p1 = "This is a custom property."
// formatter 的支持
var a4 = Date.now.formatted(.dateTime
.hour()
.minute()
.weekday()
.attributed
)
let c4AMPM = AttributeContainer().dateField(.amPM)
let c4AMPMColor = AttributeContainer().foregroundColor(.green)
a4.replaceAttributes(c4AMPM, with: c4AMPMColor)
let c4Week = AttributeContainer().dateField(.weekday)
let c4WeekColor = AttributeContainer().foregroundColor(.purple)
a4.replaceAttributes(c4Week, with: c4WeekColor)
a1.append(a2)
a1.append(a3)
a1.append(a4)
// Runs 视图
for r in a1.runs {
print(r)
}
/// 这是一个 {
/// SwiftUI.Font = Font(provider: SwiftUI.(unknown context at $7ff91d4a5e90).FontBox<SwiftUI.Font.(unknown context at $7ff91d4ad5d8).TextStyleProvider>)
/// SwiftUI.ForegroundColor = secondary
/// }
/// Attribute {
/// SwiftUI.Font = Font(provider: SwiftUI.(unknown context at $7ff91d4a5e90).FontBox<SwiftUI.Font.(unknown context at $7ff91d4ad5d8).TextStyleProvider>)
/// }
/// String {
/// SwiftUI.ForegroundColor = secondary
/// SwiftUI.BaselineOffset = 10.0
/// NSColor = sRGB IEC61966-2.1 colorspace 1 1 0 1
/// SwiftUI.Font = Font(provider: SwiftUI.(unknown context at $7ff91d4a5e90).FontBox<SwiftUI.Font.(unknown context at $7ff91d4ad5d8).TextStyleProvider>)
/// p1 = This is a custom property.
/// }
/// Tue {
/// SwiftUI.ForegroundColor = purple
/// }
/// {
/// }
/// 5 {
/// Foundation.DateFormatField = hour
/// }
/// : {
/// }
/// 16 {
/// Foundation.DateFormatField = minute
/// }
/// {
/// }
/// PM {
/// SwiftUI.ForegroundColor = green
/// }
return a1
}()
var body: some View {
Text(aStr)
}
}
// MARK: - 自定 AttributedString 属性
struct PAKP1: AttributedStringKey {
typealias Value = String
static var name: String = "p1"
}
struct PAKP2: CodableAttributedStringKey, MarkdownDecodableAttributedStringKey {
public enum P2: String, Codable {
case one, two, three
}
static var name: String = "p2"
typealias Value = P2
}
struct PAKP3: CodableAttributedStringKey, MarkdownDecodableAttributedStringKey {
public struct P3: Codable, Hashable {
let k1: Int
let k2: Int
}
typealias Value = P3
static var name: String = "p3"
}
extension AttributeScopes {
public struct NewScope: AttributeScope {
let p1: PAKP1
let p2: PAKP2
let p3: PAKP3
}
var newScope: NewScope.Type {
NewScope.self
}
}
extension AttributeDynamicLookup{
subscript<T>(dynamicMember keyPath:KeyPath<AttributeScopes.NewScope,T>) -> T where T:AttributedStringKey {
self[T.self]
}
}时间的显示
// MARK: - 时间
struct PDateTextView: View {
let date: Date = Date()
let df: DateFormatter = {
let df = DateFormatter()
df.dateStyle = .long
df.timeStyle = .short
return df
}()
var dv: String {
return df.string(from: date)
}
var body: some View {
HStack {
Text(dv)
}
.environment(\.locale, Locale(identifier: "zh_cn"))
}
}插值使用
// MARK: - 插值
struct PTextViewInterpolation: View {
let nf: NumberFormatter = {
let f = NumberFormatter()
f.numberStyle = .currencyPlural
return f
}()
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("图文 \(Image(systemName: "sun.min"))")
Text("💰 \(999 as NSNumber, formatter: nf)")
.environment(\.locale, Locale(identifier: "zh_cn"))
Text("数组: \(["one", "two"])")
Text("红字:\(red: "变红了"),带图标的字:\(sun: "天晴")")
}
}
}
// 扩展 LocalizedStringKey.StringInterpolation 自定义插值
extension LocalizedStringKey.StringInterpolation {
// 特定类型处理
mutating func appendInterpolation(_ value: [String]) {
for s in value {
appendLiteral(s + "")
appendInterpolation(Text(s + " ").bold().foregroundColor(.secondary))
}
}
// 实现不同情况处理,可以简化设置修改器设置
mutating func appendInterpolation(red value: LocalizedStringKey) {
appendInterpolation(Text(value).bold().foregroundColor(.red))
}
mutating func appendInterpolation(sun value: String) {
appendInterpolation(Image(systemName: "sun.max.fill"))
appendLiteral(value)
}
}Link
使用方法如下:
struct PlayLinkView: View {
@Environment(\.openURL) var openURL
var aStr: AttributedString {
var a = AttributedString("戴铭的博客")
a.link = URL(string: "https://ming1016.github.io/")
return a
}
var body: some View {
VStack {
// 普通
Link("前往 www.starming.com", destination: URL(string: "http://www.starming.com")!)
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
Link(destination: URL(string: "https://twitter.com/daiming_cn")!) {
Label("My Twitter", systemImage: "message.circle.fill")
}
// AttributedString 链接
Text(aStr)
// markdown 链接
Text("[Go Ming's GitHub](https://github.com/ming1016)")
// 控件使用 OpenURL
Link("小册子源码", destination: URL(string: "https://github.com/ming1016/SwiftPamphletApp")!)
.environment(\.openURL, OpenURLAction { url in
return .systemAction
/// return .handled 不会返回系统打开浏览器动作,只会处理 return 前的事件。
/// .discard 和 .handled 类似。
/// .systemAction(URL(string: "https://www.anotherurl.com")) 可以返回另外一个 url 来替代指定的url
})
// 扩展 View 后更简洁的使用 OpenURL
Link("戴铭的微博", destination: URL(string: "https://weibo.com/allstarming")!)
.goOpenURL { url in
print(url.absoluteString)
return .systemAction
}
// 根据内容返回不同链接
Text("戴铭博客有好几个,存在[GitHub Page](github)、[自建服务器](starming)和[知乎](zhihu)上")
.environment(\.openURL, OpenURLAction { url in
switch url.absoluteString {
case "github":
return .systemAction(URL(string: "https://ming1016.github.io/")!)
case "starming":
return .systemAction(URL(string: "http://www.starming.com")!)
case "zhihu":
return .systemAction(URL(string: "https://www.zhihu.com/people/starming/posts")!)
default:
return .handled
}
})
} // end VStack
.padding()
}
// View 支持 openURL 的能力
func goUrl(_ url: URL, done: @escaping (_ accepted: Bool) -> Void) {
openURL(url, completion: done)
}
}
// 为 View 扩展一个 OpenURL 方法
extension View {
func goOpenURL(done: @escaping (URL) -> OpenURLAction.Result) -> some View {
environment(\.openURL, OpenURLAction(handler: done))
}
}View 的 onOpenURL 方法可以处理 Universal Links。
struct V: View {
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("hi")
}
.onOpenURL { url in
print(url.absoluteString)
}
}
}Label

struct PlayLabelView: View {
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 10) {
Label("一个 Label", systemImage: "bolt.circle")
Label("只显示 icon", systemImage: "heart.fill")
.labelStyle(.iconOnly)
.foregroundColor(.red)
// 自建 Label
Label {
Text("自建 Label")
.foregroundColor(.orange)
.bold()
.font(.largeTitle)
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 1, x: 0, y: 2)
} icon: {
Image("p3")
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
.frame(width: 30)
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 1, x: 0, y: 2)
}
// 自定义 LabelStyle
Label("有边框的 Label", systemImage: "b.square.fill")
.labelStyle(.border)
Label("仅标题有边框", systemImage: "text.bubble")
.labelStyle(.borderOnlyTitle)
// 扩展的 Label
Label("扩展的 Label", originalSystemImage: "cloud.sun.bolt.fill")
} // end VStack
} // end body
}
// 对 Label 做扩展
extension Label where Title == Text, Icon == Image {
init(_ title: LocalizedStringKey, originalSystemImage systemImageString: String) {
self.init {
Text(title)
} icon: {
Image(systemName: systemImageString)
.renderingMode(.original) // 让 SFSymbol 显示本身的颜色
}
}
}
// 添加自定义 LabelStyle,用来加上边框
struct BorderLabelStyle: LabelStyle {
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
Label(configuration)
.padding()
.overlay(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 20)
.stroke(.purple, lineWidth: 4))
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 4, x: 0, y: 5)
.labelStyle(.automatic) // 样式擦除器,防止样式被 .iconOnly、.titleOnly 这样的 LabelStyle 擦除了样式。
}
}
extension LabelStyle where Self == BorderLabelStyle {
internal static var border: BorderLabelStyle {
BorderLabelStyle()
}
}
// 只给标题加边框
struct BorderOnlyTitleLabelStyle: LabelStyle {
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
HStack {
configuration.icon
configuration.title
.padding()
.overlay(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 20)
.stroke(.pink, lineWidth: 4))
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 1, x: 0, y: 1)
.labelStyle(.automatic)
}
}
}
extension LabelStyle where Self == BorderOnlyTitleLabelStyle {
internal static var borderOnlyTitle: BorderOnlyTitleLabelStyle {
BorderOnlyTitleLabelStyle()
}
}TextEditor

对应的代码如下:
import SwiftUI
import CodeEditorView
struct PlayTextEditorView: View {
// for TextEditor
@State private var txt: String = "一段可编辑文字...\n"
@State private var count: Int = 0
// for CodeEditorView
@Environment(\.colorScheme) private var colorScheme: ColorScheme
@State private var codeMessages: Set<Located<Message>> = Set ()
@SceneStorage("editLocation") private var editLocation: CodeEditor.Location = CodeEditor.Location()
var body: some View {
// 使用 SwiftUI 自带 TextEditor
TextEditor(text: $txt)
.font(.title)
.lineSpacing(10)
.disableAutocorrection(true)
.padding()
.onChange(of: txt) { newValue in
count = txt.count
}
Text("字数:\(count)")
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
.font(.footnote)
// 使用的 CodeEditorView 显示和编辑代码高亮的代码,还有 minimap
CodeEditor(text: .constant("""
static func number() {
// Int
let i1 = 100
let i2 = 22
print(i1 / i2) // 向下取整得 4
// Float
let f1: Float = 100.0
let f2: Float = 22.0
print(f1 / f2) // 4.5454545
let f4: Float32 = 5.0
let f5: Float64 = 5.0
print(f4, f5) // 5.0 5.0 5.0
// Double
let d1: Double = 100.0
let d2: Double = 22.0
print(d1 / d2) // 4.545454545454546
// 字面量
print(Int(0b10101)) // 0b 开头是二进制
print(Int(0x00afff)) // 0x 开头是十六进制
print(2.5e4) // 2.5x10^4 十进制用 e
print(0xAp2) // 10*2^2 十六进制用 p
print(2_000_000) // 2000000
// isMultiple(of:) 方法检查一个数字是否是另一个数字的倍数
let i3 = 36
print(i3.isMultiple(of: 9)) // true
}
"""),
messages: $codeMessages,
language: .swift,
layout: CodeEditor.LayoutConfiguration(showMinimap: true)
)
.environment(\.codeEditorTheme, colorScheme == .dark ? Theme.defaultDark : Theme.defaultLight)
// 包装的 NSTextView
HSplitView {
PNSTextView(text: .constant("左边写...\n"), onDidChange: { (s, i) in
print("Typing \(i) times.")
})
.padding()
PNSTextView(text: .constant("右边写...\n"))
.padding()
} // end HSplitView
} // end body
}
// MARK: - 自己包装 NSTextView
struct PNSTextView: NSViewRepresentable {
@Binding var text: String
var onBeginEditing: () -> Void = {}
var onCommit: () -> Void = {}
var onDidChange: (String, Int) -> Void = { _,_ in }
// 返回要包装的 NSView
func makeNSView(context: Context) -> PNSTextConfiguredView {
let t = PNSTextConfiguredView(text: text)
t.delegate = context.coordinator
return t
}
func updateNSView(_ view: PNSTextConfiguredView, context: Context) {
view.text = text
view.selectedRanges = context.coordinator.sRanges
}
// 回调
func makeCoordinator() -> TextViewDelegate {
TextViewDelegate(self)
}
}
// 处理 delegate 回调
extension PNSTextView {
class TextViewDelegate: NSObject, NSTextViewDelegate {
var tView: PNSTextView
var sRanges: [NSValue] = []
var typeCount: Int = 0
init(_ v: PNSTextView) {
self.tView = v
}
// 开始编辑
func textDidBeginEditing(_ notification: Notification) {
guard let textView = notification.object as? NSTextView else {
return
}
self.tView.text = textView.string
self.tView.onBeginEditing()
}
// 每次敲字
func textDidChange(_ notification: Notification) {
guard let textView = notification.object as? NSTextView else {
return
}
typeCount += 1
self.tView.text = textView.string
self.sRanges = textView.selectedRanges
self.tView.onDidChange(textView.string, typeCount)
}
// 提交
func textDidEndEditing(_ notification: Notification) {
guard let textView = notification.object as? NSTextView else {
return
}
self.tView.text = textView.string
self.tView.onCommit()
}
}
}
// 配置 NSTextView
final class PNSTextConfiguredView: NSView {
weak var delegate: NSTextViewDelegate?
private lazy var tv: NSTextView = {
let contentSize = sv.contentSize
let textStorage = NSTextStorage()
let layoutManager = NSLayoutManager()
textStorage.addLayoutManager(layoutManager)
let textContainer = NSTextContainer(containerSize: sv.frame.size)
textContainer.widthTracksTextView = true
textContainer.containerSize = NSSize(
width: contentSize.width,
height: CGFloat.greatestFiniteMagnitude
)
layoutManager.addTextContainer(textContainer)
let t = NSTextView(frame: .zero, textContainer: textContainer)
t.delegate = self.delegate
t.isEditable = true
t.allowsUndo = true
t.font = .systemFont(ofSize: 24)
t.textColor = NSColor.labelColor
t.drawsBackground = true
t.backgroundColor = NSColor.textBackgroundColor
t.maxSize = NSSize(width: CGFloat.greatestFiniteMagnitude, height: CGFloat.greatestFiniteMagnitude)
t.minSize = NSSize(width: 0, height: contentSize.height)
t.autoresizingMask = .width
t.isHorizontallyResizable = false
t.isVerticallyResizable = true
return t
}()
private lazy var sv: NSScrollView = {
let s = NSScrollView()
s.drawsBackground = true
s.borderType = .noBorder
s.hasVerticalScroller = true
s.hasHorizontalRuler = false
s.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
s.autoresizingMask = [.width, .height]
return s
}()
var text: String {
didSet {
tv.string = text
}
}
var selectedRanges: [NSValue] = [] {
didSet {
guard selectedRanges.count > 0 else {
return
}
tv.selectedRanges = selectedRanges
}
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("Error coder")
}
init(text: String) {
self.text = text
super.init(frame: .zero)
}
override func viewWillDraw() {
super.viewWillDraw()
sv.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
addSubview(sv)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
sv.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: topAnchor),
sv.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: trailingAnchor),
sv.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: bottomAnchor),
sv.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: leadingAnchor)
])
sv.documentView = tv
} // end viewWillDraw
}SwiftUI 中用 NSView,可以通过 NSViewRepresentable 来包装视图,这个协议主要是实现 makeNSView、updateNSView 和 makeCoordinator 三个方法。makeNSView 要求返回需要包装的 NSView。每当 SwiftUI 的状态变化时触发 updateNSView 方法的调用。为了实现 NSView 里的 delegate 和 SwiftUI 通信,就要用 makeCoordinator 返回一个用于处理 delegate 的实例。
TextField
使用方法如下:
struct PlayTextFieldView: View {
@State private var t = "Starming"
@State private var showT = ""
@State private var isEditing = false
var placeholder = "输入些文字..."
@FocusState private var isFocus: Bool
var body: some View {
VStack {
TextField(placeholder, text: $t)
// 样式设置
TextField(placeholder, text: $t)
.padding(10)
.textFieldStyle(.roundedBorder) // textFieldStyle 有三个预置值 automatic、plain 和 roundedBorder。
.multilineTextAlignment(.leading) // 对齐方式
.font(.system(size: 14, weight: .heavy, design: .rounded))
.border(.teal, width: 4)
.background(.white)
.foregroundColor(.brown)
.textCase(.uppercase)
// 多视图组合
HStack {
Image(systemName: "lock.circle")
.foregroundColor(.gray).font(.headline)
TextField(placeholder, text: $t)
.textFieldStyle(.plain)
.submitLabel(.done)
.onSubmit {
showT = t
isFocus = true
}
.onChange(of: t) { newValue in
t = String(newValue.prefix(20)) // 限制字数
}
Image(systemName: "eye.slash")
.foregroundColor(.gray)
.font(.headline)
}
.padding()
.overlay(
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 8)
.stroke(.gray, lineWidth: 1)
)
.padding(.horizontal)
Text(showT)
// 自定义 textFieldStyle 样式
TextField(placeholder, text: $t)
.textFieldStyle(PClearTextStyle())
.focused($isFocus)
}
.padding()
} // end body
}
struct PClearTextStyle: TextFieldStyle {
@ViewBuilder
func _body(configuration: TextField<_Label>) -> some View {
let mirror = Mirror(reflecting: configuration)
let bindingText: Binding<String> = mirror.descendant("_text") as! Binding<String>
configuration
.overlay(alignment: .trailing) {
Button(action: {
bindingText.wrappedValue = ""
}, label: {
Image(systemName: "clear")
})
}
let text: String = mirror.descendant("_text", "_value") as! String
configuration
.padding()
.background(
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 16)
.strokeBorder(text.count > 10 ? .pink : .gray, lineWidth: 4)
)
} // end func
}目前iOS 和 iPadOS上支持的键盘有:
- asciiCapable:能显示标准 ASCII 字符的键盘
- asciiCapableNumberPad:只输出 ASCII 数字的数字键盘
- numberPad:用于输入 PIN 码的数字键盘
- numbersAndPunctuation:数字和标点符号的键盘
- decimalPad:带有数字和小数点的键盘
- phonePad:电话中使用的键盘
- namePhonePad:用于输入人名或电话号码的小键盘
- URL:用于输入URL的键盘
- emailAddress:用于输入电子邮件地址的键盘
- twitter:用于Twitter文本输入的键盘,支持@和#字符简便输入
- webSearch:用于网络搜索词和URL输入的键盘
可以通过 keyboardType 修改器来指定。
支持多行,使用 Axis.vertical 以允许多行。TextField 超过行限制可以变成滚动视图。
今年 TextField 可以嵌到 .alert 里了。
Button

struct PlayButtonView: View {
var asyncAction: () async -> Void = {
do {
try await Task.sleep(nanoseconds: 300_000_000)
} catch {}
}
@State private var isFollowed: Bool = false
var body: some View {
VStack {
// 常用方式
Button {
print("Clicked")
} label: {
Image(systemName: "ladybug.fill")
Text("Report Bug")
}
// 图标
Button(systemIconName: "ladybug.fill") {
print("bug")
}
.buttonStyle(.plain) // 无背景
.simultaneousGesture(LongPressGesture().onEnded({ _ in
print("长按") // macOS 暂不支持
}))
.simultaneousGesture(TapGesture().onEnded({ _ in
print("短按") // macOS 暂不支持
}))
// iOS 15 修改器的使用。role 在 macOS 上暂不支持
Button("要删除了", role: .destructive) {
print("删除")
}
.tint(.purple)
.controlSize(.large) // .regular 是默认大小
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent) // borderedProminent 可显示 tint 的设置。还有 bordered、plain 和 borderless 可选。
.clipShape(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 5))
.accentColor(.pink)
.buttonBorderShape(.automatic) // 会依据 controlSize 调整边框样式
.background(.ultraThinMaterial, in: Capsule()) // 添加材质就像在视图和背景间加了个透明层达到模糊的效果。效果由高到底分别是.ultraThinMaterial、.thinMaterial、.regularMaterial、.thickMaterial、.ultraThickMaterial。
// 风格化
Button(action: {
//
}, label: {
Text("风格化").font(.largeTitle)
})
.buttonStyle(PStarmingButtonStyle())
// 自定义 Button
PCustomButton("点一下触发") {
print("Clicked!")
}
// 自定义 ButtonStyle
Button {
print("Double Clicked!")
} label: {
Text("点两下触发")
}
.buttonStyle(PCustomPrimitiveButtonStyle())
// 将 Text 视图加上另一个 Text 视图中,类型仍还是 Text。
PCustomButton(Text("点我 ").underline() + Text("别犹豫").font(.title) + Text("🤫悄悄说声,有惊喜").font(.footnote).foregroundColor(.secondary)) {
print("多 Text 组合标题按钮点击!")
}
// 异步按钮
ButtonAsync {
await asyncAction()
isFollowed = true
} label: {
if isFollowed == true {
Text("已关注")
} else {
Text("关注")
}
}
.font(.largeTitle)
.disabled(isFollowed)
.buttonStyle(PCustomButtonStyle(backgroundColor: isFollowed == true ? .gray : .pink))
}
.padding()
.background(Color.skeumorphismBG)
}
}
// MARK: - 异步操作的按钮
struct ButtonAsync<Label: View>: View {
var doAsync: () async -> Void
@ViewBuilder var label: () -> Label
@State private var isRunning = false // 避免连续点击造成重复执行事件
var body: some View {
Button {
isRunning = true
Task {
await doAsync()
isRunning = false
}
} label: {
label().opacity(isRunning == true ? 0 : 1)
if isRunning == true {
ProgressView()
}
}
.disabled(isRunning)
}
}
// MARK: - 扩展 Button
// 使用 SFSymbol 做图标
extension Button where Label == Image {
init(systemIconName: String, done: @escaping () -> Void) {
self.init(action: done) {
Image(systemName: systemIconName)
.renderingMode(.original)
}
}
}
// MARK: - 自定义 Button
struct PCustomButton: View {
let desTextView: Text
let act: () -> Void
init(_ des: LocalizedStringKey, act: @escaping () -> Void) {
self.desTextView = Text(des)
self.act = act
}
var body: some View {
Button {
act()
} label: {
desTextView.bold()
}
.buttonStyle(.starming)
}
}
extension PCustomButton {
init(_ desTextView: Text, act: @escaping () -> Void) {
self.desTextView = desTextView
self.act = act
}
}
// 点语法使用自定义样式
extension ButtonStyle where Self == PCustomButtonStyle {
static var starming: PCustomButtonStyle {
PCustomButtonStyle(cornerRadius: 15)
}
}
// MARK: - ButtonStyle
struct PCustomButtonStyle: ButtonStyle {
var cornerRadius:Double = 10
var backgroundColor: Color = .pink
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
HStack {
Spacer()
configuration.label
Spacer()
}
.padding()
.background(
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: cornerRadius, style: .continuous)
.fill(backgroundColor)
.shadow(color: configuration.isPressed ? .white : .black, radius: 1, x: 0, y: 1)
)
.opacity(configuration.isPressed ? 0.5 : 1)
.scaleEffect(configuration.isPressed ? 0.99 : 1)
}
}
// MARK: - PrimitiveButtonStyle
struct PCustomPrimitiveButtonStyle: PrimitiveButtonStyle {
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
// 双击触发
configuration.label
.onTapGesture(count: 2) {
configuration.trigger()
}
// 手势识别
Button(configuration)
.gesture(
LongPressGesture()
.onEnded({ _ in
configuration.trigger()
})
)
}
}
// MARK: - 风格化
struct PStarmingButtonStyle: ButtonStyle {
var backgroundColor = Color.skeumorphismBG
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
HStack {
Spacer()
configuration.label
Spacer()
}
.padding(20)
.background(
ZStack {
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10, style: .continuous)
.shadow(color: .white, radius: configuration.isPressed ? 7 : 10, x: configuration.isPressed ? -5 : -10, y: configuration.isPressed ? -5 : -10)
.shadow(color: .black, radius: configuration.isPressed ? 7 : 10, x: configuration.isPressed ? 5 : 10, y: configuration.isPressed ? 5 : 10)
.blendMode(.overlay)
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10, style: .continuous)
.fill(backgroundColor)
}
)
.scaleEffect(configuration.isPressed ? 0.98 : 1)
}
}
extension Color {
static let skeumorphismBG = Color(hex: "f0f0f3")
}
extension Color {
init(hex: String) {
var rgbValue: UInt64 = 0
Scanner(string: hex).scanHexInt64(&rgbValue)
let r = (rgbValue & 0xff0000) >> 16
let g = (rgbValue & 0xff00) >> 8
let b = rgbValue & 0xff
self.init(red: Double(r) / 0xff, green: Double(g) / 0xff, blue: Double(b) / 0xff)
}
}.buttonStyle 可组合,示例如下:
struct PButtonStyleComposition: View {
@State private var isT = false
var body: some View {
Section("标签") {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
HStack {
Toggle("Swift", isOn: $isT)
Toggle("SwiftUI", isOn: $isT)
}
HStack {
Toggle("Swift Chart", isOn: $isT)
Toggle("Navigation API", isOn: $isT)
}
}
.toggleStyle(.button)
.buttonStyle(.bordered)
}
}
}Tap Location 可以获取点击的位置,示例代码如下:
Rectangle()
.fill(.green)
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
.onTapGesture(coordinateSpace: .global) { location in
print("Tap in \(location)")
}其中 coordinateSpace 指定为 .global 表示位置是相对屏幕左上角,默认是相对当前视图的左上角的位置。
进度
用 ProgressViewStyle 协议,可以创建自定义的进度条视图。在 WatchOS 上会多一个 Guage 视图。
struct PlayProgressView: View {
@State private var v: CGFloat = 0.0
var body: some View {
VStack {
// 默认旋转
ProgressView()
// 有进度条
ProgressView(value: v / 100)
.tint(.yellow)
ProgressView(value: v / 100) {
Image(systemName: "music.note.tv")
}
.progressViewStyle(CircularProgressViewStyle(tint: .pink))
// 自定义样式
ProgressView(value: v / 100)
.padding(.vertical)
.progressViewStyle(PCProgressStyle1(borderWidth: 3))
ProgressView(value: v / 100)
.progressViewStyle(PCProgressStyle2())
.frame(height:200)
Slider(value: $v, in: 0...100, step: 1)
}
.padding(20)
}
}
// 自定义 Progress 样式
struct PCProgressStyle1: ProgressViewStyle {
var lg = LinearGradient(colors: [.purple, .black, .blue], startPoint: .topLeading, endPoint: .bottomTrailing)
var borderWidth: Double = 2
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
let fc = configuration.fractionCompleted ?? 0
return VStack {
ZStack(alignment: .topLeading) {
GeometryReader { g in
Rectangle()
.fill(lg)
.frame(maxWidth: g.size.width * CGFloat(fc))
}
}
.frame(height: 20)
.cornerRadius(10)
.overlay(
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10)
.stroke(lg, lineWidth: borderWidth)
)
// end ZStack
} // end VStack
}
}
struct PCProgressStyle2: ProgressViewStyle {
var lg = LinearGradient(colors: [.orange, .yellow, .green, .blue, .purple], startPoint: .topLeading, endPoint: .bottomTrailing)
var borderWidth: Double = 20
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
let fc = configuration.fractionCompleted ?? 0
func strokeStyle(_ g: GeometryProxy) -> StrokeStyle {
StrokeStyle(lineWidth: 0.1 * min(g.size.width, g.size.height), lineCap: .round)
}
return VStack {
GeometryReader { g in
ZStack {
Group {
Circle()
.trim(from: 0, to: 1)
.stroke(lg, style: strokeStyle(g))
.padding(borderWidth)
.opacity(0.2)
Circle()
.trim(from: 0, to: fc)
.stroke(lg, style: strokeStyle(g))
.padding(borderWidth)
}
.rotationEffect(.degrees(90 + 360 * 0.5), anchor: .center)
.offset(x: 0, y: 0.1 * min(g.size.width, g.size.height))
}
Text("读取 \(Int(fc * 100)) %")
.bold()
.font(.headline)
}
// end ZStack
} // end VStack
}
}SwiftUI 引入一个新显示进度的视图 Gauge。
简单示例如下:
struct PGauge: View {
@State private var progress = 0.45
var body: some View {
Gauge(value: progress) {
Text("进度")
} currentValueLabel: {
Text(progress.formatted(.percent))
} minimumValueLabel: {
Text(0.formatted(.percent))
} maximumValueLabel: {
Text(100.formatted(.percent))
}
Gauge(value: progress) {
} currentValueLabel: {
Text(progress.formatted(.percent))
.font(.footnote)
}
.gaugeStyle(.accessoryCircularCapacity)
.tint(.cyan)
}
}Image
struct PlayImageView: View {
var body: some View {
Image("logo")
.resizable()
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
Image("logo")
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
.clipShape(Circle())
.overlay(
Circle().stroke(.cyan, lineWidth: 4)
)
.shadow(radius: 10)
// SF Symbols
Image(systemName: "scissors")
.imageScale(.large)
.foregroundColor(.pink)
.frame(width: 40, height: 40)
// SF Symbols 多色时使用原色
Image(systemName: "thermometer.sun.fill")
.renderingMode(.original)
.imageScale(.large)
}
}ControlGroup
struct PlayControlGroupView: View {
var body: some View {
ControlGroup {
Button {
print("plus")
} label: {
Image(systemName: "plus")
}
Button {
print("minus")
} label: {
Image(systemName: "minus")
}
}
.padding()
.controlGroupStyle(.automatic) // .automatic 是默认样式,还有 .navigation
}
}GroupBox

struct PlayGroupBoxView: View {
var body: some View {
GroupBox {
Text("这是 GroupBox 的内容")
} label: {
Label("标题一", systemImage: "t.square.fill")
}
.padding()
GroupBox {
Text("还是 GroupBox 的内容")
} label: {
Label("标题二", systemImage: "t.square.fill")
}
.padding()
.groupBoxStyle(PCGroupBoxStyle())
}
}
struct PCGroupBoxStyle: GroupBoxStyle {
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
configuration.label
.font(.title)
configuration.content
}
.padding()
.background(.pink)
.clipShape(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 8, style: .continuous))
}
}Stack
Stack View 有 VStack、HStack 和 ZStack

struct PlayStackView: View {
var body: some View {
// 默认是 VStack 竖排
// 横排
HStack {
Text("左")
Spacer()
Text("右")
}
.padding()
// Z 轴排
ZStack(alignment: .top) {
Image("logo")
Text("戴铭的开发小册子")
.font(.title)
.bold()
.foregroundColor(.white)
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 1, x: 0, y: 2)
.padding()
}
Color.cyan
.cornerRadius(10)
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
.overlay(
Text("一段文字")
)
}
}Advanced layout control
session Compose custom layouts with SwiftUI
提供了新的 Grid 视图来同时满足 VStack 和 HStack。还有一个更低级别 Layout 接口,可以完全控制构建应用所需的布局。另外还有 ViewThatFits 可以自动选择填充可用空间的方式。
Grid 示例代码如下:
Grid {
GridRow {
Text("One")
Text("One")
Text("One")
}
GridRow {
Text("Two")
Text("Two")
}
Divider()
GridRow {
Text("Three")
Text("Three")
.gridCellColumns(2)
}
}gridCellColumns() modifier 可以让一个单元格跨多列。
ViewThatFits 的新视图,允许根据适合的大小放视图。ViewThatFits 会自动选择对于当前屏幕大小合适的子视图进行显示。Ryan Lintott 的示例效果 ,对应示例代码 LayoutThatFits.swift 。
新的 Layout 协议可以观看 Swift Talk 第 308 期 The Layout Protocol 。
通过符合 Layout 协议,我们可以自定义一个自定义的布局容器,直接参与 SwiftUI 的布局过程。新的 ProposedViewSize 结构,它是容器视图提供的大小。 Layout.Subviews 是布局视图的子视图代理集合,我们可以在其中为每个子视图请求各种布局属性。
public protocol Layout: Animatable {
static var layoutProperties: LayoutProperties { get }
associatedtype Cache = Void
typealias Subviews = LayoutSubviews
func updateCache(_ cache: inout Self.Cache, subviews: Self.Subviews)
func spacing(subviews: Self.Subviews, cache: inout Self.Cache) -> ViewSpacing
/// We return our view size here, use the passed parameters for computing the
/// layout.
func sizeThatFits(
proposal: ProposedViewSize,
subviews: Self.Subviews,
cache: inout Self.Cache // 👈🏻 use this for calculated data shared among Layout methods
) -> CGSize
/// Use this to tell your subviews where to appear.
func placeSubviews(
in bounds: CGRect, // 👈🏻 region where we need to place our subviews into, origin might not be .zero
proposal: ProposedViewSize,
subviews: Self.Subviews,
cache: inout Self.Cache
)
// ... there are more a couple more optional methods
}下面例子是一个自定义的水平 stack 视图,为其所有子视图提供其最大子视图的宽度:
struct MyEqualWidthHStack: Layout {
/// Returns a size that the layout container needs to arrange its subviews.
/// - Tag: sizeThatFitsHorizontal
func sizeThatFits(
proposal: ProposedViewSize,
subviews: Subviews,
cache: inout Void
) -> CGSize {
guard !subviews.isEmpty else { return .zero }
let maxSize = maxSize(subviews: subviews)
let spacing = spacing(subviews: subviews)
let totalSpacing = spacing.reduce(0) { $0 + $1 }
return CGSize(
width: maxSize.width * CGFloat(subviews.count) + totalSpacing,
height: maxSize.height)
}
/// Places the stack's subviews.
/// - Tag: placeSubviewsHorizontal
func placeSubviews(
in bounds: CGRect,
proposal: ProposedViewSize,
subviews: Subviews,
cache: inout Void
) {
guard !subviews.isEmpty else { return }
let maxSize = maxSize(subviews: subviews)
let spacing = spacing(subviews: subviews)
let placementProposal = ProposedViewSize(width: maxSize.width, height: maxSize.height)
var nextX = bounds.minX + maxSize.width / 2
for index in subviews.indices {
subviews[index].place(
at: CGPoint(x: nextX, y: bounds.midY),
anchor: .center,
proposal: placementProposal)
nextX += maxSize.width + spacing[index]
}
}
/// Finds the largest ideal size of the subviews.
private func maxSize(subviews: Subviews) -> CGSize {
let subviewSizes = subviews.map { $0.sizeThatFits(.unspecified) }
let maxSize: CGSize = subviewSizes.reduce(.zero) { currentMax, subviewSize in
CGSize(
width: max(currentMax.width, subviewSize.width),
height: max(currentMax.height, subviewSize.height))
}
return maxSize
}
/// Gets an array of preferred spacing sizes between subviews in the
/// horizontal dimension.
private func spacing(subviews: Subviews) -> [CGFloat] {
subviews.indices.map { index in
guard index < subviews.count - 1 else { return 0 }
return subviews[index].spacing.distance(
to: subviews[index + 1].spacing,
along: .horizontal)
}
}
}自定义 layout 只能访问子视图代理 Layout.Subviews ,而不是视图或数据模型。我们可以通过 LayoutValueKey 在每个子视图上存储自定义值,通过 layoutValue(key:value:) modifier 设置。
private struct Rank: LayoutValueKey {
static let defaultValue: Int = 1
}
extension View {
func rank(_ value: Int) -> some View { // 👈🏻 convenience method
layoutValue(key: Rank.self, value: value) // 👈🏻 the new modifier
}
}然后,我们就可以通过 Layout 方法中的 Layout.Subviews 代理读取自定义 LayoutValueKey 值:
func placeSubviews(
in bounds: CGRect,
proposal: ProposedViewSize,
subviews: Subviews,
cache: inout Void
) {
let ranks = subviews.map { subview in
subview[Rank.self] // 👈🏻
}
// ...
}要在布局之间变化使用动画,需要用 AnyLayout,代码示例如下:
struct PAnyLayout: View {
@State private var isVertical = false
var body: some View {
let layout = isVertical ? AnyLayout(VStack()) : AnyLayout(HStack())
layout {
Image(systemName: "star").foregroundColor(.yellow)
Text("Starming.com")
Text("戴铭")
}
Button("Click") {
withAnimation {
isVertical.toggle()
}
} // end button
} // end body
}同时 Text 和图片也支持了样式布局变化,代码示例如下:
struct PTextTransitionsView: View {
@State private var expandMessage = true
private let mintWithShadow: AnyShapeStyle = AnyShapeStyle(Color.mint.shadow(.drop(radius: 2)))
private let primaryWithoutShadow: AnyShapeStyle = AnyShapeStyle(Color.primary.shadow(.drop(radius: 0)))
var body: some View {
Text("Dai Ming Swift Pamphlet")
.font(expandMessage ? .largeTitle.weight(.heavy) : .body)
.foregroundStyle(expandMessage ? mintWithShadow : primaryWithoutShadow)
.onTapGesture { withAnimation { expandMessage.toggle() }}
.frame(maxWidth: expandMessage ? 150 : 250)
.drawingGroup()
.padding(20)
.background(.cyan.opacity(0.3), in: RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 6))
}
}Navigation
控制导航启动状态、管理 size class 之间的 transition 和响应 deep link。
Navigation bar 有新的默认行为,如果没有提供标题,导航栏默认为 inline title 显示模式。使用 navigationBarTitleDisplayMode(_:) 改变显示模式。如果 navigation bar 没有标题、工具栏项或搜索内容,它就会自动隐藏。使用 .toolbar(.visible) modifier 显示一个空 navigation bar。
参考:
- Migrating to New Navigation Types 官方迁移指南
- NavigationStack
- NavigationSplitView
- The SwiftUI cookbook for navigation
NavigationStack 的示例:
struct PNavigationStack: View {
@State private var a = [1, 3, 9] // 深层链接
var body: some View {
NavigationStack(path: $a) {
List(1..<10) { i in
NavigationLink(value: i) {
Label("第 \(i) 行", systemImage: "\(i).circle")
}
}
.navigationDestination(for: Int.self) { i in
Text("第 \(i) 行内容")
}
.navigationTitle("NavigationStack Demo")
}
}
}这里的 path 设置了 stack 的深度路径。
NavigationSplitView 两栏的例子:
struct PNavigationSplitViewTwoColumn: View {
@State private var a = ["one", "two", "three"]
@State private var choice: String?
var body: some View {
NavigationSplitView {
List(a, id: \.self, selection: $choice, rowContent: Text.init)
} detail: {
Text(choice ?? "选一个")
}
}
}NavigationSplitView 三栏的例子:
struct PNavigationSplitViewThreeColumn: View {
struct Group: Identifiable, Hashable {
let id = UUID()
var title: String
var subs: [String]
}
@State private var gps = [
Group(title: "One", subs: ["o1", "o2", "o3"]),
Group(title: "Two", subs: ["t1", "t2", "t3"])
]
@State private var choiceGroup: Group?
@State private var choiceSub: String?
@State private var cv = NavigationSplitViewVisibility.automatic
var body: some View {
NavigationSplitView(columnVisibility: $cv) {
List(gps, selection: $choiceGroup) { g in
Text(g.title).tag(g)
}
.navigationSplitViewColumnWidth(250)
} content: {
List(choiceGroup?.subs ?? [], id: \.self, selection: $choiceSub) { s in
Text(s)
}
} detail: {
Text(choiceSub ?? "选一个")
Button("点击") {
cv = .all
}
}
.navigationSplitViewStyle(.prominentDetail)
}
}navigationSplitViewColumnWidth() 是用来自定义宽的,navigationSplitViewStyle 设置为 .prominentDetail 是让 detail 的视图尽量保持其大小。
SwiftUI 新加了个功能可以配置是否隐藏 Tabbar,这样在从主页进入下一级时就可以选择不显示底部标签栏了,示例代码如下:
ContentView().toolbar(.hidden, in: .tabBar)相比较以前 NavigationView 增强的是 destination 可以根据值的不同类型展示不同的目的页面,示例代码如下:
struct PNavigationStackDestination: View {
var body: some View {
NavigationStack {
List {
NavigationLink(value: "字符串") {
Text("字符串")
}
NavigationLink(value: Color.red) {
Text("红色")
}
}
.navigationTitle("不同类型 Destination")
.navigationDestination(for: Color.self) { c in
c.clipShape(Circle())
}
.navigationDestination(for: String.self) { s in
Text("\(s) 的 detail")
}
}
}
}对 toolbar 的自定义,示例如下:
.toolbar(id: "toolbar") {
ToolbarItem(id: "new", placement: .secondaryAction) {
Button(action: {}) {
Label("New Invitation", systemImage: "envelope")
}
}
}
.toolbarRole(.editor)以下是废弃的 NavigationView 的用法。

对应代码如下:
struct PlayNavigationView: View {
let lData = 1...10
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
ZStack {
LinearGradient(colors: [.pink, .orange], startPoint: .topLeading, endPoint: .bottomTrailing)
.ignoresSafeArea()
List(lData, id: \.self) { i in
NavigationLink {
PNavDetailView(contentStr: "\(i)")
} label: {
Text("\(i)")
}
}
}
ZStack {
LinearGradient(colors: [.mint, .yellow], startPoint: .topLeading, endPoint: .bottomTrailing)
.ignoresSafeArea()
VStack {
Text("一个 NavigationView 的示例")
.bold()
.font(.largeTitle)
.shadow(color: .white, radius: 9, x: 0, y: 0)
.scaleEffect(2)
}
}
.safeAreaInset(edge: .bottom) {
HStack {
Button("bottom1") {}
.font(.headline)
Button("bottom2") {}
Button("bottom3") {}
Spacer()
}
.padding(5)
.background(LinearGradient(colors: [.purple, .blue], startPoint: .topLeading, endPoint: .bottomTrailing))
}
}
.foregroundColor(.white)
.navigationTitle("数字列表")
.toolbar {
// placement 共有 keyboard、destructiveAction、cancellationAction、confirmationAction、status、primaryAction、navigation、principal、automatic 这些
ToolbarItem(placement: .primaryAction) {
Button("primaryAction") {}
.background(.ultraThinMaterial)
.font(.headline)
}
// 通过 ToolbarItemGroup 可以简化相同位置 ToolbarItem 的编写。
ToolbarItemGroup(placement: .navigation) {
Button("返回") {}
Button("前进") {}
}
PCToolbar(doDestruct: {
print("删除了")
}, doCancel: {
print("取消了")
}, doConfirm: {
print("确认了")
})
ToolbarItem(placement: .status) {
Button("status") {}
}
ToolbarItem(placement: .principal) {
Button("principal") {
}
}
ToolbarItem(placement: .keyboard) {
Button("Touch Bar Button") {}
}
} // end toolbar
}
}
// MARK: - NavigationView 的目的页面
struct PNavDetailView: View {
@Environment(\.presentationMode) var pMode: Binding<PresentationMode>
var contentStr: String
var body: some View {
ZStack {
LinearGradient(colors: [.purple, .blue], startPoint: .topLeading, endPoint: .bottomTrailing)
.ignoresSafeArea()
VStack {
Text(contentStr)
Button("返回") {
pMode.wrappedValue.dismiss()
}
}
} // end ZStack
} // end body
}
// MARK: - 自定义 toolbar
// 通过 ToolbarContent 创建可重复使用的 toolbar 组
struct PCToolbar: ToolbarContent {
let doDestruct: () -> Void
let doCancel: () -> Void
let doConfirm: () -> Void
var body: some ToolbarContent {
ToolbarItem(placement: .destructiveAction) {
Button("删除", action: doDestruct)
}
ToolbarItem(placement: .cancellationAction) {
Button("取消", action: doCancel)
}
ToolbarItem(placement: .confirmationAction) {
Button("确定", action: doConfirm)
}
}
}toolbar 的位置设置可选项如下:
- primaryAction:放置到最主要位置,macOS 就是放在 toolbar 的最左边
- automatic:根据平台不同放到默认位置
- confirmationAction:一些确定的动作
- cancellationAction:取消动作
- destructiveAction:删除的动作
- status:状态变化,比如检查更新等动作
- navigation:导航动作,比如浏览器的前进后退
- principal:突出的位置,iOS 和 macOS 会出现在中间的位置
- keyboard:macOS 会出现在 Touch Bar 里。iOS 会出现在弹出的虚拟键盘上。
List

List 除了能够展示数据外,还有下拉刷新、过滤搜索和侧滑 Swipe 动作提供更多 Cell 操作的能力。
通过 List 的可选子项参数提供数据模型的关键路径来制定子项路劲,还可以实现大纲视图,使用 DisclosureGroup 和 OutlineGroup 可以进一步定制大纲视图。
下面是 List 使用,包括了 DisclosureGroup 和 OutlineGroup 的演示代码:
struct PlayListView: View {
@StateObject var l: PLVM = PLVM()
@State private var s: String = ""
var outlineModel = [
POutlineModel(title: "文件夹一", iconName: "folder.fill", children: [
POutlineModel(title: "个人", iconName: "person.crop.circle.fill"),
POutlineModel(title: "群组", iconName: "person.2.circle.fill"),
POutlineModel(title: "加好友", iconName: "person.badge.plus")
]),
POutlineModel(title: "文件夹二", iconName: "folder.fill", children: [
POutlineModel(title: "晴天", iconName: "sun.max.fill"),
POutlineModel(title: "夜间", iconName: "moon.fill"),
POutlineModel(title: "雨天", iconName: "cloud.rain.fill", children: [
POutlineModel(title: "雷加雨", iconName: "cloud.bolt.rain.fill"),
POutlineModel(title: "太阳雨", iconName: "cloud.sun.rain.fill")
])
]),
POutlineModel(title: "文件夹三", iconName: "folder.fill", children: [
POutlineModel(title: "电话", iconName: "phone"),
POutlineModel(title: "拍照", iconName: "camera.circle.fill"),
POutlineModel(title: "提醒", iconName: "bell")
])
]
var body: some View {
HStack {
// List 通过$语法可以将集合的元素转换成可绑定的值
List {
ForEach($l.ls) { $d in
PRowView(s: d.s, i: d.i)
.listRowInsets(EdgeInsets(top: 5, leading: 15, bottom: 5, trailing: 15))
.listRowBackground(Color.black.opacity(0.2))
}
}
.refreshable {
// 下拉刷新
}
.searchable(text: $s) // 搜索
.onChange(of: s) { newValue in
print("搜索关键字:\(s)")
}
Divider()
// 自定义 List
VStack {
PCustomListView($l.ls) { $d in
PRowView(s: d.s, i: d.i)
}
// 添加数据
Button {
l.ls.append(PLModel(s: "More", i: 0))
} label: {
Text("添加")
}
}
.padding()
Divider()
// 使用大纲
List(outlineModel, children: \.children) { i in
Label(i.title, systemImage: i.iconName)
}
Divider()
// 自定义大纲视图
VStack {
Text("可点击标题展开")
.font(.headline)
PCOutlineListView(d: outlineModel, c: \.children) { i in
Label(i.title, systemImage: i.iconName)
}
}
.padding()
Divider()
// 使用 OutlineGroup 实现大纲视图
VStack {
Text("OutlineGroup 实现大纲")
OutlineGroup(outlineModel, children: \.children) { i in
Label(i.title, systemImage: i.iconName)
}
// OutlineGroup 和 List 结合
Text("OutlineGroup 和 List 结合")
List {
ForEach(outlineModel) { s in
Section {
OutlineGroup(s.children ?? [], children: \.children) { i in
Label(i.title, systemImage: i.iconName)
}
} header: {
Label(s.title, systemImage: s.iconName)
}
} // end ForEach
} // end List
} // end VStack
} // end HStack
} // end body
}
// MARK: - 自定义大纲视图
struct PCOutlineListView<D, Content>: View where D: RandomAccessCollection, D.Element: Identifiable, Content: View {
private let v: PCOutlineView<D, Content>
init(d: D, c: KeyPath<D.Element, D?>, content: @escaping (D.Element) -> Content) {
self.v = PCOutlineView(d: d, c: c, content: content)
}
var body: some View {
List {
v
}
}
}
struct PCOutlineView<D, Content>: View where D: RandomAccessCollection, D.Element: Identifiable, Content: View {
let d: D
let c: KeyPath<D.Element, D?>
let content: (D.Element) -> Content
@State var isExpanded = true // 控制初始是否展开的状态
var body: some View {
ForEach(d) { i in
if let sub = i[keyPath: c] {
PCDisclosureGroup(content: PCOutlineView(d: sub, c: c, content: content), label: content(i))
} else {
content(i)
} // end if
} // end ForEach
} // end body
}
struct PCDisclosureGroup<C, L>: View where C: View, L: View {
@State var isExpanded = false
var content: C
var label: L
var body: some View {
DisclosureGroup(isExpanded: $isExpanded) {
content
} label: {
Button {
isExpanded.toggle()
} label: {
label
}
.buttonStyle(.plain)
}
}
}
// MARK: - 大纲模式数据模型
struct POutlineModel: Hashable, Identifiable {
var id = UUID()
var title: String
var iconName: String
var children: [POutlineModel]?
}
// MARK: - List 的抽象,数据兼容任何集合类型
struct PCustomListView<D: RandomAccessCollection & MutableCollection & RangeReplaceableCollection, Content: View>: View where D.Element: Identifiable {
@Binding var data: D
var content: (Binding<D.Element>) -> Content
init(_ data: Binding<D>, content: @escaping (Binding<D.Element>) -> Content) {
self._data = data
self.content = content
}
var body: some View {
List {
Section {
ForEach($data, content: content)
.onMove { indexSet, offset in
data.move(fromOffsets: indexSet, toOffset: offset)
}
.onDelete { indexSet in
data.remove(atOffsets: indexSet) // macOS 暂不支持
}
} header: {
Text("第一栏,共 \(data.count) 项")
} footer: {
Text("The End")
}
}
.listStyle(.plain) // 有.automatic、.inset、.plain、sidebar,macOS 暂不支持的有.grouped 和 .insetGrouped
}
}
// MARK: - Cell 视图
struct PRowView: View {
var s: String
var i: Int
var body: some View {
HStack {
Text("\(i):")
Text(s)
}
}
}
// MARK: - 数据模型设计
struct PLModel: Hashable, Identifiable {
let id = UUID()
var s: String
var i: Int
}
final class PLVM: ObservableObject {
@Published var ls: [PLModel]
init() {
ls = [PLModel]()
for i in 0...20 {
ls.append(PLModel(s: "\(i)", i: i))
}
}
}list 支持 Section footer。
list 分隔符可以自定义,使用 HorizontalEdge.leading 和 HorizontalEdge.trailing 。
list 不使用 UITableView 了。
今年 list 还新增了一个 EditOperation 可以自动生成移动和删除,新增了 edits 参数,传入 [.delete, .move] 数组即可。这也是一个演示如何更好扩展和配置功能的方式。
.searchable 支持 token 和 scope,示例如下:
struct PSearchTokensAndScopes: View {
enum AttendanceScope {
case inPerson, online
}
@State private var queryText: String
@State private var queryTokens: [InvitationToken]
@State private var scope: AttendanceScope
var body: some View {
invitationCountView()
.searchable(text: $queryText, tokens: $queryTokens, scope: $scope) { token in
Label(token.diplayName, systemImage: token.systemImage)
} scopes: {
Text("In Person").tag(AttendanceScope.inPerson)
Text("Online").tag(AttendanceScope.online)
}
}
}LazyVStack 和 LazyHStack
LazyVStack 和 LazyHStack 里的视图只有在滚到时才会被创建。
struct PlayLazyVStackAndLazyHStackView: View {
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
LazyVStack {
ForEach(1...300, id: \.self) { i in
PLHSRowView(i: i)
}
}
}
}
}
struct PLHSRowView: View {
let i: Int
var body: some View {
Text("第 \(i) 个")
}
init(i: Int) {
print("第 \(i) 个初始化了") // 用来查看什么时候创建的。
self.i = i
}
}LazyVGrid 和 LazyHGrid

列的设置有三种,这三种也可以组合用。
- GridItem(.fixed(10)) 会固定设置有多少列。
- GridItem(.flexible()) 会充满没有使用的空间。
- GridItem(.adaptive(minimum: 10)) 表示会根据设置大小自动设置有多少列展示。
示例:
struct PlayLazyVGridAndLazyHGridView: View {
@State private var colors: [String:Color] = [
"red" : .red,
"orange" : .orange,
"yellow" : .yellow,
"green" : .green,
"mint" : .mint,
"teal" : .teal,
"cyan" : .cyan,
"blue" : .blue,
"indigo" : .indigo,
"purple" : .purple,
"pink" : .pink,
"brown" : .brown,
"gray" : .gray,
"black" : .black
]
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
LazyVGrid(columns: [
GridItem(.adaptive(minimum: 50), spacing: 10)
], pinnedViews: [.sectionHeaders]) {
Section(header:
Text("🎨调色板")
.font(.title)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity)
.background(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 0)
.fill(.black.opacity(0.1)))
) {
ForEach(Array(colors.keys), id: \.self) { k in
colors[k].frame(height:Double(Int.random(in: 50...150)))
.overlay(
Text(k)
)
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 2, x: 0, y: 2)
}
}
}
.padding()
LazyVGrid(columns: [
GridItem(.adaptive(minimum: 20), spacing: 10)
]) {
Section(header: Text("图标集").font(.title)) {
ForEach(1...30, id: \.self) { i in
Image("p\(i)")
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 2, x: 0, y: 2)
}
}
}
.padding()
}
}
}table
今年 iOS 和 iPadOS 也可以使用去年只能在 macOS 上使用的 Table了,据 digital lounges 里说,iOS table 的性能和 list 差不多,table 默认为 plian list。我想 iOS 上加上 table 只是为了兼容 macOS 代码吧。
table 使用示例如下:
Table(attendeeStore.attendees) {
TableColumn("Name") { attendee in
AttendeeRow(attendee)
}
TableColumn("City", value: \.city)
TableColumn("Status") { attendee in
StatusRow(attendee)
}
}
.contextMenu(forSelectionType: Attendee.ID.self) { selection in
if selection.isEmpty {
Button("New Invitation") { addInvitation() }
} else if selection.count == 1 {
Button("Mark as VIP") { markVIPs(selection) }
} else {
Button("Mark as VIPs") { markVIPs(selection) }
}
}ScrollView
ScrollView 使用 scrollTo 可以直接滚动到指定的位置。ScrollView 还可以透出偏移量,利用偏移量可以定义自己的动态视图,比如向下向上滚动视图时有不同效果,到顶部显示标题视图等。
示例代码如下:
struct PlayScrollView: View {
@State private var scrollOffset: CGFloat = .zero
var infoView: some View {
GeometryReader { g in
Text("移动了 \(Double(scrollOffset).formatted(.number.precision(.fractionLength(1)).rounded()))")
.padding()
}
}
var body: some View {
// 标准用法
ScrollViewReader { s in
ScrollView {
ForEach(0..<300) { i in
Text("\(i)")
.id(i)
}
}
Button("跳到150") {
withAnimation {
s.scrollTo(150, anchor: .top)
}
} // end Button
} // end ScrollViewReader
// 自定义的 ScrollView 透出 offset 供使用
ZStack {
PCScrollView {
ForEach(0..<100) { i in
Text("\(i)")
}
} whenMoved: { d in
scrollOffset = d
}
infoView
} // end ZStack
} // end body
}
// MARK: - 自定义 ScrollView
struct PCScrollView<C: View>: View {
let c: () -> C
let whenMoved: (CGFloat) -> Void
init(@ViewBuilder c: @escaping () -> C, whenMoved: @escaping (CGFloat) -> Void) {
self.c = c
self.whenMoved = whenMoved
}
var offsetReader: some View {
GeometryReader { g in
Color.clear
.preference(key: OffsetPreferenceKey.self, value: g.frame(in: .named("frameLayer")).minY)
}
.frame(height:0)
}
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
offsetReader
c()
.padding(.top, -8)
}
.coordinateSpace(name: "frameLayer")
.onPreferenceChange(OffsetPreferenceKey.self, perform: whenMoved)
} // end body
}
private struct OffsetPreferenceKey: PreferenceKey {
static var defaultValue: CGFloat = .zero
static func reduce(value: inout CGFloat, nextValue: () -> CGFloat) {}
}新增 modifier
ScrollView {
ForEach(0..<300) { i in
Text("\(i)")
.id(i)
}
}
.scrollDisabled(false)
.scrollDismissesKeyboard(.interactively)
.scrollIndicators(.visible)浮层

浮层有 HUD、ContextMenu、Sheet、Alert、ConfirmationDialog、Popover、ActionSheet 等几种方式。这些方式实现代码如下:
struct PlaySuperposedLayerView: View {
@StateObject var hudVM = PHUDVM()
@State private var isShow = false
@State private var isShowAlert = false
@State private var isShowConfirmationDialog = false
@State private var isShowPopover = false
var body: some View {
VStack {
List {
ForEach(0..<100) { i in
Text("\(i)")
.contextMenu {
// 在 macOS 上右键会出现的菜单
Button {
print("\(i) is clicked")
} label: {
Text("Click \(i)")
}
}
}
}
.navigationTitle("列表")
.toolbar {
ToolbarItemGroup(placement: .automatic) {
Button("查看 Sheet") {
isShow = true
}
Button("查看 Alert") {
isShowAlert = true
}
Button("查看 confirmationDialog", role: .destructive) {
isShowConfirmationDialog = true
}
// Popover 样式默认是弹出窗口置于按钮上方,指向底部。
Button("查看 Popover") {
isShowPopover = true
}
.popover(isPresented: $isShowPopover, attachmentAnchor: .point(.trailing), arrowEdge: .trailing) {
Text("Popover 的内容")
.padding()
}
} // end ToolbarItemGroup
} // end toolbar
.alert(isPresented: $isShowAlert) {
Alert(title: Text("弹框标题"), message: Text("弹框内容"))
}
.sheet(isPresented: $isShow) {
print("dismiss")
} content: {
VStack {
Label("Sheet", systemImage: "brain.head.profile")
Button("关闭") {
isShow = false
}
}
.padding(20)
}
.confirmationDialog("确定删除?", isPresented: $isShowConfirmationDialog, titleVisibility: .hidden) {
Button("确定") {
// do good thing
}
.keyboardShortcut(.defaultAction) // 使用 keyboardShortcut 可以设置成为默认选项样式
Button("不不", role: .cancel) {
// good choice
}
} message: {
Text("这个东西还有点重要哦")
}
Button {
hudVM.show(title: "您有一条新的短消息", systemImage: "ellipsis.bubble")
} label: {
Label("查看 HUD", systemImage: "switch.2")
}
.padding()
}
.environmentObject(hudVM)
.hud(isShow: $hudVM.isShow) {
Label(hudVM.title, systemImage: hudVM.systemImage)
}
}
}
// MARK: - 供全局使用的 HUD
final class PHUDVM: ObservableObject {
@Published var isShow: Bool = false
var title: String = ""
var systemImage: String = ""
func show(title: String, systemImage: String) {
self.title = title
self.systemImage = systemImage
withAnimation {
isShow = true
}
}
}
// MARK: - 扩展 View 使其能够有 HUD 的能力
extension View {
func hud<V: View>(
isShow: Binding<Bool>,
@ViewBuilder v: () -> V
) -> some View {
ZStack(alignment: .top) {
self
if isShow.wrappedValue == true {
PHUD(v: v)
.transition(AnyTransition.move(edge: .top).combined(with: .opacity))
.onAppear {
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 2) {
withAnimation {
isShow.wrappedValue = false
}
}
}
.zIndex(1)
.padding()
}
}
}
}
// MARK: - 自定义 HUD
struct PHUD<V: View>: View {
@ViewBuilder let v: V
var body: some View {
v
.padding()
.foregroundColor(.black)
.background(
Capsule()
.foregroundColor(.white)
.shadow(color: .black.opacity(0.2), radius: 12, x: 0, y: 5)
)
}
}SwiftUI 新推出的 presentationDetents() modifier 可以创建一个可以定制的 bottom sheet。示例代码如下:
struct PSheet: View {
@State private var isShow = false
var body: some View {
Button("显示 Sheet") {
isShow.toggle()
}
.sheet(isPresented: $isShow) {
Text("这里是 Sheet 的内容")
.presentationDetents([.medium, .large])
}
}
}detent 默认值是 .large。也可以提供一个百分比,比如 .presentationDetents([.fraction(0.7)]),或者直接指定高度 .presentationDetents([.height(100)])。
presentationDragIndicator modifier 可以用来显示隐藏拖动标识。
TabView
struct PlayTabView: View {
@State private var selection = 0
var body: some View {
ZStack(alignment: .bottom) {
TabView(selection: $selection) {
Text("one")
.tabItem {
Text("首页")
.hidden()
}
.tag(0)
Text("two")
.tabItem {
Text("二栏")
}
.tag(1)
Text("three")
.tabItem {
Text("三栏")
}
.tag(2)
Text("four")
.tag(3)
Text("five")
.tag(4)
Text("six")
.tag(5)
Text("seven")
.tag(6)
Text("eight")
.tag(7)
Text("nine")
.tag(8)
Text("ten")
.tag(9)
} // end TabView
HStack {
Button("上一页") {
if selection > 0 {
selection -= 1
}
}
.keyboardShortcut(.cancelAction)
Button("下一页") {
if selection < 9 {
selection += 1
}
}
.keyboardShortcut(.defaultAction)
} // end HStack
.padding()
}
}
}.tabViewStyle(PageTabViewStyle(indexDisplayMode: .never)) 可以实现 UIPageViewController 的效果,如果要给小白点加上背景,可以多添加一个 .indexViewStyle(PageIndexViewStyle(backgroundDisplayMode: .always)) 修改器。
Swift Charts
可视化数据,使用 SwiftUI 语法来创建。还可以使用 ChartRenderer 接口将图标渲染成图。
官方文档 Swift Charts
入门参看 Hello Swift Charts
Apple 文章 Creating a chart using Swift Charts
高级定制和创建更精细图表,可以看这个 session Swift Charts: Raise the bar 这个 session 也会提到如何在图表中进行交互。这里是 session 对应的代码示例 Visualizing your app’s data 。
图表设计的 session,Design an effective chart 和 Design app experiences with charts 。
下面是一个简单的代码示例:
import Charts
struct PChartModel: Hashable {
var day: String
var amount: Int = .random(in: 1..<100)
}
extension PChartModel {
static var data: [PChartModel] {
let calendar = Calendar(identifier: .gregorian)
let days = calendar.shortWeekdaySymbols
return days.map { day in
PChartModel(day: day)
}
}
}
struct PlayCharts: View {
var body: some View {
Chart(PChartModel.data, id: \.self) { v in
BarMark(x: .value("天", v.day), y: .value("数量", v.amount))
}
.padding()
}
}
struct PSwiftCharts: View {
struct CData: Identifiable {
let id = UUID()
let i: Int
let v: Double
}
@State private var a: [CData] = [
.init(i: 0, v: 2),
.init(i: 1, v: 20),
.init(i: 2, v: 3),
.init(i: 3, v: 30),
.init(i: 4, v: 8),
.init(i: 5, v: 80)
]
var body: some View {
Chart(a) { i in
LineMark(x: .value("Index", i.i), y: .value("Value", i.v))
BarMark(x: .value("Index", i.i), yStart: .value("开始", 0), yEnd: .value("结束", i.v))
.foregroundStyle(by: .value("Value", i.v))
} // end Chart
} // end body
}BarMark 用于创建条形图,LineMark 用于创建折线图。SwiftUI Charts 框架还提供 PointMark、AxisMarks、AreaMark、RectangularMark 和 RuleMark 用于创建不同类型的图表。注释使用 .annotation modifier,修改颜色可以使用 .foregroundStyle modifier。.lineStyle modifier 可以修改线宽。
AxisMarks 的示例如下:
struct MonthlySalesChart: View {
var body: some View {
Chart(data, id: \.month) {
BarMark(
x: .value("Month", $0.month, unit: .month),
y: .value("Sales", $0.sales)
)
}
.chartXAxis {
AxisMarks(values: .stride(by: .month)) { value in
if value.as(Date.self)!.isFirstMonthOfQuarter {
AxisGridLine().foregroundStyle(.black)
AxisTick().foregroundStyle(.black)
AxisValueLabel(
format: .dateTime.month(.narrow)
)
} else {
AxisGridLine()
}
}
}
}
}可交互图表示例如下:
struct InteractiveBrushingChart: View {
@State var range: (Date, Date)? = nil
var body: some View {
Chart {
ForEach(data, id: \.day) {
LineMark(
x: .value("Month", $0.day, unit: .day),
y: .value("Sales", $0.sales)
)
.interpolationMethod(.catmullRom)
.symbol(Circle().strokeBorder(lineWidth: 2))
}
if let (start, end) = range {
RectangleMark(
xStart: .value("Selection Start", start),
xEnd: .value("Selection End", end)
)
.foregroundStyle(.gray.opacity(0.2))
}
}
.chartOverlay { proxy in
GeometryReader { nthGeoItem in
Rectangle().fill(.clear).contentShape(Rectangle())
.gesture(DragGesture()
.onChanged { value in
// Find the x-coordinates in the chart’s plot area.
let xStart = value.startLocation.x - nthGeoItem[proxy.plotAreaFrame].origin.x
let xCurrent = value.location.x - nthGeoItem[proxy.plotAreaFrame].origin.x
// Find the date values at the x-coordinates.
if let dateStart: Date = proxy.value(atX: xStart),
let dateCurrent: Date = proxy.value(atX: xCurrent) {
range = (dateStart, dateCurrent)
}
}
.onEnded { _ in range = nil } // Clear the state on gesture end.
)
}
}
}
}社区做的更多 Swift Charts 范例 Swift Charts Examples 。
Toggle

Toggle 可以设置 toggleStyle,可以自定义样式。使用示例如下
struct PlayToggleView: View {
@State private var isEnable = false
var body: some View {
// 普通样式
Toggle(isOn: $isEnable) {
Text("\(isEnable ? "开了" : "关了")")
}
.padding()
// 按钮样式
Toggle(isOn: $isEnable) {
Label("\(isEnable ? "打开了" : "关闭了")", systemImage: "cloud.moon")
}
.padding()
.tint(.pink)
.controlSize(.large)
.toggleStyle(.button)
// Switch 样式
Toggle(isOn: $isEnable) {
Text("\(isEnable ? "开了" : "关了")")
}
.toggleStyle(SwitchToggleStyle(tint: .orange))
.padding()
// 自定义样式
Toggle(isOn: $isEnable) {
Text(isEnable ? "录音中" : "已静音")
}
.toggleStyle(PCToggleStyle())
}
}
// MARK: - 自定义样式
struct PCToggleStyle: ToggleStyle {
func makeBody(configuration: Configuration) -> some View {
return HStack {
configuration.label
Image(systemName: configuration.isOn ? "mic.square.fill" : "mic.slash.circle.fill")
.renderingMode(.original)
.resizable()
.frame(width: 30, height: 30)
.onTapGesture {
configuration.isOn.toggle()
}
}
}
}Picker

有 Picker 视图,还有颜色和时间选择的 ColorPicker 和 DatePicker。
示例代码如下:
struct PlayPickerView: View {
@State private var select = 1
@State private var color = Color.red.opacity(0.3)
var dateFt: DateFormatter {
let ft = DateFormatter()
ft.dateStyle = .long
return ft
}
@State private var date = Date()
var body: some View {
// 默认是下拉的风格
Form {
Section("选区") {
Picker("选一个", selection: $select) {
Text("1")
.tag(1)
Text("2")
.tag(2)
}
}
}
.padding()
// Segment 风格,
Picker("选一个", selection: $select) {
Text("one")
.tag(1)
Text("two")
.tag(2)
}
.pickerStyle(SegmentedPickerStyle())
.padding()
// 颜色选择器
ColorPicker("选一个颜色", selection: $color, supportsOpacity: false)
.padding()
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 8)
.fill(color)
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
// 时间选择器
VStack {
DatePicker(selection: $date, in: ...Date(), displayedComponents: .date) {
Text("选时间")
}
DatePicker("选时间", selection: $date)
.datePickerStyle(GraphicalDatePickerStyle())
.frame(maxHeight: 400)
Text("时间:\(date, formatter: dateFt)")
}
.padding()
}
}选择多个日期
MultiDatePicker 视图会显示一个日历,用户可以选择多个日期,可以设置选择范围。示例如下:
struct PMultiDatePicker: View {
@Environment(\.calendar) var cal
@State var dates: Set<DateComponents> = []
var body: some View {
MultiDatePicker("选择个日子", selection: $dates, in: Date.now...)
Text(s)
}
var s: String {
dates.compactMap { c in
cal.date(from:c)?.formatted(date: .long, time: .omitted)
}
.formatted()
}
}PhotosPick
支持图片选择,示例代码如下:
import PhotosUI
import CoreTransferable
struct ContentView: View {
@ObservedObject var viewModel: FilterModel = .shared
var body: some View {
NavigationStack {
Gallery()
.navigationTitle("Birthday Filter")
.toolbar {
PhotosPicker(
selection: $viewModel.imageSelection,
matching: .images
) {
Label("Pick a photo", systemImage: "plus.app")
}
Button {
viewModel.applyFilter()
} label: {
Label("Apply Filter", systemImage: "camera.filters")
}
}
}
}
}Slider
struct PlaySliderView: View {
@State var count: Double = 0
var body: some View {
Slider(value: $count, in: 0...100)
.padding()
Text("\(Int(count))")
}
}Stepper
struct PlayStepperView: View {
@State private var count: Int = 0
var body: some View {
Stepper(value: $count, step: 2) {
Text("共\(count)")
} onEditingChanged: { b in
print(b)
} // end Stepper
}
}Form
Form 今年也得到了增强,示例如下:
Form {
Section {
LabeledContent("Location") {
AddressView(location)
}
DatePicker("Date", selection: $date)
TextField("Description", text: $eventDescription, axis: .vertical)
.lineLimit(3, reservesSpace: true)
}
Section("Vibe") {
Picker("Accent color", selection: $accent) {
ForEach(Theme.allCases) { accent in
Text(accent.rawValue.capitalized).tag(accent)
}
}
Picker("Color scheme", selection: $scheme) {
Text("Light").tag(ColorScheme.light)
Text("Dark").tag(ColorScheme.dark)
}
#if os(macOS)
.pickerStyle(.inline)
#endif
Toggle(isOn: $extraGuests) {
Text("Allow extra guests")
Text("The more the merrier!")
}
if extraGuests {
Stepper("Guests limit", value: $spacesCount, format: .number)
}
}
Section("Decorations") {
Section {
List(selection: $selectedDecorations) {
DisclosureGroup {
HStack {
Toggle("Balloons 🎈", isOn: $includeBalloons)
Spacer()
decorationThemes[.balloon].map { $0.swatch }
}
.tag(Decoration.balloon)
HStack {
Toggle("Confetti 🎊", isOn: $includeConfetti)
Spacer()
decorationThemes[.confetti].map { $0.swatch }
}
.tag(Decoration.confetti)
HStack {
Toggle("Inflatables 🪅", isOn: $includeInflatables)
Spacer()
decorationThemes[.inflatables].map { $0.swatch }
}
.tag(Decoration.inflatables)
HStack {
Toggle("Party Horns 🥳", isOn: $includeBlowers)
Spacer()
decorationThemes[.noisemakers].map { $0.swatch }
}
.tag(Decoration.noisemakers)
} label: {
Toggle("All Decorations", isOn: [
$includeBalloons, $includeConfetti,
$includeInflatables, $includeBlowers
])
.tag(Decoration.all)
}
#if os(macOS)
.toggleStyle(.checkbox)
#endif
}
Picker("Decoration theme", selection: themes) {
Text("Blue").tag(Theme.blue)
Text("Black").tag(Theme.black)
Text("Gold").tag(Theme.gold)
Text("White").tag(Theme.white)
}
#if os(macOS)
.pickerStyle(.radioGroup)
#endif
}
}
}
.formStyle(.grouped)Keyboard
键盘快捷键的使用方法如下:
struct PlayKeyboard: View {
var body: some View {
Button(systemIconName: "camera.shutter.button") {
print("按了回车键")
}
.keyboardShortcut(.defaultAction) // 回车
Button("ESC", action: {
print("按了 ESC")
})
.keyboardShortcut(.cancelAction) // ESC 键
Button("CMD + p") {
print("按了 CMD + p")
}
.keyboardShortcut("p")
Button("SHIFT + p") {
print("按了 SHIFT + p")
}
.keyboardShortcut("p", modifiers: [.shift])
}
}Transferable
Transferable 协议使数据可以用于剪切板、拖放和 Share Sheet。
可以在自己应用程序之间或你的应用和其他应用之间发送或接受可传输项目。
支持 SwiftUI 来使用。
官方文档 Core Transferable
session Meet Transferable
新增一个专门用来接受 Transferable 的按钮视图 PasteButton,使用示例如下:
struct PPasteButton: View {
@State private var s = "戴铭"
var body: some View {
TextField("输入", text: $s)
.textFieldStyle(.roundedBorder)
PasteButton(payloadType: String.self) { str in
guard let first = str.first else { return }
s = first
}
}
}ShareLink
ShareLink 视图可以让你轻松共享数据。示例代码如下:
struct PShareLink: View {
let url = URL(string: "https://ming1016.github.io/")!
var body: some View {
ShareLink(item: url, message: Text("戴铭的博客"))
ShareLink("戴铭的博客", item: url)
ShareLink(item: url) {
Label("戴铭的博客", systemImage: "swift")
}
}
}视觉
Color
struct PlayColor: View {
var body: some View {
ZStack {
Color.black.edgesIgnoringSafeArea(.all) // Color 也是一个 View
VStack(spacing: 10) {
Text("这是一个适配了暗黑的文字颜色")
.foregroundColor(light: .purple, dark: .pink)
.background(Color(nsColor: .quaternaryLabelColor)) // 使用以前 NSColor
Text("自定义颜色")
.foregroundColor(Color(red: 0, green: 0, blue: 100))
}
.padding()
}
}
}
// MARK: - 暗黑适配颜色
struct PCColorModifier: ViewModifier {
@Environment(\.colorScheme) private var colorScheme
var light: Color
var dark: Color
private var adaptColor: Color {
switch colorScheme {
case .light:
return light
case .dark:
return dark
@unknown default:
return light
}
}
func body(content: Content) -> some View {
content.foregroundColor(adaptColor)
}
}
extension View {
func foregroundColor(light: Color, dark: Color) -> some View {
modifier(PCColorModifier(light: light, dark: dark))
}
}Effect

struct PlayEffect: View {
@State private var isHover = false
var body: some View {
ZStack {
LinearGradient(colors: [.purple, .black, .pink], startPoint: .top, endPoint: .bottom).ignoresSafeArea()
VStack(spacing: 20) {
// 材质
Text("材质效果")
.font(.system(size:30))
.padding(isHover ? 40 : 30)
.background(.regularMaterial, in: RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 8, style: .continuous))
.onHover { b in
withAnimation {
isHover = b
}
}
// 模糊
Text("模糊效果")
.font(.system(size: 30))
.padding(30)
.background {
Color.black.blur(radius: 8, opaque: false)
}
// 选择
Text("3D 旋转")
.font(.largeTitle)
.rotation3DEffect(Angle(degrees: 45), axis: (x: 0, y: 20, z: 0))
.scaleEffect(1.5)
.blendMode(.hardLight)
.blur(radius: 3)
}
}
}
}材质厚度从低到高有:
- .regularMaterial
- .thinMaterial
- .ultraThinMaterial
- .thickMaterial
- .ultraThickMaterial
Gradient 和 Shadow 的 2022 的更新
下面是个简单示例:
struct PGradientAndShadow: View {
var body: some View {
Image(systemName: "bird")
.frame(width: 150, height: 150)
.background(in: Rectangle())
.backgroundStyle(.cyan.gradient)
.foregroundStyle(.white.shadow(.drop(radius: 1, y: 3.0)))
.font(.system(size: 60))
}
}Paul Hudson 使用 Core Motion 做了一个阴影随设备倾斜而变化的效果,非常棒,How to use inner shadows to simulate depth with SwiftUI and Core Motion 。
Animation
SwiftUI 里实现动画的方式包括有 .animation 隐式动画、withAnimation 和 withTransaction 显示动画、matchedGeometryEffect Hero 动画和 TimelineView 等。
示例代码如下:
struct PlayAnimation: View {
@State private var isChange = false
private var anis:[String: Animation] = [
"p1": .default,
"p2": .linear(duration: 1),
"p3": .interpolatingSpring(stiffness: 5, damping: 3),
"p4": .easeInOut(duration: 1),
"p5": .easeIn(duration: 1),
"p6": .easeOut(duration: 1),
"p7": .interactiveSpring(response: 3, dampingFraction: 2, blendDuration: 1),
"p8": .spring(),
"p9": .default.repeatCount(3)
]
@State private var selection = 1
var body: some View {
// animation 隐式动画和 withAnimation 显示动画
Text(isChange ? "另一种状态" : "一种状态")
.font(.headline)
.padding()
.animation(.easeInOut, value: isChange) // 受限的隐式动画,只绑定某个值。
.onTapGesture {
// 使用 withAnimation 就是显式动画,效果等同 withTransaction(Transaction(animation: .default))
withAnimation {
isChange.toggle()
}
// 设置 Transaction。和隐式动画共存时,优先执行 withAnimation 或 Transaction。
var t = Transaction(animation: .linear(duration: 2))
t.disablesAnimations = true // 用来禁用隐式动画
withTransaction(t) {
isChange.toggle()
}
} // end onHover
LazyVGrid(columns: [GridItem(.adaptive(minimum: isChange ? 60 : 30), spacing: 60)]) {
ForEach(Array(anis.keys), id: \.self) { s in
Image(s)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.animation(anis[s], value: isChange)
.scaleEffect()
}
}
.padding()
Button {
isChange.toggle()
} label: {
Image(systemName: isChange ? "pause.fill" : "play.fill")
.renderingMode(.original)
}
// matchedGeometryEffect 的使用
VStack {
Text("后台")
.font(.headline)
placeStayView
Text("前台")
.font(.headline)
placeShowView
}
.padding(50)
// 通过使用相同 matchedGeometryEffect 的 id,绑定两个元素变化。
HStack {
if isChange {
Rectangle()
.fill(.pink)
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "g1", in: mgeStore)
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
}
Spacer()
Button("转换") {
withAnimation(.linear(duration: 2.0)) {
isChange.toggle()
}
}
Spacer()
if !isChange {
Circle()
.fill(.orange)
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "g1", in: mgeStore)
.frame(width: 70, height: 70)
}
HStack {
Image("p1")
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
if !isChange {
Image("p19")
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "g1", in: mgeStore)
}
Image("p1")
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
}
}
.padding()
// 使用 isSource,作为移动到相同 matchedGeometryEffect id 的方法。
HStack {
Image("p19")
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(width: isChange ? 100 : 50, height: isChange ? 100 : 50)
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: isChange ? "g2" : "", in: mgeStore, isSource: false)
Image("p19")
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "g2", in: mgeStore)
.opacity(0)
}
// 点击跟随的效果
HStack {
ForEach(Array(1...4), id: \.self) { i in
Image("p\(i)")
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(width: i == selection ? 200 : 50)
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "h\(i)", in: mgeStore)
.onTapGesture {
withAnimation {
selection = i
}
}
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 3, x: 2, y: 3)
}
}
.background(
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 8).fill(.pink)
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: "h\(selection)", in: mgeStore, isSource: false)
)
// matchedGeometryEffect 还可以应用到 List 中,通过 Array enumerated 获得 index 作为 matchedGeometryEffect 的 id。右侧固定按钮可以直接让对应 id 的视图滚动到固定按钮的位置
// TimelineView
TimelineView(.periodic(from: .now, by: 1)) { t in
Text("\(t.date)")
HStack(spacing: 20) {
let e = "p\(Int.random(in: 1...30))"
Image(e)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(height: 40)
.animation(.default.repeatCount(3), value: e)
TimelineSubView(date: t.date) // 需要传入 timeline 的时间给子视图才能够起作用。
}
.padding()
}
// matchedGeometryEffect
/// TimelineScheduler 的使用,TimelineScheduler 有以下类型
/// .animation:制定更新的频率,可以控制暂停
/// .everyMinute:每分钟更新一次
/// .explicit:所有要更新的放到一个数组里
/// .periodic:设置开始时间和更新频率
/// 也可以自定义 TimelineScheduler
TimelineView(.everySecond) { t in
let e = "p\(Int.random(in: 1...30))"
Image(e)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(height: 40)
}
// 自定义的 TimelineScheduler
TimelineView(.everyLoop(timeOffsets: [0.2, 0.7, 1, 0.5, 2])) { t in
TimelineSubView(date: t.date)
}
}
// MARK: - TimelineSubView
struct TimelineSubView: View {
let date : Date
@State private var s = "let's go"
// 顺序从数组中取值,取完再重头开始
@State private var idx: Int = 1
func advanceIndex(count: Int) {
idx = (idx + 1) % count
if idx == 0 { idx = 1 }
}
var body: some View {
HStack(spacing: 20) {
Image("p\(idx)")
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(height: 40)
.animation(.easeIn(duration: 1), value: date)
.onChange(of: date) { newValue in
advanceIndex(count: 30)
s = "\(date.hour):\(date.minute):\(date.second)"
}
.onAppear {
advanceIndex(count: 30)
}
Text(s)
}
}
}
// MARK: - 用 matchedGeometryEffect 做动画
/// matchedGeometryEffect 可以无缝的将一个图像变成另外一个图像。
@State private var placeStayItems = ["p1", "p2", "p3", "p4"]
@State private var placeShowItems: [String] = []
@Namespace private var mgeStore
private var placeStayView: some View {
LazyVGrid(columns: [GridItem(.adaptive(minimum: 30), spacing: 10)]) {
ForEach(placeStayItems, id: \.self) { s in
Image(s)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: s, in: mgeStore)
.onTapGesture {
withAnimation {
placeStayItems.removeAll { $0 == s }
placeShowItems.append(s)
}
}
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 2, x: 2, y: 4)
} // end ForEach
} // end LazyVGrid
} // private var placeStayView
private var placeShowView: some View {
LazyVGrid(columns: [GridItem(.adaptive(minimum: 150), spacing: 10)]) {
ForEach(placeShowItems, id: \.self) { s in
Image(s)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.matchedGeometryEffect(id: s, in: mgeStore)
.onTapGesture {
withAnimation {
placeShowItems.removeAll { $0 == s }
placeStayItems.append(s)
}
}
.shadow(color: .black, radius: 2, x: 0, y: 2)
.shadow(color: .white, radius: 5, x: 0, y: 2)
} // end ForEach
} // end LazyVGrid
} // end private var placeShowView
} // end struct PlayAnimation
// MARK: - 扩展 TimelineSchedule
extension TimelineSchedule where Self == PeriodicTimelineSchedule {
static var everySecond: PeriodicTimelineSchedule {
get {
.init(from: .now, by: 1)
}
}
}
// MARK: - 自定义一个 TimelineSchedule
// timeOffsets 用完,就会再重头重新再来一遍
struct PCLoopTimelineSchedule: TimelineSchedule {
let timeOffsets: [TimeInterval]
func entries(from startDate: Date, mode: TimelineScheduleMode) -> Entries {
Entries(last: startDate, offsets: timeOffsets)
}
struct Entries: Sequence, IteratorProtocol {
var last: Date
let offsets: [TimeInterval]
var idx: Int = -1
mutating func next() -> Date? {
idx = (idx + 1) % offsets.count
last = last.addingTimeInterval(offsets[idx])
return last
}
} // end Struct Entries
}
// 为自定义的 PCLoopTimelineSchedule 做一个 TimelineSchedule 的扩展函数,方便使用
extension TimelineSchedule where Self == PCLoopTimelineSchedule {
static func everyLoop(timeOffsets: [TimeInterval]) -> PCLoopTimelineSchedule {
.init(timeOffsets: timeOffsets)
}
}Canvas
Canvas 可以画路径、图片和文字、Symbols、可变的图形上下文、使用 CoreGraphics 代码和做动画。
图形上下文可以被 addFilter、clip、clipToLayer、concatenate、rotate、scaleBy、translateBy 这些方法来进行改变。
示例代码如下:
struct PlayCanvas: View {
let colors: [Color] = [.purple, .blue, .yellow, .pink]
var body: some View {
// 画路径
PCCanvasPathView(t: .rounded)
PCCanvasPathView(t: .ellipse)
PCCanvasPathView(t: .circle)
// 图片和文字
PCCanvasImageAndText(text: "Starming", colors: [.purple, .pink])
// Symbol,在 Canvas 里引用 SwiftUI 视图
Canvas { c, s in
let c0 = c.resolveSymbol(id: 0)!
let c1 = c.resolveSymbol(id: 1)!
let c2 = c.resolveSymbol(id: 2)!
let c3 = c.resolveSymbol(id: 3)!
c.draw(c0, at: .init(x: 10, y: 10), anchor: .topLeading)
c.draw(c1, at: .init(x: 30, y: 20), anchor: .topLeading)
c.draw(c2, at: .init(x: 50, y: 30), anchor: .topLeading)
c.draw(c3, at: .init(x: 70, y: 40), anchor: .topLeading)
} symbols: {
ForEach(Array(colors.enumerated()), id: \.0) { i, c in
Circle()
.fill(c)
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
.tag(i)
}
}
// Symbol 动画和 SwiftUI 视图一样,不会受影响
Canvas { c, s in
let sb = c.resolveSymbol(id: 0)!
c.draw(sb, at: CGPoint(x: s.width / 2, y: s.height / 2), anchor: .center)
} symbols: {
PCForSymbolView()
.tag(0)
}
} // end var body
}
// MARK: - 给 Symbol 用的视图
struct PCForSymbolView: View {
@State private var change = true
var body: some View {
Image(systemName: "star.fill")
.renderingMode(.original)
.font(.largeTitle)
.rotationEffect(.degrees(change ? 0 : 72))
.onAppear {
withAnimation(.linear(duration: 1.0).repeatForever(autoreverses: false)) {
change.toggle()
}
}
}
}
// MARK: - 图片和文字
struct PCCanvasImageAndText: View {
let text: String
let colors: [Color]
var fontSize: Double = 42
var body: some View {
Canvas { context, size in
let midPoint = CGPoint(x: size.width / 2, y: size.height / 2)
let font = Font.system(size: fontSize)
var resolved = context.resolve(Text(text).font(font))
let start = CGPoint(x: (size.width - resolved.measure(in: size).width) / 2.0, y: 0)
let end = CGPoint(x: size.width - start.x, y: 0)
resolved.shading = .linearGradient(Gradient(colors: colors), startPoint: start, endPoint: end)
context.draw(resolved, at: midPoint, anchor: .center)
}
}
}
// MARK: - Path
struct PCCanvasPathView: View {
enum PathType {
case rounded, ellipse, casual, circle
}
let t: PathType
var body: some View {
Canvas { context, size in
conf(context: &context, size: size, type: t)
} // end Canvas
}
func conf( context: inout GraphicsContext, size: CGSize, type: PathType) {
let rect = CGRect(origin: .zero, size: size).insetBy(dx: 25, dy: 25)
var path = Path()
switch type {
case .rounded:
path = Path(roundedRect: rect, cornerRadius: 35.0)
case .ellipse:
let cgPath = CGPath(ellipseIn: rect, transform: nil)
path = Path(cgPath)
case .casual:
path = Path {
let points: [CGPoint] = [
.init(x: 10, y: 10),
.init(x: 0, y: 50),
.init(x: 100, y: 100),
.init(x: 100, y: 0),
]
$0.move(to: .zero)
$0.addLines(points)
}
case .circle:
path = Circle().path(in: rect)
}
let gradient = Gradient(colors: [.purple, .pink])
let from = rect.origin
let to = CGPoint(x: rect.width, y: rect.height + from.y)
// Stroke path
context.stroke(path, with: .color(.blue), lineWidth: 25)
context.fill(path, with: .linearGradient(gradient, startPoint: from, endPoint: to))
}
}SF Symbol
SF Symbol 支持变量值,可以通过设置 variableValue 来填充不同部分,比如 wifi 图标,不同值会亮不同部分,Image(systemName: "wifi", variableValue: 0.5) 。
开发者
Swift官方
- tkremenek:Swift director
- DougGregor
- mikeash:Friday Q&A
社区
- onevcat:喵神
- DianQK:靛青 - SwiftGG翻译组
- kean:Nuke、Pulse
- stephencelis:Point-Free & SQLite.swift
- ibireme:YYDS
- mattt:NSHipster
- ethanhuang13:13 - [weak self]播客
- Kyle-Ye
- ming1016:戴铭
- mxcl
- lkzhao
- insidegui
- johnno1962:InjectionIII
- wigging:Back to the Mac
- Dimillian:MovieSwiftUI
- krzysztofzablocki:元编程 Sourcery
- onmyway133
- pofat:Pofat - [weak self]播客
- mecid:Swift with Majid
- hebertialmeida
- kylef:Commander
- joshaber:at GitHub
- ashfurrow:Moya
- jessesquires
探索库
新鲜事
SwiftOldDriver/iOS-Weekly
老司机 iOS 周报
Star:4222 Issue:19 开发语言:
🇨🇳 老司机技术 iOS 周报
matteocrippa/awesome-swift
Star:22100 Issue:1 开发语言:Ruby
A collaborative list of awesome Swift libraries and resources. Feel free to contribute!
ruanyf/weekly
科技爱好者周刊
Star:24124 Issue:1902 开发语言:
科技爱好者周刊,每周五发布
ming1016/SwiftPamphletApp
戴铭的开发小册子
Star:0 Issue:0 开发语言:
封装易用功能
SwifterSwift/SwifterSwift
Handy Swift extensions
Star:11409 Issue:17 开发语言:Swift
A handy collection of more than 500 native Swift extensions to boost your productivity.
JoanKing/JKSwiftExtension
Swift常用扩展、组件、协议
Star:359 Issue:1 开发语言:Swift
Swift常用扩展、组件、协议,方便项目快速搭建,提供完整清晰的Demo示例,不断的完善中……
infinum/iOS-Nuts-And-Bolts
Star:178 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
iOS bits and pieces that you can include in your project to make your life a bit easier.
gtokman/ExtensionKit
Star:101 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
Helpful extensions for iOS app development 🚀
SwiftUI 扩展
SwiftUIX/SwiftUIX
扩展 SwiftUI
Star:4777 Issue:8 开发语言:Swift
Extensions and additions to the standard SwiftUI library.
SDWebImage/SDWebImageSwiftUI
Star:1403 Issue:45 开发语言:Swift
SwiftUI Image loading and Animation framework powered by SDWebImage
apptekstudios/ASCollectionView
SwiftUI collection
Star:1208 Issue:32 开发语言:Swift
A SwiftUI collection view with support for custom layouts, preloading, and more.
siteline/SwiftUI-Introspect
SwiftUI 引入 UIKit
Star:3262 Issue:53 开发语言:Swift
Introspect underlying UIKit components from SwiftUI
AvdLee/SwiftUIKitView
在 SwiftUI 中 使用 UIKit
Star:506 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
Easily use UIKit views in your SwiftUI applications. Create Xcode Previews for UIView elements
danielsaidi/SwiftUIKit
给 SwiftUI 添加更多功能
Star:666 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
SwiftUIKit contains additional functionality for SwiftUI.
Toni77777/awesome-swiftui-libraries
SwiftUI 可使用的库
Star:199 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
:rocket: Awesome SwiftUI Libraries
rakutentech/AltSwiftUI
类 SwiftUI
Star:269 Issue:6 开发语言:Swift
Open Source UI framework based on SwiftUI syntax and features, adding backwards compatibility.
gymshark/ios-stack-kit
类 SwiftUI
Star:118 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
The power of SwiftUI with UIKit
jordibruin/Swift-Charts-Examples
Swift Charts 制作的不同类型图表示例
Star:0 Issue:0 开发语言:
图片
onevcat/Kingfisher
Star:20267 Issue:76 开发语言:Swift
A lightweight, pure-Swift library for downloading and caching images from the web.
kean/Nuke
Star:6721 Issue:6 开发语言:Swift
Image loading system
suzuki-0000/SKPhotoBrowser
图片浏览
Star:2358 Issue:94 开发语言:Swift
Simple PhotoBrowser/Viewer inspired by facebook, twitter photo browsers written by swift
文字处理
gonzalezreal/MarkdownUI
Star:730 Issue:14 开发语言:Swift
Render Markdown text in SwiftUI
tophat/RichTextView
Star:1073 Issue:31 开发语言:Swift
iOS Text View (UIView) that Properly Displays LaTeX, HTML, Markdown, and YouTube/Vimeo Links
keitaoouchi/MarkdownView
Star:1778 Issue:32 开发语言:Swift
Markdown View for iOS.
johnxnguyen/Down
fast Markdown
Star:1963 Issue:25 开发语言:C
Blazing fast Markdown / CommonMark rendering in Swift, built upon cmark.
qeude/SwiftDown
Swift 写的可换主题的 Markdown 编辑器组件
Star:115 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
📦 A themable markdown editor component for your SwiftUI apps.
JohnSundell/Ink
Markdown 解析器
Star:2117 Issue:22 开发语言:Swift
A fast and flexible Markdown parser written in Swift.
tnantoka/edhita
Star:1194 Issue:15 开发语言:Swift
Fully open source text editor for iOS written in Swift.
glushchenko/fsnotes
Star:5025 Issue:222 开发语言:Swift
Notes manager for macOS/iOS
coteditor/CotEditor
Star:4602 Issue:96 开发语言:Swift
Lightweight Plain-Text Editor for macOS
mchakravarty/CodeEditorView
SwiftUI 写的代码编辑器
Star:400 Issue:30 开发语言:Swift
SwiftUI code editor view for iOS and macOS
CodeEditApp/CodeEdit
原生,性能好的代码编辑器
Star:10816 Issue:93 开发语言:Swift
CodeEdit App for macOS – Elevate your code editing experience. Open source, free forever.
ZeeZide/CodeEditor
使用 Highlight.js 的来做语法高亮的 SwiftUI 编辑器
Star:202 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
A SwiftUI TextEditor with syntax highlighting using Highlight.js
tw93/MiaoYan
轻灵的 Markdown 笔记本伴你写出妙言
Star:0 Issue:0 开发语言:
动画
recherst/kavsoft-swiftui-animations
Star:132 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
SwiftUI animation tutorials, all of demos are consisted of youtube videos at website of kavsoft. 🔗 https://kavsoft.dev
timdonnelly/Advance
Physics-based animations
Star:4463 Issue:4 开发语言:Swift
Physics-based animations for iOS, tvOS, and macOS.
MengTo/Spring
动画
Star:13987 Issue:167 开发语言:Swift
A library to simplify iOS animations in Swift.
持久化存储
stephencelis/SQLite.swift
Star:8349 Issue:88 开发语言:Swift
A type-safe, Swift-language layer over SQLite3.
groue/GRDB.swift
Star:5185 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
A toolkit for SQLite databases, with a focus on application development
caiyue1993/IceCream
CloudKit 同步 Realm 数据库
Star:1732 Issue:46 开发语言:Swift
Sync Realm Database with CloudKit
realm/realm-cocoa
Star:15375 Issue:367 开发语言:Objective-C
Realm is a mobile database: a replacement for Core Data & SQLite
PostgresApp/PostgresApp
PostgreSQL macOS 应用
Star:6332 Issue:125 开发语言:Makefile
The easiest way to get started with PostgreSQL on the Mac
编程范式
ReactiveX/RxSwift
函数响应式编程
Star:22278 Issue:10 开发语言:Swift
Reactive Programming in Swift
pointfreeco/swift-composable-architecture
Star:6377 Issue:20 开发语言:Swift
A library for building applications in a consistent and understandable way, with composition, testing, and ergonomics in mind.
onmyway133/awesome-ios-architecture
Star:4628 Issue:0 开发语言:
:japanese_castle: Better ways to structure iOS apps
ReSwift/ReSwift
单页面状态和数据管理
Star:7206 Issue:39 开发语言:Swift
Unidirectional Data Flow in Swift - Inspired by Redux
gre4ixin/ReduxUI
SwiftUI Redux 架构
Star:29 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
💎 Redux like architecture for SwiftUI
BohdanOrlov/iOS-Developer-Roadmap
Star:5834 Issue:7 开发语言:Swift
Roadmap to becoming an iOS developer in 2018.
ReactiveCocoa/ReactiveCocoa
Star:19983 Issue:4 开发语言:Swift
Cocoa framework and Obj-C dynamism bindings for ReactiveSwift.
mehdihadeli/awesome-software-architecture
软件架构
Star:291 Issue:2 开发语言:
A curated list of awesome articles, videos, and other resources to learn and practice software architecture, patterns, and principles.
nalexn/clean-architecture-swiftui
干净完整的SwiftUI+Combine例子,包含网络和单元测试等
Star:3517 Issue:17 开发语言:Swift
SwiftUI sample app using Clean Architecture. Examples of working with CoreData persistence, networking, dependency injection, unit testing, and more.
krzysztofzablocki/Sourcery
Swift 元编程
Star:6644 Issue:55 开发语言:Swift
Meta-programming for Swift, stop writing boilerplate code.
路由
pointfreeco/swiftui-navigation
Star:866 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
Tools for making SwiftUI navigation simpler, more ergonomic and more precise.
静态检查
realm/SwiftLint
Star:16224 Issue:312 开发语言:Swift
A tool to enforce Swift style and conventions.
系统能力
devicekit/DeviceKit
UIDevice 易用封装
Star:3700 Issue:46 开发语言:Swift
DeviceKit is a value-type replacement of UIDevice.
kishikawakatsumi/KeychainAccess
Star:6935 Issue:39 开发语言:Swift
Simple Swift wrapper for Keychain that works on iOS, watchOS, tvOS and macOS.
nvzqz/FileKit
文件操作
Star:2217 Issue:11 开发语言:Swift
Simple and expressive file management in Swift
JohnSundell/Files
文件操作
Star:2298 Issue:23 开发语言:Swift
A nicer way to handle files & folders in Swift
kylef/PathKit
文件操作
Star:1348 Issue:12 开发语言:Swift
Effortless path operations in Swift
rushisangani/BiometricAuthentication
FaceID or TouchID authentication
Star:798 Issue:14 开发语言:Swift
Use Apple FaceID or TouchID authentication in your app using BiometricAuthentication.
sunshinejr/SwiftyUserDefaults
Star:4653 Issue:48 开发语言:Swift
Modern Swift API for NSUserDefaults
MonitorControl/MonitorControl
亮度和声音控制
Star:16608 Issue:65 开发语言:Swift
🖥 Control your display’s brightness & volume on your Mac as if it was a native Apple Display. Use Apple Keyboard keys or custom shortcuts. Shows the native macOS OSDs.
carekit-apple/CareKit
使用 SwiftUI 开发健康相关的库
Star:2224 Issue:71 开发语言:Swift
CareKit is an open source software framework for creating apps that help people better understand and manage their health.
Cay-Zhang/SwiftSpeech
苹果语言识别封装库,已适配 SwiftUI
Star:269 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
A speech recognition framework designed for SwiftUI.
malcommac/SwiftDate
Swift编写的时间时区,时间比较等复杂处理的包装
Star:6943 Issue:68 开发语言:Swift
🐔 Toolkit to parse, validate, manipulate, compare and display dates, time & timezones in Swift.
接口
OAuthSwift/OAuthSwift
Star:3017 Issue:42 开发语言:Swift
Swift based OAuth library for iOS
p2/OAuth2
Star:1067 Issue:74 开发语言:Swift
OAuth2 framework for macOS and iOS, written in Swift.
public-apis/public-apis
Star:197421 Issue:19 开发语言:Python
A collective list of free APIs
接口应用
bpisano/Weather
天气应用
Star:282 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
A Weather app in SwiftUI.
Dimillian/MovieSwiftUI
电影 MovieDB 应用
Star:6063 Issue:8 开发语言:Swift
SwiftUI & Combine app using MovieDB API. With a custom Flux (Redux) implementation.
chojnac/NotionSwift
Star:29 Issue:4 开发语言:Swift
Unofficial Notion API SDK for iOS & macOS
Dimillian/RedditOS
SwiftUI 写的 Reddit客户端
Star:3605 Issue:16 开发语言:Swift
The product name is Curiosity, a SwiftUI Reddit client for macOS Big Sur
carson-katri/reddit-swiftui
SwiftUI 写的 Reddit客户端
Star:1127 Issue:7 开发语言:Swift
A cross-platform Reddit client built in SwiftUI
Dimillian/SwiftHN
Hacker News 阅读
Star:1685 Issue:20 开发语言:Swift
A Hacker News reader in Swift
tatsuz0u/EhPanda
Star:1507 Issue:24 开发语言:Swift
An unofficial E-Hentai App for iOS built with SwiftUI & TCA.
Dimillian/MortyUI
GraphQL + SwiftUI 开发的瑞克和莫蒂应用
Star:431 Issue:4 开发语言:Swift
A very simple Rick & Morty app to demo GraphQL + SwiftUI
Finb/V2ex-Swift
V2EX 客户端
Star:1513 Issue:11 开发语言:Swift
An iOS client written in Swift for V2EX
v2er-app/iOS
V2EX 客户端
Star:194 Issue:4 开发语言:Swift
The source of V2er.iOS
sinaweibosdk/weibo_ios_sdk
Star:1423 Issue:66 开发语言:Objective-C
新浪微博 IOS SDK
miniLV/MNWeibo
Swift5 + MVVM 微博客户端
Star:251 Issue:4 开发语言:Swift
Swift5 + MVVM + 文艺复兴微博(纯代码 + 纯Swift),可作为第一个上手的Swift项目.
nerdishbynature/octokit.swift
Swift API Client for GitHub
Star:400 Issue:10 开发语言:Swift
A Swift API Client for GitHub and GitHub Enterprise
GitHawkApp/GitHawk
iOS app for GitHub
Star:2838 Issue:460 开发语言:Swift
The (second) best iOS app for GitHub.
fangzesheng/free-api
Star:12335 Issue:28 开发语言:
收集免费的接口服务,做一个api的搬运工
nerdsupremacist/Graphaello
SwiftUI 中使用 GraphQL 的工具
Star:454 Issue:22 开发语言:Swift
A Tool for Writing Declarative, Type-Safe and Data-Driven Applications in SwiftUI using GraphQL
nerdsupremacist/tmdb
GraphQL 包装电影数据接口
Star:16 Issue:1 开发语言:Swift
A GraphQL Wrapper for The Movie Database
macOS
serhii-londar/open-source-mac-os-apps
开源 macOS 程序合集
Star:30760 Issue:65 开发语言:Swift
🚀 Awesome list of open source applications for macOS. https://t.me/s/opensourcemacosapps
Ranchero-Software/NetNewsWire
Star:5773 Issue:551 开发语言:Swift
RSS reader for macOS and iOS.
overtake/TelegramSwift
Star:3876 Issue:485 开发语言:Swift
Source code of Telegram for macos on Swift 5.0
eonist/FileWatcher
macOS 上监听文件变化
Star:159 Issue:5 开发语言:Swift
Monitoring file system changes in macOS
waylybaye/XcodeCleaner-SwiftUI
清理 Xcode
Star:1204 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
Make Xcode Clean Again
gao-sun/eul
SwiftUI 写的 macOS 状态监控工具
Star:7658 Issue:55 开发语言:Swift
🖥️ macOS status monitoring app written in SwiftUI.
Dimillian/ACHNBrowserUI
SwiftUI 写的动物之森小助手程序
Star:1528 Issue:32 开发语言:Swift
Animal Crossing New Horizon companion app in SwiftUI
lexrus/RegExPlus
正则表达式
Star:186 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
A nifty RegEx test tool built with SwiftUI
v2ex/launcher
用来启动那些本地开发时需要的各种进程,及查看其输出
Star:212 Issue:5 开发语言:Swift
lukakerr/Pine
Markdown 编辑器
Star:2988 Issue:45 开发语言:Swift
A modern, native macOS markdown editor
root3nl/SupportApp
企业支持 macOS 软件
Star:283 Issue:20 开发语言:Swift
The Support App is developed by Root3, specialized in managing Apple devices. Root3 offers consultancy and support for organizations to get the most out of their Apple devices and is based in The Netherlands (Haarlem).
jaywcjlove/awesome-mac
macOS 软件大全
Star:49993 Issue:126 开发语言:JavaScript
Now we have become very big, Different from the original idea. Collect premium software in various categories.
insidegui/WWDC
Star:8216 Issue:33 开发语言:Swift
The unofficial WWDC app for macOS
sindresorhus/Actions
Star:904 Issue:11 开发语言:Swift
⚙️ Supercharge your shortcuts
ObuchiYuki/DevToysMac
开发者工具合集
Star:5552 Issue:40 开发语言:Swift
DevToys For mac
jacklandrin/OnlySwitch
macOS 状态栏一键设置工具,隐藏桌面图标、清理 Xcode 缓存、一键隐藏刘海儿、进入夜览模式等数十种功能
Star:1389 Issue:10 开发语言:Swift
⚙️ All-in-One menu bar app, hide 💻MacBook Pro’s notch, dark mode, AirPods, Shortcuts
exelban/stats
macOS 系统资源监控
Star:11296 Issue:14 开发语言:Swift
macOS system monitor in your menu bar
brunophilipe/Cakebrew
可视化管理 Homebrew 软件包
Star:4234 Issue:57 开发语言:Objective-C
Manage your Homebrew formulas with style using Cakebrew.
应用
vinhnx/Clendar
SwiftUI 写的日历应用
Star:361 Issue:58 开发语言:Swift
Clendar - universal Apple-platform calendar app. Written in SwiftUI. Available on App Store. MIT License.
SvenTiigi/WhatsNewKit
欢迎屏
Star:2560 Issue:1 开发语言:Swift
Showcase your awesome new app features 📱
kickstarter/ios-oss
Kickstarter 的 iOS 版本
Star:7968 Issue:1 开发语言:Swift
Kickstarter for iOS. Bring new ideas to life, anywhere.
CoreOffice/CryptoOffice
Swift 解析 Office Open XML(OOXML)包括 xlsx, docx, pptx
Star:27 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
Office Open XML (OOXML) formats (.xlsx, .docx, .pptx) decryption for Swift
CoreOffice/CoreXLSX
Swift编写的Excel电子表格(XLSX)格式解析器
Star:643 Issue:13 开发语言:Swift
Excel spreadsheet (XLSX) format parser written in pure Swift
analogcode/Swift-Radio-Pro
电台应用
Star:2679 Issue:13 开发语言:Swift
Professional Radio Station App for iOS!
bizz84/SwiftyStoreKit
应用内购框架
Star:6000 Issue:163 开发语言:Swift
Lightweight In App Purchases Swift framework for iOS 8.0+, tvOS 9.0+ and macOS 10.10+ ⛺
wikimedia/wikipedia-ios
Star:2462 Issue:6 开发语言:Swift
📱The official Wikipedia iOS app.
游戏
pointfreeco/isowords
单词搜索游戏
Star:1792 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
Open source game built in SwiftUI and the Composable Architecture.
michelpereira/awesome-games-of-coding
教你学编程的游戏收集
Star:1459 Issue:1 开发语言:
A curated list of games that can teach you how to learn a programming language.
OpenEmu/OpenEmu
视频游戏模拟器
Star:13964 Issue:201 开发语言:Swift
🕹 Retro video game emulation for macOS
jVirus/swiftui-2048
Star:162 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
🎲 100% SwiftUI 3.0, classic 2048 game [iOS 15.0+, iPadOS 15.0+, macOS 12.0+, Swift 5.5].
schellingb/dosbox-pure
DOS 游戏模拟器
Star:452 Issue:112 开发语言:C++
DOSBox Pure is a new fork of DOSBox built for RetroArch/Libretro aiming for simplicity and ease of use.
chrismaltby/gb-studio
拖放式复古游戏创建器
Star:6089 Issue:513 开发语言:C
A quick and easy to use drag and drop retro game creator for your favourite handheld video game system
darrellroot/Netrek-SwiftUI
SwiftUI 开发的1989年的 Netrek 游戏
Star:10 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
freeCodeCamp/LearnToCodeRPG
学习编码的游戏
Star:828 Issue:10 开发语言:Ren’Py
A visual novel video game where you learn to code and get a dev job 🎯
pmgl/microstudio
游戏开发平台集搜索、开发、学习、体验、交流等功能于一身
Star:634 Issue:37 开发语言:JavaScript
Free, open source game engine online
InvadingOctopus/octopuskit
2D游戏引擎,用的 GameplayKit + SpriteKit + SwiftUI
Star:310 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
2D ECS game engine in 100% Swift + SwiftUI for iOS, macOS, tvOS
a-little-org-called-mario/a-little-game-called-mario
用 Godot 引擎做的马里奥游戏
Star:1046 Issue:5 开发语言:GDScript
open source collective hell game
新技术展示
JakeLin/Moments-SwiftUI
SwiftUI、Async、Actor
Star:42 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
WeChat-like Moments App implemented using Swift 5.5 and SwiftUI
twostraws/HackingWithSwift
示例代码
Star:4529 Issue:10 开发语言:Swift
The project source code for hackingwithswift.com
carson-katri/awesome-result-builders
Result Builders awesome
Star:798 Issue:2 开发语言:
A list of cool DSLs made with Swift 5.4’s @resultBuilder
pointfreeco/episode-code-samples
Star:684 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
💾 Point-Free episode code.
SwiftGGTeam/the-swift-programming-language-in-chinese
中文版 Apple 官方 Swift 教程
Star:20535 Issue:5 开发语言:CSS
中文版 Apple 官方 Swift 教程《The Swift Programming Language》
jessesquires/TIL
学习笔记
Star:258 Issue:1 开发语言:
Things I’ve learned and/or things I want to remember. Notes, links, advice, example code, etc.
Combine 扩展
OpenCombine/OpenCombine
Combine 的开源实现
Star:2228 Issue:13 开发语言:Swift
Open source implementation of Apple’s Combine framework for processing values over time.
CombineCommunity/CombineExt
对 Combine 的补充
Star:1198 Issue:23 开发语言:Swift
CombineExt provides a collection of operators, publishers and utilities for Combine, that are not provided by Apple themselves, but are common in other Reactive Frameworks and standards.
聚合
dkhamsing/open-source-ios-apps
开源的完整 App 例子
Star:30612 Issue:0 开发语言:
:iphone: Collaborative List of Open-Source iOS Apps
vlondon/awesome-swiftui
Star:1246 Issue:5 开发语言:
A collaborative list of awesome articles, talks, books, videos and code examples about SwiftUI.
ivanvorobei/SwiftUI
Star:3896 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
Examples projects using SwiftUI released by WWDC2019. Include Layout, UI, Animations, Gestures, Draw and Data.
kon9chunkit/GitHub-Chinese-Top-Charts
GitHub中文排行榜
Star:46675 Issue:88 开发语言:Java
:cn: GitHub中文排行榜,各语言分设「软件 | 资料」榜单,精准定位中文好项目。各取所需,高效学习。
onmyway133/awesome-swiftui
Star:402 Issue:4 开发语言:
🌮 Awesome resources, articles, libraries about SwiftUI
Juanpe/About-SwiftUI
汇总 SwiftUI 的资料
Star:6225 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
Gathering all info published, both by Apple and by others, about new framework SwiftUI.
sindresorhus/awesome
内容广
Star:206308 Issue:37 开发语言:
😎 Awesome lists about all kinds of interesting topics
SwiftPackageIndex/PackageList
Swift 开源库索引
Star:627 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
The master list of repositories for the Swift Package Index.
matteocrippa/awesome-swift
Star:22100 Issue:1 开发语言:Ruby
A collaborative list of awesome Swift libraries and resources. Feel free to contribute!
性能、工程构建及自动化
tuist/tuist
创建和维护 Xcode projects 文件
Star:2782 Issue:131 开发语言:Swift
🚀 Create, maintain, and interact with Xcode projects at scale
swift-server/vscode-swift
VSCode 的 Swift 扩展
Star:316 Issue:33 开发语言:TypeScript
Visual Studio Code Extension for Swift
peripheryapp/periphery
检测 Swift 无用代码
Star:3438 Issue:31 开发语言:Swift
A tool to identify unused code in Swift projects.
nalexn/ViewInspector
SwiftUI Runtime introspection 和 单元测试
Star:1251 Issue:24 开发语言:Swift
Runtime introspection and unit testing of SwiftUI views
shibapm/Komondor
Git Hooks for Swift projects
Star:513 Issue:20 开发语言:Swift
Git Hooks for Swift projects 🐩
SwiftGen/SwiftGen
代码生成
Star:7987 Issue:91 开发语言:Swift
The Swift code generator for your assets, storyboards, Localizable.strings, … — Get rid of all String-based APIs!
hyperoslo/Cache
Star:2602 Issue:23 开发语言:Swift
:package: Nothing but Cache.
kylef/Commander
命令行
Star:1492 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
Compose beautiful command line interfaces in Swift
Carthage/Carthage
Star:14605 Issue:169 开发语言:Swift
A simple, decentralized dependency manager for Cocoa
NARKOZ/hacker-scripts
程序员的活都让机器干的脚本(真实故事)
Star:44591 Issue:67 开发语言:JavaScript
Based on a true story
RobotsAndPencils/XcodesApp
Xcode 多版本安装
Star:3276 Issue:51 开发语言:Swift
The easiest way to install and switch between multiple versions of Xcode - with a mouse click.
ZeeZide/5GUIs
可以分析程序用了哪些库,用了LLVM objdump
Star:189 Issue:11 开发语言:Swift
A tiny macOS app that can detect the GUI technologies used in other apps.
faisalmemon/ios-crash-dump-analysis-book
iOS Crash Dump Analysis Book
Star:474 Issue:1 开发语言:Objective-C
iOS Crash Dump Analysis Book
majd/ipatool
下载 ipa
Star:2303 Issue:12 开发语言:Swift
Command-line tool that allows searching and downloading app packages (known as ipa files) from the iOS App Store
测试
Quick/Quick
测试框架
Star:9456 Issue:31 开发语言:Swift
The Swift (and Objective-C) testing framework.
网络
Alamofire/Alamofire
Star:37835 Issue:29 开发语言:Swift
Elegant HTTP Networking in Swift
socketio/socket.io-client-swift
Star:4814 Issue:189 开发语言:Swift
Lojii/Knot
使用 SwiftNIO 实现 HTTPS 抓包
Star:1239 Issue:3 开发语言:C
一款iOS端基于MITM(中间人攻击技术)实现的HTTPS抓包工具,完整的App,核心代码使用SwiftNIO实现
swift-server/async-http-client
使用 SwiftNIO 开发的 HTTP 客户端
Star:609 Issue:83 开发语言:Swift
HTTP client library built on SwiftNIO
kean/Get
Star:406 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
Web API client built using async/await
awesome-selfhosted/awesome-selfhosted
网络服务及上面的应用
Star:92737 Issue:151 开发语言:JavaScript
A list of Free Software network services and web applications which can be hosted on your own servers
daltoniam/Starscream
WebSocket
Star:7348 Issue:149 开发语言:Swift
Websockets in swift for iOS and OSX
shadowsocks/ShadowsocksX-NG
Star:30440 Issue:257 开发语言:Swift
Next Generation of ShadowsocksX
carson-katri/swift-request
声明式的网络请求
Star:648 Issue:7 开发语言:Swift
Declarative HTTP networking, designed for SwiftUI
alibaba/xquic
阿里巴巴发布的 XQUIC 库
Star:1132 Issue:21 开发语言:C
XQUIC Library released by Alibaba is a cross-platform implementation of QUIC and HTTP/3 protocol.
kasketis/netfox
获取所有网络请求
Star:3269 Issue:18 开发语言:Swift
A lightweight, one line setup, iOS / OSX network debugging library! 🦊
Moya/Moya
Swift 编写的网络抽象层
Star:14012 Issue:125 开发语言:Swift
Network abstraction layer written in Swift.
Kitura/BlueSocket
Star:1301 Issue:31 开发语言:Swift
Socket framework for Swift using the Swift Package Manager. Works on iOS, macOS, and Linux.
rhummelmose/BluetoothKit
蓝牙
Star:2086 Issue:35 开发语言:Swift
Easily communicate between iOS/OSX devices using BLE
WeTransfer/Mocker
Mock Alamofire and URLSession
Star:817 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
Mock Alamofire and URLSession requests without touching your code implementation
bagder/everything-curl
记录了 curl 的一切
Star:1488 Issue:0 开发语言:Perl
The book documenting the curl project, the curl tool, libcurl and more. Simply put: everything curl.
LANDrop/LANDrop
全平台局域网文件传输
Star:2787 Issue:90 开发语言:C++
Drop any files to any devices on your LAN.
图形
willdale/SwiftUICharts
用于SwiftUI的图表绘图库
Star:560 Issue:30 开发语言:Swift
A charts / plotting library for SwiftUI. Works on macOS, iOS, watchOS, and tvOS and has accessibility features built in.
lludo/SwiftSunburstDiagram
SwiftUI 图表
Star:479 Issue:12 开发语言:Swift
SwiftUI library to easily render diagrams given a tree of objects. Similar to ring chart, sunburst chart, multilevel pie chart.
ivanschuetz/SwiftCharts
Star:2399 Issue:49 开发语言:Swift
Easy to use and highly customizable charts library for iOS
danielgindi/Charts
Star:25565 Issue:832 开发语言:Swift
Beautiful charts for iOS/tvOS/OSX! The Apple side of the crossplatform MPAndroidChart.
imxieyi/waifu2x-ios
waifu2x Core ML 动漫风格图片的高清渲染
Star:430 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
iOS Core ML implementation of waifu2x
mecid/SwiftUICharts
支持 SwiftUI 的简单的线图和柱状图库
Star:1306 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
A simple line and bar charting library that supports accessibility written using SwiftUI.
Tencent/libpag
PAG(Portable Animated Graphics)实时渲染库,多个平台渲染AE动画。
Star:1809 Issue:2 开发语言:C++
The official rendering library for PAG (Portable Animated Graphics) files that renders After Effects animations natively across multiple platforms.
jathu/UIImageColors
获取图片主次颜色
Star:3100 Issue:10 开发语言:Swift
Fetches the most dominant and prominent colors from an image.
BradLarson/GPUImage3
Metal 实现
Star:2362 Issue:74 开发语言:Swift
GPUImage 3 is a BSD-licensed Swift framework for GPU-accelerated video and image processing using Metal.
exyte/Macaw
SVG
Star:5845 Issue:129 开发语言:Swift
Powerful and easy-to-use vector graphics Swift library with SVG support
exyte/SVGView
支持 SwiftUI 的 SVG 解析渲染视图
Star:173 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
SVG parser and renderer written in SwiftUI
efremidze/Magnetic
SpriteKit气泡支持SwiftUI
Star:1398 Issue:23 开发语言:Swift
SpriteKit Floating Bubble Picker (inspired by Apple Music) 🧲
NextLevel/NextLevel
相机
Star:1994 Issue:69 开发语言:Swift
⬆️ Rad Media Capture in Swift
Harley-xk/MaLiang
基于 Metal 的涂鸦绘图库
Star:1271 Issue:43 开发语言:Swift
iOS painting and drawing library based on Metal. 神笔马良有一支神笔(基于 Metal 的涂鸦绘图库)
frzi/Model3DView
毫不费力的使用 SwiftUI 渲染 3d models
Star:49 Issue:0 开发语言:Swift
Render 3d models with SwiftUI effortlessly
音视频
iina/iina
Star:30443 Issue:1348 开发语言:Swift
The modern video player for macOS.
shogo4405/HaishinKit.swift
RTMP, HLS
Star:2319 Issue:12 开发语言:Swift
Camera and Microphone streaming library via RTMP, HLS for iOS, macOS and tvOS.
AudioKit/AudioKit
Star:9194 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
Swift audio synthesis, processing, & analysis platform for iOS, macOS and tvOS
josejuanqm/VersaPlayer
Star:698 Issue:3 开发语言:Swift
Versatile Video Player implementation for iOS, macOS, and tvOS
bilibili/ijkplayer
bilibili 播放器
Star:30489 Issue:2748 开发语言:C
Android/iOS video player based on FFmpeg n3.4, with MediaCodec, VideoToolbox support.
mpv-player/mpv
命令行视频播放器
Star:19139 Issue:867 开发语言:C
🎥 Command line video player
analogcode/Swift-Radio-Pro
广播电台
Star:2679 Issue:13 开发语言:Swift
Professional Radio Station App for iOS!
安全
krzyzanowskim/CryptoSwift
Star:9121 Issue:40 开发语言:Swift
CryptoSwift is a growing collection of standard and secure cryptographic algorithms implemented in Swift
rockbruno/SwiftInfo
提取和分析一个iOS应用
Star:1094 Issue:20 开发语言:Swift
📊 Extract and analyze the evolution of an iOS app’s code.
Web
Kitura/swift-html-entities
HTML5 规范字符编码/解码器
Star:145 Issue:5 开发语言:Swift
HTML5 spec-compliant character encoder/decoder for Swift
TokamakUI/Tokamak
SwiftUI 兼容,WebAssembly 构建 HTML
Star:1732 Issue:99 开发语言:Swift
SwiftUI-compatible framework for building browser apps with WebAssembly and native apps for other platforms
johnsundell/publish
用 swift 来写网站
Star:4050 Issue:29 开发语言:Swift
A static site generator for Swift developers
highlightjs/highlight.js
语法高亮
Star:20128 Issue:64 开发语言:JavaScript
JavaScript syntax highlighter with language auto-detection and zero dependencies.
sivan/heti
赫蹏(hètí)中文排版
Star:4864 Issue:17 开发语言:SCSS
赫蹏(hètí)是专为中文内容展示设计的排版样式增强。它基于通行的中文排版规范而来,可以为网站的读者带来更好的文章阅读体验。
kevquirk/simple.css
简单大方基础 CSS 样式
Star:2619 Issue:5 开发语言:CSS
Simple.css is a classless CSS template that allows you to make a good looking website really quickly.
mozilla-mobile/firefox-ios
Star:10907 Issue:1062 开发语言:Swift
Firefox for iOS
liviuschera/noctis
好看的代码编辑器配色主题
Star:388 Issue:19 开发语言:JavaScript
Noctis is a collection of light & dark themes with a well balanced blend of warm and cold colors
服务器
vapor/vapor
Star:21853 Issue:86 开发语言:Swift
💧 A server-side Swift HTTP web framework.
Lakr233/Rayon
SSH 机器管理,Swift 编写
Star:2190 Issue:21 开发语言:Swift
yet another SSH machine manager
系统
spevans/swift-project1
Swift编写内核,可在 Mac 和 PC 启动
Star:243 Issue:1 开发语言:Swift
A minimal bare metal kernel in Swift
Web 3.0
chaozh/awesome-blockchain-cn
区块链 awesome
Star:16629 Issue:15 开发语言:JavaScript
收集所有区块链(BlockChain)技术开发相关资料,包括Fabric和Ethereum开发资料
argentlabs/web3.swift
以太坊 Swift API,支持智能合约、ENS 和 ERC20
Star:439 Issue:14 开发语言:Swift
Ethereum Swift API with support for smart contracts, ENS & ERC20
chainfeeds/RSSAggregatorforWeb3
web3 的 rss feed 订阅源
Star:1502 Issue:4 开发语言:Python
Bootstrapping your personal Web3 info hub from more than 500 RSS Feeds.
Planetable/Planet
由 IPFS 和以太坊名称系统提供支持的去中心化博客和网站
Star:531 Issue:13 开发语言:Swift
Decentralized blogs and websites powered by IPFS and Ethereum Name System
Apple
apple/swift
Star:59937 Issue:6020 开发语言:C++
The Swift Programming Language
apple/swift-evolution
提案
Star:13440 Issue:42 开发语言:Markdown
This maintains proposals for changes and user-visible enhancements to the Swift Programming Language.
apple/swift-corelibs-foundation
Star:4624 Issue:607 开发语言:Swift
The Foundation Project, providing core utilities, internationalization, and OS independence
apple/swift-package-manager
Star:8819 Issue:513 开发语言:Swift
The Package Manager for the Swift Programming Language
apple/swift-markdown
Star:1840 Issue:17 开发语言:Swift
A Swift package for parsing, building, editing, and analyzing Markdown documents.
apple/sourcekit-lsp
Star:2599 Issue:32 开发语言:Swift
Language Server Protocol implementation for Swift and C-based languages
apple/swift-nio
Star:7023 Issue:170 开发语言:Swift
Event-driven network application framework for high performance protocol servers & clients, non-blocking.
apple/swift-syntax
解析、生成、转换 Swift 代码
Star:1842 Issue:24 开发语言:Swift
SwiftPM package for SwiftSyntax library.
apple/swift-crypto
CryptoKit 的开源实现
Star:1208 Issue:10 开发语言:C
Open-source implementation of a substantial portion of the API of Apple CryptoKit suitable for use on Linux platforms.
apple/swift-driver
用 Swift 语言重新实现的编译器的驱动程序库
Star:629 Issue:25 开发语言:Swift
Swift compiler driver reimplementation in Swift
apple/swift-numerics
用简单的方式用浮点型进行数值计算
Star:1405 Issue:45 开发语言:Swift
Advanced mathematical types and functions for Swift
apple/swift-atomics
Swift 的低级原子操作
Star:763 Issue:11 开发语言:Swift
Low-level atomic operations for Swift
apple/swift-async-algorithms
Combine 的官方开源替代
Star:1546 Issue:21 开发语言:Swift
Async Algorithms for Swift
计算机科学
raywenderlich/swift-algorithm-club
Star:26593 Issue:55 开发语言:Swift
Algorithms and data structures in Swift, with explanations!
扩展知识
trimstray/the-book-of-secret-knowledge
Star:71271 Issue:19 开发语言:
A collection of inspiring lists, manuals, cheatsheets, blogs, hacks, one-liners, cli/web tools and more.
rossant/awesome-math
Star:6046 Issue:7 开发语言:Python
A curated list of awesome mathematics resources
待分类
krzysztofzablocki/KZFileWatchers
Swift编写的观察本地或者网络上,比如网盘和FTP的文件变化
Star:1029 Issue:2 开发语言:Swift
A micro-framework for observing file changes, both local and remote. Helpful in building developer tools.
博客和资讯
- Swift.org:Swift 官方博客
- Release notes from iOS-Weekly:老司机 iOS 周报
- iOS摸鱼周报:iOS 摸鱼周报
- Michael Tsai:一名 macOS 开发者的博客
- 少数派:少数派致力于更好地运用数字产品或科学方法,帮助用户提升工作效率和生活品质
- OneV’s Den:上善若水,人淡如菊。这里是王巍 (onevcat) 的博客,用来记录一些技术和想法,主要专注于 Swift 和 iOS 开发。
- SwiftLee:A weekly blog about Swift, iOS and Xcode Tips and Tricks
- Swift with Majid:Majid’s blog about Swift development
- 肘子的Swift记事本
- 戴铭的博客 - 星光社:一个人走得快,一群人走的远
- Swift by Sundell:Weekly Swift articles, podcasts and tips by John Sundell
- FIVE STARS:Exploring iOS, SwiftUI & much more.
- SwiftUI Weekly:The curated collection of links about SwiftUI. Delivered every Monday.
- Not Only Swift Weekly:Xcode tips & tricks, Swift, SwiftUI, Combine, Firebase, computing and internet history, and - of course - some fun stuff.
- SwiftlyRush Weekly:SwiftlyRush Weekly is a weekly curated publication full of interesting, relevant links, alongside industry news and updates. Subscribe now and never miss an issue.
- iOS Dev Weekly:Subscribe to a hand-picked round-up of the best iOS development links every week. Curated by Dave Verwer and published every Friday. Free.
- 阮一峰的网络日志:Ruan YiFeng’s Blog 科技爱好者周刊
- The.Swift.Dev.:Weekly Swift articles
- 爱范儿:让未来触手可及
- 机核:不止是游戏